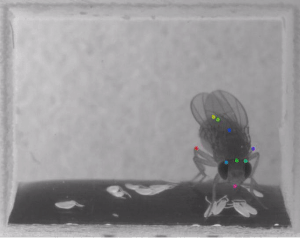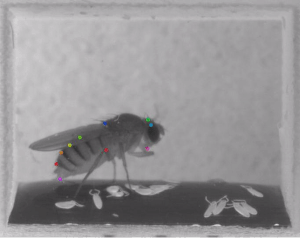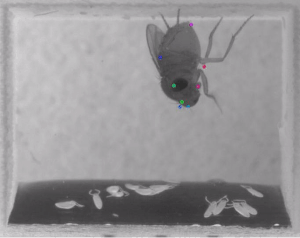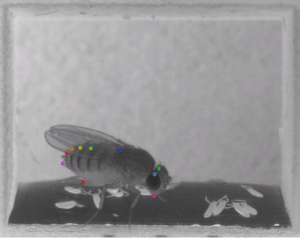
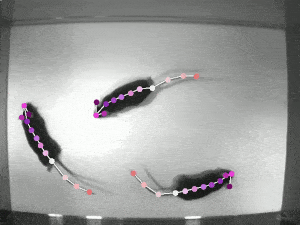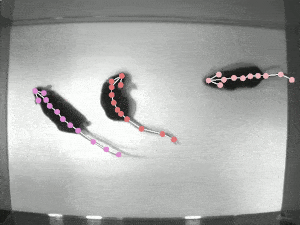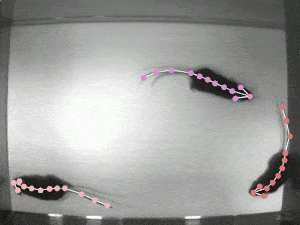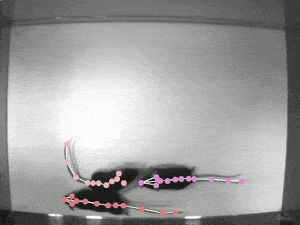
DeepLabCut is a toolbox for markerless pose estimation of animals performing various tasks. Read a short development and application summary below. As long as you can see (label) what you want to track, you can use this toolbox, as it is animal and object agnostic.
Latest updates:
💜 DeepLabCut supports multi-animal pose estimation! maDLC is out of beta/rc mode and beta is deprecated, thanks to the testers out there for feedback! Your labeled data will be backwards compatible, but not all other steps. Please see the new 2.2+ releases for what's new & how to install it, please see our new preprint, Lauer et al 2021, and the new docs on how to use it!
💜 We have a real-time package available! http://DLClive.deeplabcut.org
Very quick start: pip install "deeplabcut[gui]" that includes all GUI functions, or pip install deeplabcut (headless version).
- We recommend using our conda file, see here or the new
deeplabcut-dockerpackage.
*New: check out the docs in JupyterBook! https://deeplabcut.github.io/DeepLabCut (or on github).
An overview of the pipeline and workflow for project management. For a step-by-step user guide, please also read the Nature Protocols paper!
For a deeper understanding and more resources for you to get started with Python and DeepLabCut, please check out our free online course! http://DLCcourse.deeplabcut.org
We provide data and several Jupyter Notebooks: one that walks you through a demo dataset to test your installation, and another Notebook to run DeepLabCut from the beginning on your own data. We also show you how to use the code in Docker, and on Google Colab.
In 2018, we demonstrated the capabilities for trail tracking, reaching in mice and various Drosophila behaviors during egg-laying (see Mathis et al. for details). There is, however, nothing specific that makes the toolbox only applicable to these tasks and/or species. The toolbox has already been successfully applied (by us and others) to rats, humans, various fish species, bacteria, leeches, various robots, cheetahs, mouse whiskers and race horses. DeepLabCut utilized the feature detectors (ResNets + readout layers) of one of the state-of-the-art algorithms for human pose estimation by Insafutdinov et al., called DeeperCut, which inspired the name for our toolbox (see references below). Since this time, the package has changed substantially. The code has been re-tooled and re-factored since 2.1+: We have added faster and higher performance variants with MobileNetV2s, EfficientNets, and our own DLCRNet backbones (see Pretraining boosts out-of-domain robustness for pose estimation and Lauer et al 2021). Additionally, we have improved the inference speed and provided both additional and novel augmentation methods, added real-time, and multi-animal support. We currently provide state-of-the-art performance for animal pose estimation.
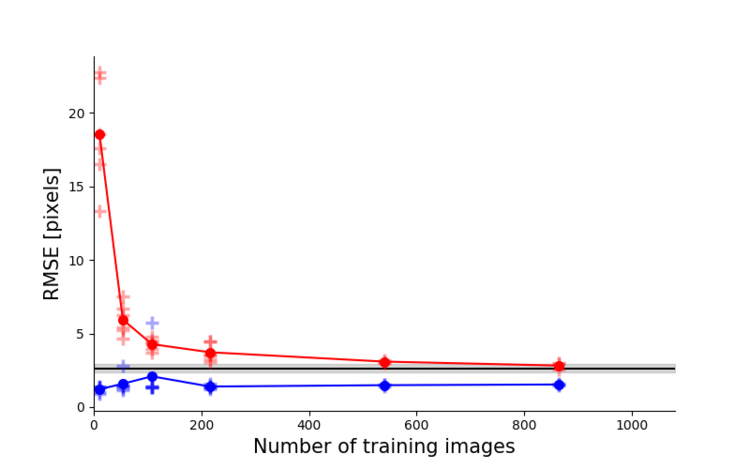
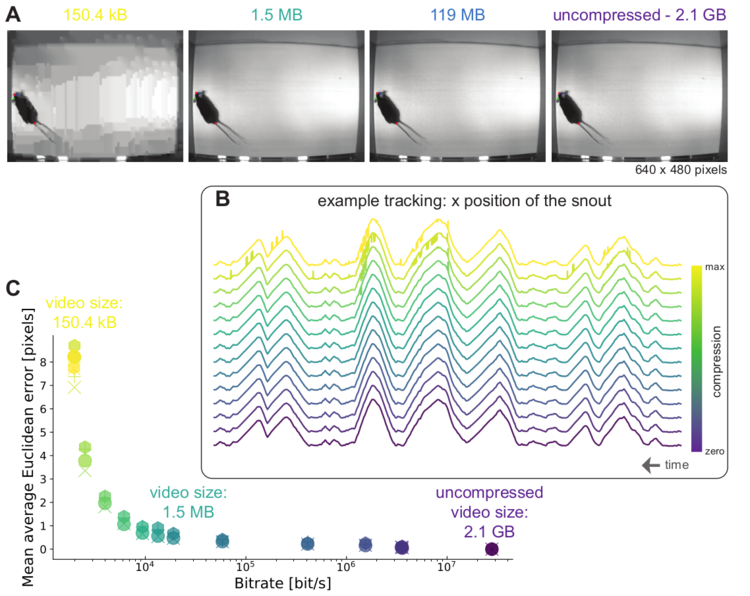
Left: Due to transfer learning it requires little training data for multiple, challenging behaviors (see Mathis et al. 2018 for details). Mid Left: The feature detectors are robust to video compression (see Mathis/Warren for details). Mid Right: It allows 3D pose estimation with a single network and camera (see Mathis/Warren). Right: It allows 3D pose estimation with a single network trained on data from multiple cameras together with standard triangulation methods (see Nath* and Mathis* et al. 2019).
DeepLabCut is embedding in a larger open-source eco-system, providing behavioral tracking for neuroscience, ecology, medical, and technical applications. Moreover, many new tools are being actively developed. See DLC-Utils for some helper code.
DLC code was originally developed by Alexander Mathis & Mackenzie Mathis, and was extended in 2.0 with Tanmay Nath, and currently (2.1+) actively developed with our CZI DLC Fellow, Jessy Lauer. DeepLabCut is an open-source tool and has benefited from suggestions and edits by many individuals including Mert Yuksekgonul, Tom Biasi, Richard Warren, Ronny Eichler, Hao Wu, Federico Claudi, Gary Kane and Jonny Saunders as well as the contributors. Please see AUTHORS for more details!
This is an actively developed package and we welcome community development and involvement.
-
We are a community partner on the
. Please post help and support questions on the forum with the tag DeepLabCut. Check out their mission statement Scientific Community Image Forum: A discussion forum for scientific image software.
-
If you encounter a previously unreported bug/code issue, please post here (we encourage you to search issues first): https://github.com/DeepLabCut/DeepLabCut/issues
-
If you want to contribute to the code, please read our guide here!
-
The project road map. Get in touch with us if you want to help!
If you use this code or data we kindly as that you please cite Mathis et al, 2018 and, if you use the Python package (DeepLabCut2.x) please also cite Nath, Mathis et al, 2019. If you utilize the MobileNetV2s or EfficientNets please cite Mathis, Biasi et al. 2021. If you use multi-animal in beta mode, please contact us; if you use the 2.2rc1+, please cite Lauer et al. 2021.
DOIs (#ProTip, for helping you find citations for software, check out CiteAs.org!):
- Mathis et al 2018: 10.1038/s41593-018-0209-y
- Nath, Mathis et al 2019: 10.1038/s41596-019-0176-0
Please check out the following references for more details:
@article{Mathisetal2018,
title = {DeepLabCut: markerless pose estimation of user-defined body parts with deep learning},
author = {Alexander Mathis and Pranav Mamidanna and Kevin M. Cury and Taiga Abe and Venkatesh N. Murthy and Mackenzie W. Mathis and Matthias Bethge},
journal = {Nature Neuroscience},
year = {2018},
url = {https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-018-0209-y}}
@article{NathMathisetal2019,
title = {Using DeepLabCut for 3D markerless pose estimation across species and behaviors},
author = {Nath*, Tanmay and Mathis*, Alexander and Chen, An Chi and Patel, Amir and Bethge, Matthias and Mathis, Mackenzie W},
journal = {Nature Protocols},
year = {2019},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-019-0176-0}}
@InProceedings{Mathis_2021_WACV,
author = {Mathis, Alexander and Biasi, Thomas and Schneider, Steffen and Yuksekgonul, Mert and Rogers, Byron and Bethge, Matthias and Mathis, Mackenzie W.},
title = {Pretraining Boosts Out-of-Domain Robustness for Pose Estimation},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV)},
month = {January},
year = {2021},
pages = {1859-1868}}
@article{Lauer2021MultianimalPE,
title = {Multi-animal pose estimation and tracking with DeepLabCut},
author = {Jessy Lauer and Mu Zhou and Shaokai Ye and William Menegas and Tanmay Nath and Mohammed Mostafizur Rahman and V. Di Santo and Daniel Soberanes and Guoping Feng and V. Murthy and G. Lauder and C. Dulac and M. Mathis and Alexander Mathis},
journal = {bioRxiv},
year = {2021}
url = {https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.04.30.442096v1}}
@article{insafutdinov2016eccv,
title = {DeeperCut: A Deeper, Stronger, and Faster Multi-Person Pose Estimation Model},
author = {Eldar Insafutdinov and Leonid Pishchulin and Bjoern Andres and Mykhaylo Andriluka and Bernt Schiele},
booktitle = {ECCV'16},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/1605.03170}}
Review articles:
@article{Mathis2020DeepLT,
title={Deep learning tools for the measurement of animal behavior in neuroscience},
author={Mackenzie W. Mathis and Alexander Mathis},
journal={Current Opinion in Neurobiology},
year={2020},
volume={60},
pages={1-11}}
@article{Mathis2020Primer,
title={A Primer on Motion Capture with Deep Learning: Principles, Pitfalls, and Perspectives},
author={Alexander Mathis and Steffen Schneider and Jessy Lauer and Mackenzie W. Mathis},
journal={Neuron},
year={2020},
volume={108},
pages={44-65}}
Other open-access pre-prints related to our work on DeepLabCut:
@article{MathisWarren2018speed,
author = {Mathis, Alexander and Warren, Richard A.},
title = {On the inference speed and video-compression robustness of DeepLabCut},
year = {2018},
doi = {10.1101/457242},
publisher = {Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory},
URL = {https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2018/10/30/457242},
eprint = {https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2018/10/30/457242.full.pdf},
journal = {bioRxiv}
}
This project is licensed under the GNU Lesser General Public License v3.0. Note that the software is provided "as is", without warranty of any kind, express or implied. If you use the code or data, please cite us! Note, artwork (DeepLabCut logo) and images are copyrighted; please do not take or use these images without written permission.
VERSION 2.2: Multi-animal pose estimation and tracking with DeepLabCut.
VERSION 2.0-2.1: This is the Python package of DeepLabCut that was originally released with our Nature Protocols paper (preprint here). This package includes graphical user interfaces to label your data, and take you from data set creation to automatic behavioral analysis. It also introduces an active learning framework to efficiently use DeepLabCut on large experimental projects, and data augmentation tools that improve network performance, especially in challenging cases (see panel b).
VERSION 1.0: The initial, Nature Neuroscience version of DeepLabCut can be found in the history of git, or here: https://github.com/AlexEMG/DeepLabCut/releases/tag/1.11
-
August 2021: 2.2 becomes the new stable release for DeepLabCut.
-
July 2021: Docs are now at https://deeplabcut.github.io/DeepLabCut and we now include TensorFlow 2 support!
-
May 2021: DeepLabCut hit 200,000 downloads! Also, Our preprint on 2.2, multi-animal DeepLabCut is released!
-
Jan 2021: Pretraining boosts out-of-domain robustness for pose estimation published in the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. We also added EfficientNet backbones to DeepLabCut, those are best trained with cosine decay (see paper). To use them, just pass "
efficientnet-b0" to "efficientnet-b6" when creating the trainingset! -
Dec 2020: We released a real-time package that allows for online pose estimation and real-time feedback. See DLClive.deeplabcut.org.
-
5/22 2020: We released 2.2beta5. This beta release has some of the features of DeepLabCut 2.2, whose major goal is to integrate multi-animal pose estimation to DeepLabCut.
-
Mar 2020: Inspired by suggestions we heard at this weeks CZI's Essential Open Source Software meeting in Berkeley, CA we updated our docs. Let us know what you think!
-
Feb 2020: Our review on animal pose estimation is published!
-
Nov 2019: DeepLabCut was recognized by the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (CZI) with funding to support this project. Read more in the Harvard Gazette, on CZI's Essential Open Source Software for Science site and in their Medium post
-
Oct 2019: DLC 2.1 released with lots of updates. In particular, a Project Manager GUI, MobileNetsV2, and augmentation packages (Imgaug and Tensorpack). For detailed updates see releases
-
Sept 2019: We published two preprints. One showing that ImageNet pretraining contributes to robustness and a review on animal pose estimation. Check them out!
-
Jun 2019: DLC 2.0.7 released with lots of updates. For updates see releases
-
Feb 2019: DeepLabCut joined twitter
-
Jan 2019: We hosted workshops for DLC in Warsaw, Munich and Cambridge. The materials are available here
-
Nov 2018: We posted a detailed guide for DeepLabCut 2.0 on BioRxiv. It also contains a case study for 3D pose estimation in cheetahs.
-
Nov 2018: Various (post-hoc) analysis scripts contributed by users (and us) will be gathered at DLCutils. Feel free to contribute! In particular, there is a script guiding you through importing a project into the new data format for DLC 2.0
-
Oct 2018: new pre-print on the speed video-compression and robustness of DeepLabCut on BioRxiv
-
Sept 2018: Nature Lab Animal covers DeepLabCut: Behavior tracking cuts deep
-
Kunlin Wei & Konrad Kording write a very nice News & Views on our paper: Behavioral Tracking Gets Real
-
August 2018: Our preprint appeared in Nature Neuroscience
-
August 2018: NVIDIA AI Developer News: AI Enables Markerless Animal Tracking
-
July 2018: Ed Yong covered DeepLabCut and interviewed several users for the Atlantic.
-
April 2018: first DeepLabCut preprint on arXiv.org