Using an Ubuntu PC connected to the robot's network, you can analyze coredumps that happen when the robot code crashes.
FTP to the robot using WPILib's tutorial on FileZilla,
but replace lvuser with admin so we can overwrite system files.
We have to edit /usr/local/natinst/etc/init.d/lvrt-wrapper on the RIO, but commands like vim and nano don't work on ssh since the
OS is pretty barebones. So, we'll use FTP instead.
Download /usr/local/natinst/etc/init.d/lvrt-wrapper to your PC.
Open your local copy in a text editor. The ulimit line needs to be changed to allow full coredumps to be saved:
# stack size
ulimit -s 256
# core file size
# uncomment to enable core dumps
#ulimit -c unlimited
# stack size
#ulimit -s 256
# core file size
# uncomment to enable core dumps
ulimit -c unlimited
Upload your copy back to the robot and overwrite the original.
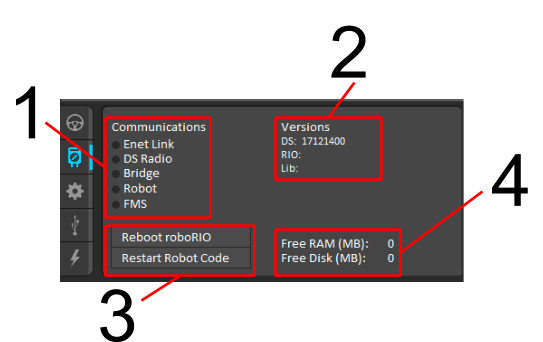
Open the driverstation and reboot the RIO:
Attempting to write to a null pointer in AutonomousInit() will cause the code to crash upon autonomous init. This will result in a core being dumped.
int* myptr = nullptr;
*myptr = 3;Now, any time your code crashes, the file /var/local/natinst/log/core_dump.!home!lvuser!frcUserProgram will be created.
Don't let the RIO lose power after it happens or you may lose the coredump.
Use FileZilla to copy that file from the RIO. It may take a minute or two to download.
--Coming soon--