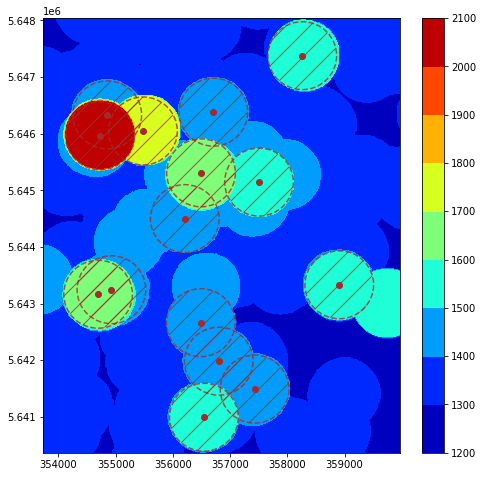
Process LiDAR aerial survey files to determine the minimum flight altitude surface over a defined area. A protection volume of 600 m horizontally and 1000 ft vertically from obstacles is used.
Aerial LiDAR survey file in .laz format can be used. They are assumed to be in UTM (zone 32N) format for horizontal coordinates.
Source for NRW LiDAR surveys: https://www.opengeodata.nrw.de/produkte/geobasis/hm/3dm_l_las/3dm_l_las_paketiert/
Data info: https://www.bezreg-koeln.nrw.de/brk_internet/geobasis/hoehenmodelle/3d-messdaten/index.html
Data manual: https://www.bezreg-koeln.nrw.de/brk_internet/geobasis/hoehenmodelle/nutzerinformationen.pdf
This script gets as input:
- a bounding box corresponding to the desired horizontal area to be covered,
- a minimum altitude (Z coordinate) below which laz points are discarded,
- a subsampling factor. The factor divides the number of points for processing and is an easy way to divide the computation time. However, too much subsampling will "erode" obstacle tops and reduce their height somewhat.
- a subbox size (in meters). Large bounding boxes are problematic because all corresponding .laz files can't fit in memory. It will be broken down in multiple sub bounding boxes, reducing memory needs (but increasing the number of times files are loaded),
- a resolution (in meters). The resolution of the ouput x, y, z arrays. Dividing the resolution by 2 multiplies the computation time by 4.
- classification of LiDAR points to consider for the processing. By default 20 and 17,
- a radius (in meters). This corresponds to the horizontal radius defined in the regulation for staying clear of obstacles over densely populated areas.
The script iterates over the sub bounding boxes. For each one, it loads all necessary .laz file, retains the points matching the criteria, and append them to a large point array.
A grid over the box is then created, and for each grid point, the script looks at the highest points within the defined radius, and saves it.
x, y, z arrays for each sub bounding boxes are appended to global lists, saved at the end of processing.
This script opens the x, y, z arrays.
It flattens the x, y arrays, then stacks all 2D z arrays horizontally and vertically so as to reconstitute the user's desired area.
It then calculate contour surfaces for defined levels, converts everything back to WGS84, and saves them as geojson for further processing.
The notebook can be used to visualise the contour with matplotlib or plotly, and also load the obstacles json with official obstacle coordinates to cross-check the LiDAR results.