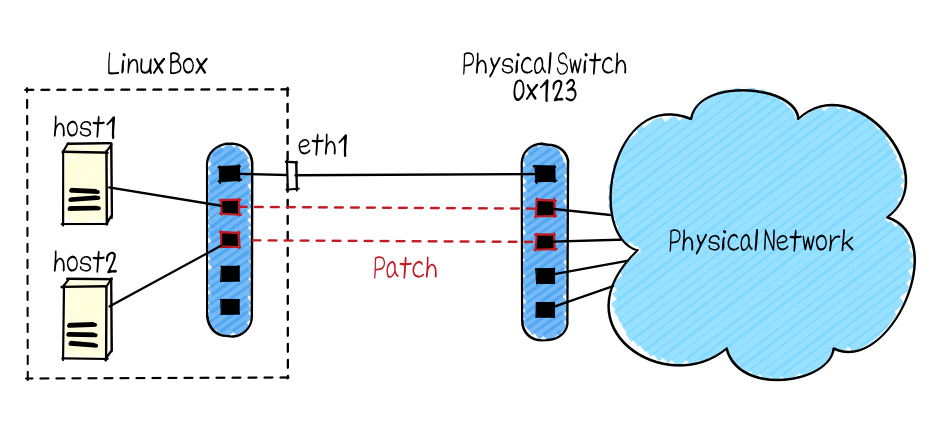
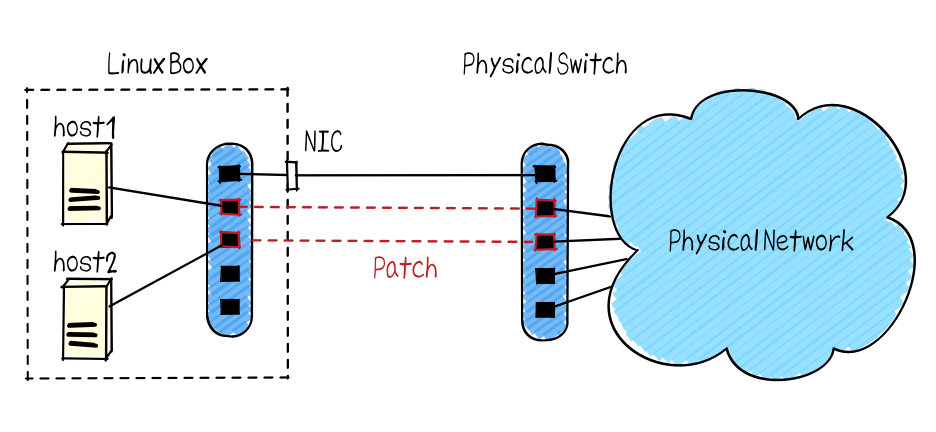
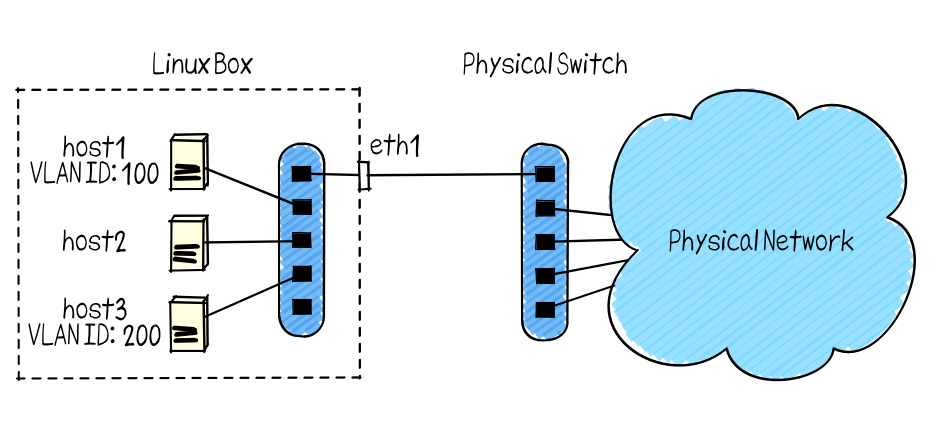
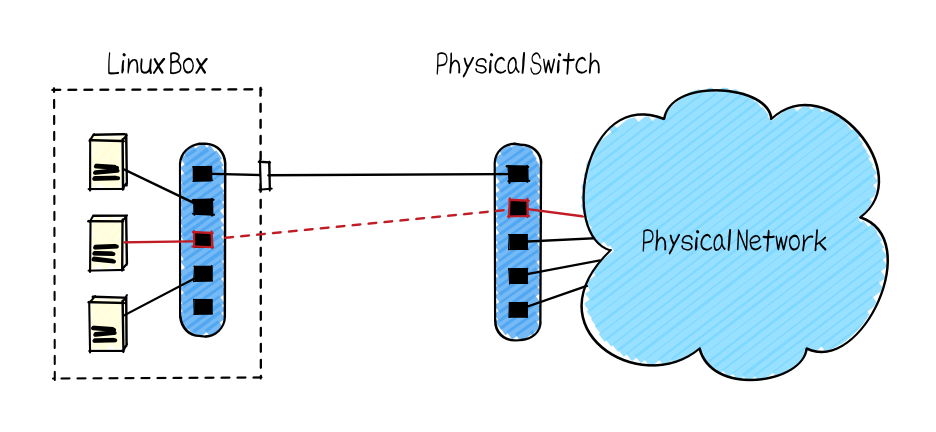
NetTester is an acceptance testing tool for physical networks. You can connect virtual hosts for testing to the physical network and automatically perform tests such as ping communication. Since the generation of the virtual host and the connection to the physical network are all done by software, time-consuming exhaustive tests can be automatically executed by test scripts.
Tests on NetTester run according to the test script. The test script can contain the following elements:
- The connection relationship between virtual hosts and the physical network
- A series of test cases such as "Ping from host1 to host."
When you run a NetTester test script, virtual hosts connect to the physical network and displays the results of sending and receiving packets. Currently, we support Cucumber as a test tool.
Feature: host1 and host2 are connected
Scenario: send and receive packets between host1 and host2
Given start NetTester with options "--nhost 2 --device eth1 --dpid 0x123"
When there are following patches:
| Virtual Port | Physical Port |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
And each host sends packets as follows:
| Source Host | Destination Host |
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 1 |
Then each host receives packets as follows:
| Source Host | Destination Host |
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 1 |features/support/hooks.rb:
require 'net_tester'
require 'active_support/core_ext/object/try'
Before do
NetTester.log_dir = File.join(Aruba.config.working_directory, 'log')
NetTester.pid_dir = File.join(Aruba.config.working_directory, 'pids')
NetTester.socket_dir = File.join(Aruba.config.working_directory, 'sockets')
device = ENV['DEVICE'] || 'eth1'
dpid = ENV['DPID'].try(&:hex) || 0x123
NetTester.run(network_device: device, physical_switch_dpid: dpid)
end
After do
NetTester.kill
endThe minimum configuration of NetTester is a Linux box and an OpenFlow physical switch only.
The Linux box starts virtual hosts that send and receive packets and a software OpenFlow switch. The OpenFlow physical switch virtually connects those virtual hosts to the physical network by creating virtual patches with the virtual OpenFlow switch. In this way, by preparing one Linux box and a physical OpenFlow switch, we can automatically test various patterns using NetTester.
You need to have some prerequisites installed:
- The Ruby language version 2.2.0 or newer
- Open vSwitch (
apt-get install openvswitch-switch).
$ git clone https://github.com/net-tester/net-tester.git
$ cd net_tester
$ bundle installThe net_tester run command starts a NetTester process.
$ ./bin/net_tester run --nhost 3 --device eth1 --dpid 0x123- --nhost: the number of virtual hosts to invoke
- --device: the device name that the virtual switch uses
- --dpid: the physical switch's DPID
The net_tester add command adds a virtual patch.
$ ./bin/net_tester add --vport 2 --port 1 --vlan 100- --vport: the port number of the virtual switch
- --port: the port number of the physical switch
- --vlan: the VLAN ID added by the physical switch port
The net_tester delete command deletes a virtual patch.
$ ./bin/net_tester delete --vport 2 --port 1- --vport: the port number of the virtual switch
- --port: the port number of the physical switch
The net_tester asend command sends test packets.
$ net_tester send --source host1 --dest host2- --source: the source host of the test packet
- --dest: the destination host of the test packet
The net_tester stats commands shows the sent and received packet stats.
$ ./bin/net_tester stats host1
Packets sent:
host1 -> host2 = 1 packet
Packets received:
host2 -> host1 = 1 packetThe net_tester kill command terminates a NetTester process.
NetTester referred to the following test tools. Thanks!
- stereocat/patch_panel is a physical network test tool that runs on Trema
- oolorg/ool-l1patch-dev is a physical network test tool that runs on Ryu