This guide walks you through writing a simple jQuery client that consumes a Spring MVC-based RESTful web service.
You will build a jQuery client that consumes a Spring-based RESTful web service. Specifically, the client will consume the service created in Building a RESTful Web Service with CORS.
The jQuery client will be accessed by opening the index.html file in your browser, and will consume the service accepting requests at:
http://rest-service.guides.spring.io/greeting
The service will respond with a JSON representation of a greeting:
{"id":1,"content":"Hello, World!"}The jQuery client will render the ID and content into the DOM.
-
About 15 minutes
-
A favorite text editor
-
A modern web browser
-
An internet connection
First, you will create the jQuery controller module that will consume the REST service:
public/hello.js
link:complete/public/hello.js[role=include]This controller module is represented as a simple JavaScript function. It uses jQuery’s $.ajax() method to consume the REST service at http://rest-service.guides.spring.io/greeting. If successful, it will assign the JSON received to data, effectively making it a Greeting model object. The id and content are then appended to the greeting-id and greeting-content DOM elements respectively.
Note the use of the jQuery promise .then(). This directs jQuery to execute the anonymous function when the $.ajax() method completes, passing the data result from the completed AJAX request.
Now that you have a jQuery controller, you will create the HTML page that will load the client into the user’s web browser:
public/index.html
link:complete/public/index.html[role=include]Note the following two script tags within the <head> section.
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.10.2/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="hello.js"></script>The first script tag loads the minified jQuery library (jquery.min.js) from a content delivery network (CDN) so that you don’t have to download jQuery and place it in your project. It also loads the controller code (hello.js) from the application’s path.
Also note that the <p> tags include class attributes.
<p class="greeting-id">The ID is </p>
<p class="greeting-content">The content is </p>These class attributes help jQuery to reference the HTML elements and update the text with the values from the id and content properties of the JSON received from the REST service.
To run the client, you’ll need to serve it from a web server to your browser. The Spring Boot CLI (Command Line Interface) includes an embedded Tomcat server, which offers a simple approach to serving web content. See Building an Application with Spring Boot for more information about installing and using the CLI.
In order to serve static content from Spring Boot’s embedded Tomcat server, you’ll also need to create a minimal amount of web application code so that Spring Boot knows to start Tomcat. The following app.groovy script is sufficient for letting Spring Boot know that you want to run Tomcat:
app.groovy
link:complete/app.groovy[role=include]You can now run the app using the Spring Boot CLI:
spring run app.groovy
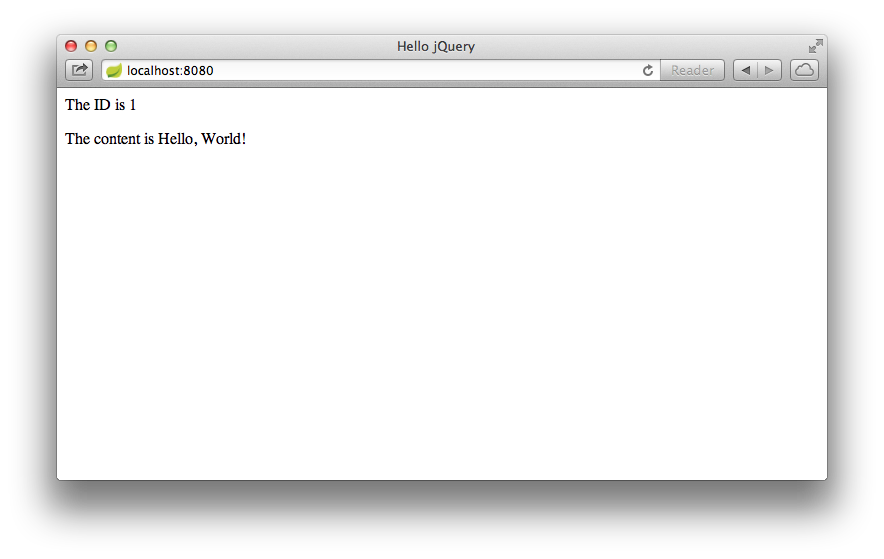
Once the app starts, open http://localhost:8080 in your browser, where you see:
The ID value will increment each time you refresh the page.
Congratulations! You’ve just developed a jQuery client that consumes a Spring-based RESTful web service.
The following guides may also be helpful: