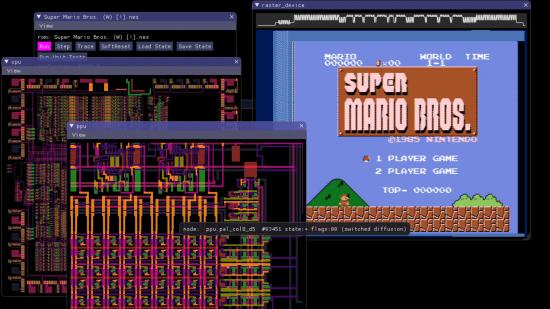
A NES (Nintendo Entertainment System) emulator replicates the original NES console's hardware in software, enabling users to play classic NES games on modern devices. It interprets game ROM files, which are digital copies of NES cartridges, to recreate the original gaming experience.
- CPU: Emulates the Ricoh 2A03/2A07, based on the MOS Technology 6502 microprocessor.
- PPU: Handles graphics rendering, including sprites, backgrounds, and palettes.
- APU: Produces sound effects and music.
- Memory:
- RAM: 2 KB of onboard RAM.
- VRAM: 2 KB for video.
- ROM: Game data stored in cartridges, often with mappers for additional features.
- Input: NES controller support (A, B, Start, Select).
- Clock Speed: 1.79 MHz (NTSC) / 1.66 MHz (PAL).
-
CPU Emulation
- 6502 Instruction Set: Implementing the full range of CPU instructions and addressing modes.
-
PPU Emulation
- Graphics Rendering: Sprite rendering, background scrolling, color palettes, and video memory layout.
- Rendering Cycles: Emulate the precise timing of the PPU.
-
APU Emulation
- Sound Channels: Pulse waves, triangle waves, noise, and DPCM synthesis.
- Audio Synchronization: Ensure sound matches the video output.
-
Memory Management
- RAM and ROM: Implement memory mapping for the NES's RAM, ROM, and I/O registers.
- Cartridge Mappers: Support various mappers (e.g., MMC1, MMC3) to extend functionality.
-
Input Handling
- Controller Input: Read and process inputs from NES controllers, mapping them to modern devices.
-
Display Output
- Graphics Library: Use SDL, OpenGL, or similar libraries for rendering.
- Smooth Rendering: Achieve 60 FPS (NTSC) or 50 FPS (PAL).
-
Audio Output
- Audio Library: Output sound using an appropriate library.
- Synchronization: Ensure audio is in sync with the video.
-
Game Loading
- ROM Parsing: Load ROM files, parse iNES headers, and manage game data.
- Concurrency: Utilize Go's goroutines for parallel tasks like audio processing, input handling, and video rendering.
- Performance Optimization: Critical for maintaining precise timing and synchronization in the emulator.
- Libraries: Go bindings for SDL or other libraries for handling graphics and audio.