Rust Analyzer is an ordinary Rust project, which is organized as a Cargo workspace, builds on stable and doesn't depend on C libraries. So, just
$ cargo test
should be enough to get you started!
To learn more about how rust-analyzer works, see ./architecture.md document.
We also publish rustdoc docs to pages:
https://rust-analyzer.github.io/rust-analyzer/ra_ide/
Various organizational and process issues are discussed in this document.
Rust Analyzer is a part of RLS-2.0 working group. Discussion happens in this Zulip stream:
https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/185405-t-compiler.2Fwg-rls-2.2E0
- good-first-issue are good issues to get into the project.
- E-has-instructions issues have links to the code in question and tests.
- E-easy, E-medium, E-hard, labels are estimates for how hard would be to write a fix.
- fun is for cool, but probably hard stuff.
We use GitHub Actions for CI. Most of the things, including formatting, are checked by
cargo test so, if cargo test passes locally, that's a good sign that CI will
be green as well. The only exception is that some long-running tests are skipped locally by default.
Use env RUN_SLOW_TESTS=1 cargo test to run the full suite.
We use bors-ng to enforce the not rocket science rule.
You can run cargo xtask install-pre-commit-hook to install git-hook to run rustfmt on commit.
All Rust code lives in the crates top-level directory, and is organized as a
single Cargo workspace. The editors top-level directory contains code for
integrating with editors. Currently, it contains the plugin for VS Code (in
TypeScript). The docs top-level directory contains both developer and user
documentation.
We have some automation infra in Rust in the xtask package. It contains
stuff like formatting checking, code generation and powers cargo xtask install.
The latter syntax is achieved with the help of cargo aliases (see .cargo
directory).
Debugging the language server can be tricky: LSP is rather chatty, so driving it from the command line is not really feasible, driving it via VS Code requires interacting with two processes.
For this reason, the best way to see how rust-analyzer works is to find a relevant test and execute it (VS Code includes an action for running a single test).
However, launching a VS Code instance with a locally built language server is possible. There's "Run Extension (Debug Build)" launch configuration for this.
In general, I use one of the following workflows for fixing bugs and implementing features.
If the problem concerns only internal parts of rust-analyzer (i.e. I don't need
to touch the rust-analyzer crate or TypeScript code), there is a unit-test for it.
So, I use Rust Analyzer: Run action in VS Code to run this single test, and
then just do printf-driven development/debugging. As a sanity check after I'm
done, I use cargo xtask install --server and Reload Window action in VS
Code to sanity check that the thing works as I expect.
If the problem concerns only the VS Code extension, I use Run Installed Extension
launch configuration from launch.json. Notably, this uses the usual
rust-analyzer binary from PATH. For this, it is important to have the following
in your settings.json file:
{
"rust-analyzer.serverPath": "rust-analyzer"
}After I am done with the fix, I use cargo xtask install --client-code to try the new extension for real.
If I need to fix something in the rust-analyzer crate, I feel sad because it's
on the boundary between the two processes, and working there is slow. I usually
just cargo xtask install --server and poke changes from my live environment.
Note that this uses --release, which is usually faster overall, because
loading stdlib into debug version of rust-analyzer takes a lot of time. To speed
things up, sometimes I open a temporary hello-world project which has
"rust-analyzer.withSysroot": false in .code/settings.json. This flag causes
rust-analyzer to skip loading the sysroot, which greatly reduces the amount of
things rust-analyzer needs to do, and makes printf's more useful. Note that you
should only use the eprint! family of macros for debugging: stdout is used for LSP
communication, and print! would break it.
If I need to fix something simultaneously in the server and in the client, I feel even more sad. I don't have a specific workflow for this case.
Additionally, I use cargo run --release -p rust-analyzer -- analysis-stats path/to/some/rust/crate to run a batch analysis. This is primarily useful for
performance optimizations, or for bug minimization.
Our approach to "clean code" is two-fold:
- We generally don't block PRs on style changes.
- At the same time, all code in rust-analyzer is constantly refactored.
It is explicitly OK for a reviewer to flag only some nits in the PR, and then send a follow-up cleanup PR for things which are easier to explain by example, cc-ing the original author. Sending small cleanup PRs (like renaming a single local variable) is encouraged.
Everyone knows that it's better to send small & focused pull requests. The problem is, sometimes you have to, eg, rewrite the whole compiler, and that just doesn't fit into a set of isolated PRs.
The main things to keep an eye on are the boundaries between various components. There are three kinds of changes:
-
Internals of a single component are changed. Specifically, you don't change any
pubitems. A good example here would be an addition of a new assist. -
API of a component is expanded. Specifically, you add a new
pubfunction which wasn't there before. A good example here would be expansion of assist API, for example, to implement lazy assists or assists groups. -
A new dependency between components is introduced. Specifically, you add a
pub usereexport from another crate or you add a new line to the[dependencies]section ofCargo.toml. A good example here would be adding reference search capability to the assists crates.
For the first group, the change is generally merged as long as:
- it works for the happy case,
- it has tests,
- it doesn't panic for the unhappy case.
For the second group, the change would be subjected to quite a bit of scrutiny and iteration. The new API needs to be right (or at least easy to change later). The actual implementation doesn't matter that much. It's very important to minimize the amount of changed lines of code for changes of the second kind. Often, you start doing a change of the first kind, only to realise that you need to elevate to a change of the second kind. In this case, we'll probably ask you to split API changes into a separate PR.
Changes of the third group should be pretty rare, so we don't specify any specific process for them.
That said, adding an innocent-looking pub use is a very simple way to break encapsulation, keep an eye on it!
Note: if you enjoyed this abstract hand-waving about boundaries, you might appreciate https://www.tedinski.com/2018/02/06/system-boundaries.html
We separate import groups with blank lines
mod x;
mod y;
use std::{ ... }
use crate_foo::{ ... }
use crate_bar::{ ... }
use crate::{}
use super::{} // but prefer `use crate::`Items from hir and ast should be used qualified:
// Good
use ra_syntax::ast;
fn frobnicate(func: hir::Function, strukt: ast::StructDef) {}
// Not as good
use hir::Function;
use ra_syntax::ast::StructDef;
fn frobnicate(func: Function, strukt: StructDef) {}Avoid local use MyEnum::* imports.
Prefer use crate::foo::bar to use super::bar.
Optimize for the reader who sees the file for the first time, and wants to get the general idea about what's going on. People read things from top to bottom, so place most important things first.
Specifically, if all items except one are private, always put the non-private item on top.
Put structs and enums first, functions and impls last.
Do
// Good
struct Foo {
bars: Vec<Bar>
}
struct Bar;rather than
// Not as good
struct Bar;
struct Foo {
bars: Vec<Bar>
}We generally use boring and long names for local variables (yay code completion).
The default name is a lowercased name of the type: global_state: GlobalState.
Avoid ad-hoc acronyms and contractions, but use the ones that exist consistently (db, ctx, acc).
The default name for "result of the function" local variable is res.
Function preconditions should generally be expressed in types and provided by the caller (rather than checked by callee):
// Good
fn frbonicate(walrus: Walrus) {
...
}
// Not as good
fn frobnicate(walrus: Option<Walrus>) {
let walrus = match walrus {
Some(it) => it,
None => return,
};
...
}While we don't specifically optimize code yet, avoid writing code which is slower than it needs to be.
Don't allocate a Vec where an iterator would do, don't allocate strings needlessly.
// Good
use itertools::Itertools;
let (first_word, second_word) = match text.split_ascii_whitespace().collect_tuple() {
Some(it) => it,
None => return,
}
// Not as good
let words = text.split_ascii_whitespace().collect::<Vec<_>>();
if words.len() != 2 {
return
}For .md and .adoc files, prefer a sentence-per-line format, don't wrap lines.
If the line is too long, you want to split the sentence in two :-)
We don't have specific rules around git history hygiene. Maintaining clean git history is encouraged, but not enforced. We use rebase workflow, it's OK to rewrite history during PR review process.
Avoid @mentioning people in commit messages, as such messages create a lot of duplicate notification traffic during rebases.
This section tries to document high-level design constraints, which are not always obvious from the low-level code.
Syntax trees are by design incomplete and do not enforce well-formedness.
If an AST method returns an Option, it can be None at runtime, even if this is forbidden by the grammar.
rust-analyzer is independent from LSP.
It provides features for a hypothetical perfect Rust-specific IDE client.
Internal representations are lowered to LSP in the rust-analyzer crate (the only crate which is allowed to use LSP types).
There's a semi-hard split between "compiler" and "IDE", at the ra_hir crate.
Compiler derives new facts about source code.
It explicitly acknowledges that not all info is available (i.e. you can't look at types during name resolution).
IDE assumes that all information is available at all times.
IDE should use only types from ra_hir, and should not depend on the underling compiler types.
ra_hir is a facade.
The main IDE crate (ra_ide) uses "Plain Old Data" for the API.
Rather than talking in definitions and references, it talks in Strings and textual offsets.
In general, API is centered around UI concerns -- the result of the call is what the user sees in the editor, and not what the compiler sees underneath.
The results are 100% Rust specific though.
Tests for the parser (ra_parser) live in the ra_syntax crate (see test_data directory).
There are two kinds of tests:
- Manually written test cases in
parser/okandparser/err - "Inline" tests in
parser/inline(these are generated) from comments inra_parsercrate.
The purpose of inline tests is not to achieve full coverage by test cases, but to explain to the reader of the code what each particular if and match is responsible for.
If you are tempted to add a large inline test, it might be a good idea to leave only the simplest example in place, and move the test to a manual parser/ok test.
To update test data, run with UPDATE_EXPECTATIONS variable:
env UPDATE_EXPECTATIONS=1 cargo qtLogging is done by both rust-analyzer and VS Code, so it might be tricky to figure out where logs go.
Inside rust-analyzer, we use the standard log crate for logging, and
env_logger for logging frontend. By default, log goes to stderr, but the
stderr itself is processed by VS Code.
To see stderr in the running VS Code instance, go to the "Output" tab of the
panel and select rust-analyzer. This shows eprintln! as well. Note that
stdout is used for the actual protocol, so println! will break things.
To log all communication between the server and the client, there are two choices:
-
you can log on the server side, by running something like
env RA_LOG=gen_lsp_server=trace code . -
you can log on the client side, by enabling
"rust-analyzer.trace.server": "verbose"workspace setting. These logs are shown in a separate tab in the output and could be used with LSP inspector. Kudos to @DJMcNab for setting this awesome infra up!
There are also two VS Code commands which might be of interest:
-
Rust Analyzer: Statusshows some memory-usage statistics. To take full advantage of it, you need to compile rust-analyzer with jemalloc support:$ cargo install --path crates/rust-analyzer --force --features jemallocThere's an alias for this:
cargo xtask install --server --jemalloc. -
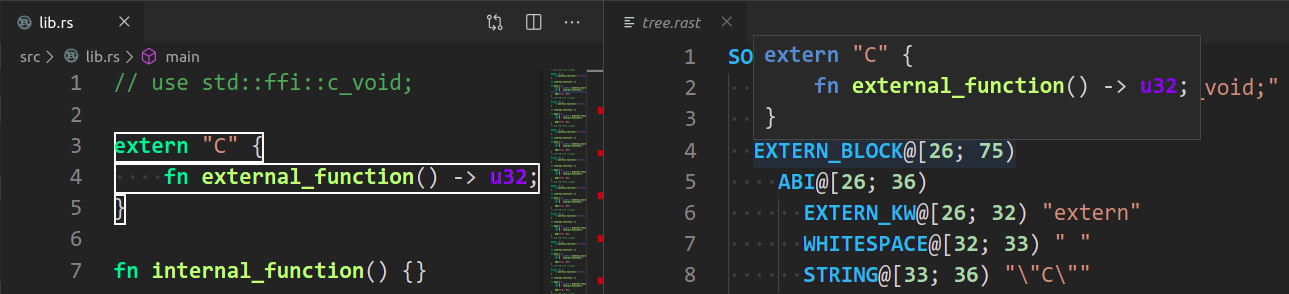
Rust Analyzer: Syntax Treeshows syntax tree of the current file/selection.You can hover over syntax nodes in the opened text file to see the appropriate rust code that it refers to and the rust editor will also highlight the proper text range.
If you trigger Go to Definition in the inspected Rust source file, the syntax tree read-only editor should scroll to and select the appropriate syntax node token.
We have a built-in hierarchical profiler, you can enable it by using RA_PROFILE env-var:
RA_PROFILE=* // dump everything
RA_PROFILE=foo|bar|baz // enabled only selected entries
RA_PROFILE=*@3>10 // dump everything, up to depth 3, if it takes more than 10 ms
In particular, I have export RA_PROFILE='*>10' in my shell profile.
To measure time for from-scratch analysis, use something like this:
$ cargo run --release -p rust-analyzer -- analysis-stats ../chalk/
For measuring time of incremental analysis, use either of these:
$ cargo run --release -p rust-analyzer -- analysis-bench ../chalk/ --highlight ../chalk/chalk-engine/src/logic.rs
$ cargo run --release -p rust-analyzer -- analysis-bench ../chalk/ --complete ../chalk/chalk-engine/src/logic.rs:94:0