Docker
+Introduction to Docker
+ +
+What is Docker?
+-
+
Platform for developing, shipping and running applications.
+Infrastructure as application / code.
+First version: 2013.
+Company: originally dotCloud (2010), later named Docker.
+Established Open Container Initiative.
+
As a software:
+-
+
- +
Docker Enterprise Edition.
+
There is an increasing number of alternative container technologies and providers. Many of them are actually based on software components originally from the Docker stack and they normally try to address some specific use cases or weakpoints. As a example, Singularity, that we introduce later in this couse, is focused in HPC environments. Another case, Podman, keeps a high functional compatibility with Docker but with a different focus on technology (not keeping a daemon) and permissions.
+Docker components
+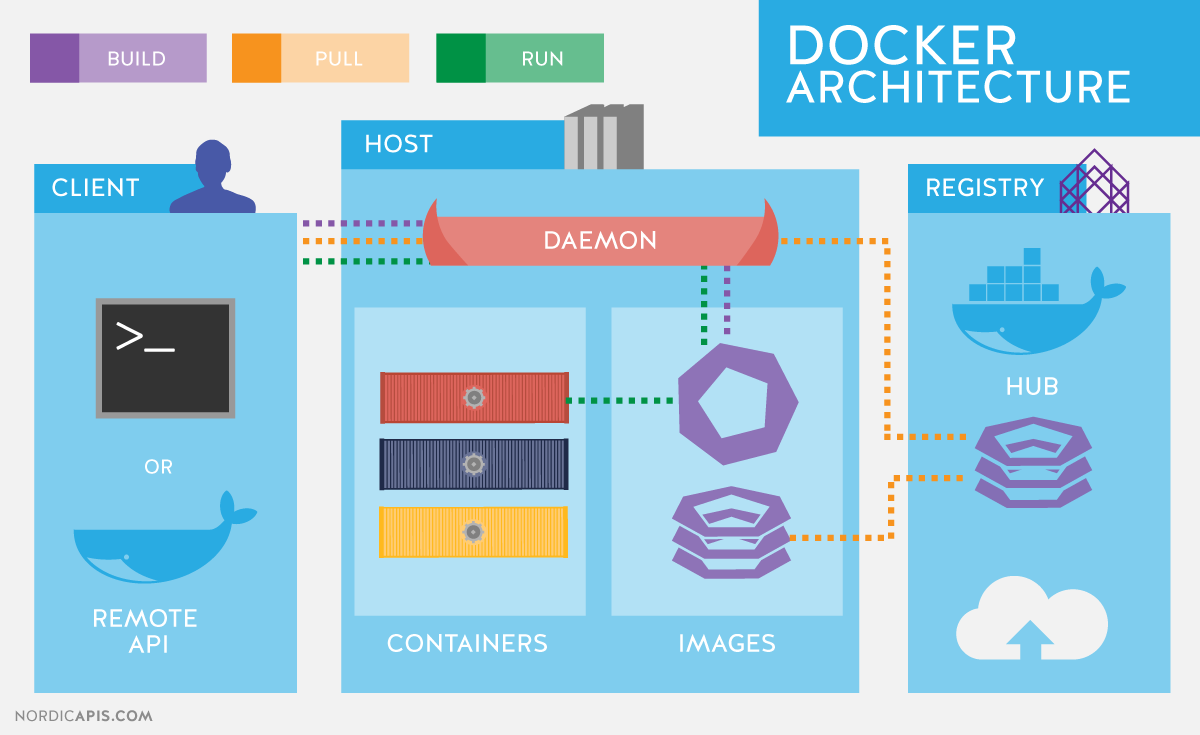 +
+-
+
Read-only templates.
+Containers are run from them.
+Images are not run.
+Images have several layers.
+
 +
+Images versus containers
+-
+
Image: A set of layers, read-only templates, inert.
+An instance of an image is called a container.
+
When you start an image, you have a running container of this image. You can have many running containers of the same image.
+“The image is the recipe, the container is the cake; you can make as many cakes as you like with a given recipe.”
+ +Docker vocabulary
+docker
+ +
+Get help:
+docker run --help
+ +
+Using existing images
+Explore Docker hub
+Images can be stored locally or shared in a registry.
+Docker hub is the main public registry for Docker images.
+Let’s search the keyword ubuntu:
+ +
+docker pull: import image
+-
+
get latest image / latest release
+
docker pull ubuntu
+ +
+-
+
choose the version of Ubuntu you are fetching: check the different tags
+
 +
+docker pull ubuntu:18.04
+Biocontainers
+ +Specific directory of Bioinformatics related entries
+-
+
Entries in Docker hub and/or Quay.io (RedHat registry)
+Normally created from Bioconda
+
Example: FastQC
+https://biocontainers.pro/#/tools/fastqc
+docker pull biocontainers/fastqc:v0.11.9_cv7
+docker images: list images
+docker images
+ +
+Each image has a unique IMAGE ID.
+docker run: run image, i.e. start a container
+Now we want to use what is inside the image.
+docker run creates a fresh container (active instance of the image) from a Docker (static) image, and runs it.
+The format is:
+docker run image:tag command
+docker run ubuntu:18.04 /bin/ls
+ +
+Now execute ls in your current working directory: is the result the same?
+You can execute any program/command that is stored inside the image:
+docker run ubuntu:18.04 /bin/whoami
+docker run ubuntu:18.04 cat /etc/issue
+You can either execute programs in the image from the command line (see above) or execute a container interactively, i.e. “enter” the container.
+docker run -it ubuntu:18.04 /bin/bash
+Run container as daemon (in background)
+docker run --detach ubuntu:18.04 tail -f /dev/null
+Run container as daemon (in background) with a given name
+docker run --detach --name myubuntu ubuntu:18.04 tail -f /dev/null
+docker ps: check containers status
+List running containers:
+docker ps
+List all containers (whether they are running or not):
+docker ps -a
+Each container has a unique ID.
+docker exec: execute process in running container
+docker exec myubuntu uname -a
+-
+
Interactively
+
docker exec -it myubuntu /bin/bash
+docker stop, start, restart: actions on container
+Stop a running container:
+docker stop myubuntu
+
+docker ps -a
+Start a stopped container (does NOT create a new one):
+docker start myubuntu
+
+docker ps -a
+Restart a running container:
+docker restart myubuntu
+
+docker ps -a
+Run with restart enabled
+docker run --restart=unless-stopped --detach --name myubuntu2 ubuntu:18.04 tail -f /dev/null
+-
+
Restart policies: no (default), always, on-failure, unless-stopped
+
Update restart policy
+docker update --restart unless-stopped myubuntu
+docker rm, docker rmi: clean up!
+docker rm myubuntu
+docker rm -f myubuntu
+docker rmi ubuntu:18.04
+Major clean
+Check used space
+docker system df
+Remove unused containers (and others) - DO WITH CARE
+docker system prune
+Remove ALL non-running containers, images, etc. - DO WITH MUCH MORE CARE!!!
+docker system prune -a
+Exercise
+-
+
-
+
Imagemagick
+
+Pull the imagemagick image from: https://hub.docker.com/r/acleancoder/imagemagick-full
+Check the version of the convert command.
+Start a container interactively.
+Inside the container: download this png image (https://www.docker.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/vertical-logo-monochromatic.png)
+Convert it to .jpg using the convert command of imagemagick (format; convert image.png image.jpg).
+Exit the container.
+Copy the jpg image back from the stopped container! Try new command docker cp.
+
Suggested solution
# Pull image
+docker pull acleancoder/imagemagick-full
+
+# Check version of `convert`
+docker run acleancoder/imagemagick-full convert --version
+
+# Start interactive container
+docker run -it acleancoder/imagemagick-full
+ # fetch png image
+ > wget https://www.docker.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/vertical-logo-monochromatic.png
+ # convert to jpg
+ > convert vertical-logo-monochromatic.png myimage.jpg
+ # exit container
+
+# fetch container ID with `ps -a` and use `docker cp` to copy jpg file from the stopped container to the host
+docker cp *CONTAINER_ID*:/myimage.jpg .
+Volumes
+Docker containers are fully isolated. It is necessary to mount volumes in order to handle input/output files.
+Syntax: –volume/-v host:container
+mkdir datatest
+touch datatest/test
+docker run --detach --volume $(pwd)/datatest:/scratch --name fastqc_container biocontainers/fastqc:v0.11.9_cv7 tail -f /dev/null
+docker exec -ti fastqc_container /bin/bash
+> ls -l /scratch
+> exit
+Ports
+The same as with volumes, but with ports, to access Internet services.
+Syntax: –publish/-p host:container
+docker run --detach --name webserver nginx
+curl localhost:80
+docker exec webserver curl localhost:80
+docker rm -f webserver
+docker run --detach --name webserver --publish 80:80 nginx
+curl localhost:80
+docker rm -f webserver
+docker run --detach --name webserver -p 8080:80 nginx
+curl localhost:80
+curl localhost:8080
+docker exec webserver curl localhost:80
+docker exec webserver curl localhost:8080
+docker rm -f webserver
+Volume exercises
+-
+
Copy the 2 fastq files from available datasets in Github repository and place them in mounted directory
+Run fastqc interactively (inside container):
`fastqc /scratch/*.gz`
+Run fastqc non-interactively (outside the container)
+
docker run –user
+It is possible to run certain containers with a specific user, appending `run --user`.
A convenient command would be:
+docker run --user $(id -u):$(id -g) --detach --volume $(pwd)/datatest:/scratch --name user_test biocontainers/fastqc:v0.11.9_cv7 touch /scratch/userfile
+