diff --git a/.ruby-version b/.ruby-version
index 2714f53..37c2961 100644
--- a/.ruby-version
+++ b/.ruby-version
@@ -1 +1 @@
-2.6.4
+2.7.2
diff --git a/try-coding-fe/assets/solution.png b/try-coding-fe/assets/solution.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..61c2478
Binary files /dev/null and b/try-coding-fe/assets/solution.png differ
diff --git a/try-coding-fe/control-flow/index.md b/try-coding-fe/control-flow/index.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..fa7faa4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/try-coding-fe/control-flow/index.md
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+---
+layout: lesson
+---
+
+### Go Back
+
+- [Welcome and Introductions](../)
+- [JavaScript Intro](../js-intro)
+
+# Control Flow
+
+The control flow is the order in which the computer executes the statements in our text editor. Code normally runs from the first line in the file to the last line, top to bottom, unless something changes that. Enter Control Flow.
+
+## What is Control Flow?
+
+You probably noticed the program we wrote before isn’t very flexible. We can ask the user a question and store their input, but we pretty much always say the same thing in response. What if we wanted the flexibility to change the behavior in reaction to the data?
+
+Control flow gives us the flexibility we’re looking for. We can change the response depending on the information the user types. Take a look at the code below and see if you can guess what the output might look like. Be prepared to share.
+
+```js
+var age = 35;
+
+if (age >= 21) {
+ console.log("Welcome to Sierra Nevada Brewing Company!");
+} else {
+ console.log("Sorry, you’re not old enough to access our site. Come back later!");
+}
+```
+
+## if Statements
+
+JavaScript's if statement is always followed by an expression, which is a fancy way of saying something that evaluates to true or false. If the expression evaluates to true, anything inside that code block is executed. However, if the expression is false, JavaScript skips over that block of code. Here’s an example of what that might look like:
+
+```js
+if (5 > 4) {
+ console.log("You will see this statement in the console, because five is greater than four!");
+}
+```
+
+The way our code is written now, if the expression evaluates to false, we don’t see any output in the console. In order to have another statement that runs if the expression is false, we need an else statement. Here’s an example:
+
+```js
+if (5 < 4) {
+ console.log("This statement won’t print, because five is NOT less than 4.");
+} else {
+ console.log("This statement will print instead!");
+}
+```
+
+We can also check a second condition if we want using an else if statement.
+
+```js
+if (5 < 4) {
+ console.log("This statement won’t print, because five is NOT less than 4.");
+} else if (5 > 4) {
+ console.log("This statement will print, because five is greater than 4.");
+} else {
+ console.log("This statement won’t print, because a true expression was already found!");
+}
+```
+
+
+
Try It: Control Flow with if Statements
+
Back in your sandbox replit, write a program that will check the user’s age and determine whether or not they can rent a car using the following guidelines:
+
+
If the driver is below 20 years old, they cannot rent a car.
+
If the driver is between 20 and 24 years old, they can rent the car, but they need to pay an underage driver fee.
+
If the driver is over the age of 25, they can rent the car.
+
+
+
+
+### Up Next
+
+- [User Input](../user-input)
diff --git a/try-coding-fe/index.md b/try-coding-fe/index.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..02e6f49
--- /dev/null
+++ b/try-coding-fe/index.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+---
+layout: lesson
+---
+
+# Try Coding - JavaScript Focus
+
+Please sign up for a free replit.com account before beginning this workshop.
+
+## Welcome
+
+- Open up replit.com in a browser (preferably Chrome) and log into your account.
+- Change your Zoom display name to your first name, last initial, and pronouns – Kaitlyn V. (she/her). To do that, hover over your image in the gallery view, click the three dots, and select Rename.
+- Heads up! We will ask you to introduce yourself in a moment.
+
+## What to Expect
+
+Over the course of the day, we will write code, practice the habits of successful developers, and learn a little more about Turing. We will ask you to introduce yourself, ask questions, and occasionally share answers to the technical work we do! By the end of today, you will build your very own “Guess the Number” console game. Below is our agenda for the day:
+
+- Welcome & Introductions (30 minutes)
+- Instruction (90 minutes)
+- Wrap-Up (15 minutes)
+
+## Learning Norms
+
+- No question is too small and no question is a bad question. Ask them!
+- We all benefit from each other's ideas! Push yourself to share at least one time today.
+- Keep your camera on during the session (if you can).
+- **Questions?** Type into the zoom chat, raise your hand, or come off of mute! Please avoid direct messages unless it is a specific issue only to yourself.
+- **Disconnected?** Jump back on!
+
+
+## Zoom Practice
+
+There are several ways to get my attention throughout the workshop today. Let’s practice using some of these tools now.
+
+- **Type in the chat to everyone.** What is your favorite genre of music?
+- **Send the instructor a direct message.** What word describes how you are feeling today?
+- **Raise your hand.** Find your zoom toolbar, click Reactions, then Raise Hand.
+- **Introduce yourself!** Share your name, pronouns, and your location. Then, share why you’re here.
+
+1. I’m looking for a career change and I’m trying coding for the first time.
+2. I already know I want to attend Turing, but I need to pick a program!
+3. My friend or family member won’t stop bugging me about checking this out, so here I am!
+
+### Up Next
+
+- [What is Front End and Back End Engineering?](./what-is-fe-be)
+- [JavaScript Introduction](./js-intro)
+- [Control Flow](./control-flow)
+- [User Input](./user-input)
+- [Ruby Number Guesser](./rb-number-guesser)
+- [Wrap-Up](./wrap-up)
diff --git a/try-coding-fe/js-intro/index.md b/try-coding-fe/js-intro/index.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d8e2908
--- /dev/null
+++ b/try-coding-fe/js-intro/index.md
@@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
+---
+layout: lesson
+---
+
+### Go Back
+
+- [Welcome and Introductions](../)
+- [What is Front End and Back End Engineering?](../what-is-fe-be)
+
+# JavaScript Introduction
+
+JavaScript is a language that allows us to _interact_ with a webpage. We can write JavaScript that can access HTML elements and change their appearance or content based on the way a user interacts with the page.
+
+## Forking Your First Replit
+
+Replit is a web-based interactive development environment or IDE. It allows us to write code and see the output in the console at the same time. To get started today, we will be working in this JavaScript sandbox replit. When you open this replit, click the blue "Fork Repl" button to make your own copy on your account. From here, you can add code or delete code as much as you like. It's yours!
+
+A sandbox is a place where we can play around with code! Use this space to take notes or try things throughout the workshop today.
+
+
+
Important Note:
+
In order to run the code, click on "Dev Tools" to see the console where the code will print out, then click the green "Run" button.
+
+
+## console.log()
+
+In your sandbox replit, complete the activity that follows.
+
+
+
Try It: Exploring console.log()
+
Read the following JavaScript code, copy & paste it into the script.js file in your sandbox, then run it!
What does the output tell you about the job of the console.log() command?
+
+
+
+
+
Takeaways
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
console.log() is a command that is built into the JavaScript language
+
console.log() will print the value it is instructed to print and creates a line break after printing the data
+
+
+
+
+
+## Variables
+
+In order to store a piece of data and reference it later, possibly many times throughout our code, we need to use variables. You can think of a variable like a storage container with a label on it where we can hold items we care about. In JavaScript we define variables by typing the keyword var followed by the name of the variable we wish to create, the assignment operator (=), and then the value we want to store in that variable. We end each statement in our code with a semi-colon.
+
+When working with JavaScript, we use camelCase for variable names, which means that words are joined without spaces, and each new word begins with a capital letter.
+
+```js
+var email = "helloworld@gmail.com";
+var firstName = "Brandi";
+var location = "Tampa, FL 🌴";
+```
+
+
+
Try It: Variables in JavaScript
+
Back in your sandbox replit, declare three variables that describe yourself, using the names name, email, and location.
+
Make sure to console.log each variable to verify you've stored it correctly!
+
+
+## Data Types
+
+In JavaScript, your data (information) can be different types. There are two data types we will be working with today: Number (any numeric value), and String (words or phrases like "JavaScript is fun!"). We use the Number data type if we are storing data that may be manipulated in some way. We use the String data type if our data needs to remain consistent. With String data, anything inside of the quotation marks is preserved.
+
+
+
Deciding on a Data Type
+
For each item listed below, determine which data type is most appropriate for the information.
+
+
Username
+
Age
+
Zip Code
+
Balance on a bank account
+
Caption for an image
+
+
+
+
+
+
Try It: Data Types
+
Back in your replit, add two more variables about yourself assigned to Number values. Write a variable called numberOfPets and another variable of your choosing. Use console.log() to verify that the data was stored in the variable as expected!
+
+
+ 🌶Click here for a Spicy Challenge🌶
+
+
+
What happens if you add your two number variables together and console.log() the result?
+
+
+
+
+## Interpolation
+
+We can use string interpolation to combine static data with dynamic (or variable) data. Here's an example of the syntax:
+
+```js
+var firstName = "Amy";
+console.log(`Hello, ${firstName}!`);
+```
+
+The code above will make "Hello, Amy!" appear in the console.
+
+Note that _back ticks_ are the characters that surround this combination of the string an `${}` syntax. You can find the back-tick key at the top-left of your keyboard, next to the `1`.
+
+Anything inside the back ticks will be read as a string. But, when the interpreter sees the `${`, it will stop and wait for JavaScript code to read. Typically, we provide a variable name here. When the interpreter read the matching closing bracket - `}` - it goes back to treating characters as part of the string.
+
+
+
Try It: Interpolation
+
Using interpolation and at least two of the variables you declared in the previous section, write a sentence about yourself! Make sure to print that sentence out to the console.
+
Change the value of one of the Strings you interpolated and re-run your code. Is the difference reflected in the output?
+
+
+
+ 🌶Click here for a Spicy Challenge🌶
+
+
+
What happens if you interpolate numberOfPets * 4? What does that tell you about how interpolation works?
+
+
+
+
+### Up Next
+
+- [Control Flow](../control-flow)
diff --git a/try-coding-fe/rb-number-guesser/index.md b/try-coding-fe/rb-number-guesser/index.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..b5b49e7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/try-coding-fe/rb-number-guesser/index.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+---
+layout: lesson
+---
+
+### Go Back
+
+- [Welcome and Introductions](../)
+- [User Input](../user-input)
+
+# Ruby Number Guesser
+
+Your JavaScript number guesser code probably looks something like this:
+
+```js
+var input = document.querySelector("input");
+var button = document.querySelector("button");
+var paragraph = document.querySelector("p");
+
+var secretNumber = 6;
+
+button.addEventListener("click", checkGuess);
+
+function checkGuess() {
+ var guess = input.value;
+
+ if (guess > secretNumber) {
+ paragraph.innerText = "Too high!";
+ } else if (guess < secretNumber) {
+ paragraph.innerText = "Too low!";
+ } else {
+ paragraph.innerText = "Great job! You got it!";
+ }
+}
+```
+
+This is something you might build if you were in the Front End program at Turing.
+
+Now let's take a look at what this same code would look like if you were implementing Ruby in our Back End program.
+
+### Explore: Back End Number Guesser
+
+Take a few minutes to explore the code below.
+Consider: What are the similarities and differences you see between the Ruby code and the JavaScript code?
+
+```ruby
+secret_number = 6
+
+puts "Guess the secret number!"
+
+guess = gets.chomp.to_i
+
+if guess > secret_number
+ puts "Too high!"
+elsif guess < secret_number
+ puts "Too low!"
+else
+ puts "Great job! You got it!"
+end
+```
+
+## Front End versus Back End
+
+Whether we're working on the Front End or the Back End of an application, there is a lot of logic and data manipulation involved as illustrated by the number guessing code. The difference in Front End and Back End comes in what you'd work on next.
+
+If you're in the Front End program your next steps in this number guesser program might be to change the user interface, what the user sees and interacts with. Think about the webpage for this number guessing application.
+
+- What would the styling of this page be? (colors, fonts, shading)
+- How would the user input their guess and what would that _element_ look like?
+- Would there be any animations on the page to engage the user?
+
+If you're in the Back End program, your next steps might be in dealing with how to store this data and what to do with the data.
+
+- How should we store the information in the database?
+- Do we need to manipulate the data before storing it?
+- Is there any additional information we can get from the data such as averages, sums, or counts?
+
+## Questions
+
+What questions do you have about any of the content we've covered so far?
+
+## Up Next:
+
+- [Wrap Up](../wrap-up)
diff --git a/try-coding-fe/user-input/index.md b/try-coding-fe/user-input/index.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0a1d1b9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/try-coding-fe/user-input/index.md
@@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
+---
+layout: lesson
+---
+
+### Go Back
+
+- [Welcome and Introductions](../)
+- [Control Flow](../control-flow)
+
+# User Input
+
+Our programs haven’t been very exciting so far because we already know what will happen just by looking at the code. What if your program incorporated dynamic input from the user? For Front-End development, that's where HTML comes into play!
+
+## What is HTML?
+
+Of all of the major technologies used on the web, on either the Front-End or the Back-End, HTML, or Hyper Text Markup Language, is the oldest. [In the beginning](http://info.cern.ch/), the web was just a bunch of HTML documents that you wrote by hand. They had these _cool_ things called hyperlinks that would allow a user to click on a word on one page and be taken to another page.
+
+HTML is still an essential part of modern web applications. It holds the content and creates the structure of a webpage.
+
+
After forking the replit, be sure to open the dev tools, then take a few minutes to look through the code in all the different files.
+
Here are some things to consider as you explore:
+
+
Does anything happen when you hit the green Run button?
+
What about if we type something in the input and click on the button - do we see anything print out in the console?
+
+
+
+After exploring, let's take a look at some specific parts of the code below:
+
+### HTML
+
+```html
+
Hello World!
+
+
+```
+
+HTML is made up of a series of **elements**. Each of the lines above represents a different element. In order, we have one for putting text on the page, another for grabbing input from the user, and lastly a button that can be clicked on!
+
+### JavaScript
+
+```js
+var paragraph = document.querySelector('p'); // a variable forthe paragraph element
+var input = document.querySelector('input'); // a variable for the input element
+
+var userInput = input.value; // a variable that stores the input from the user
+console.log(paragraph.innerText); // printing the text of the paragraph to the console
+console.log(userInput); // printing any text the user writes to the console
+```
+
+## Changing HTML from JavaScript
+
+Displaying the information that's already on the page, in the console, is not all that helpful. It was just a stepping stone.
+
+The next stepping stone is learning how to _change_ the text inside an HTML element from our JavaScript code.
+
+
+
Apply & Explore
+
Using the Replit you just forked:
+
+
On line 6 in your script.js file, type something like: paragraph.innerText = "new text";
+
Hit Run and look in the mini browser - it should display the text you typed in that last line of code!
+
+
+
+### Listening for Button Clicks
+
+You may have noticed that the code you wrote changed the title of the page whenever we hit the Run button, and there were some other lines of code that only printed to the console when we clicked on the Click Me! button from the user interface.
+
+What if we want to run some code that only happens when the button is clicked?
+
+For now, we just need to know that the following code is responsible for running the code that happens when the button is cliked:
+
+```js
+var button = document.querySelector('button');
+
+button.addEventListener('click', doSomething);
+
+function doSomething() {
+ // code you want to be run ONLY when button
+ // is clicked, goes here.
+}
+```
+
+
+
Next Level
+
For this challenge, you'll use the same Replit you used for the previous one! In the previous challenge, you changed the title, but it happened on page load, so it wasn't very exciting.
+
Your Challenge: Combine the two new pieces of knowledge/skill you have to change the title only when the button is clicked.
+
+
Hint: You will need to use the paragraph.innerText and set it equal to the input.value
+
+
+
+
+
Solution:
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Here is our revised script.js file:
+
+
Inside of the doSomething() function, we set the text of the paragraph equal to the value that the user typed into the input field!
+
+
+
+
+
Building a "Guess the Number" Game
+
Use this replit as a starting point. We are going to build a “Guess the Number” game for a user in the console. In the starter kit, you already have a secretNumber variable assigned to 6 and a some other JavaScript that connects the HTML to the game. Follow the steps below to keep going!
+
Inside of the checkGuess function, write some code that will do the following:
+
+
If the guess is less than the secret number, tell the user, "Not quite. Too low."
+
If the guess is greater than the secret number, tell the user, "Oops. Too high."
+
Otherwise, tell the user they guessed the number with the statement, "You did it!"
+
Test your code a few times to make sure you can generate all 3 responses.
+
+
+
Hint: You will need to put together what we learned about Control Flow in the previous lesson, with changing the text on the screen.
+
+
+### Up Next
+
+- [Ruby Number Guesser](../rb-number-guesser)
diff --git a/try-coding-fe/what-is-fe-be/index.md b/try-coding-fe/what-is-fe-be/index.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..6e941c8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/try-coding-fe/what-is-fe-be/index.md
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
+---
+layout: lesson
+---
+
+### Go Back
+
+- [Welcome and Introductions](../)
+
+# What is Front End and Back End Engineering?
+
+## How Does the Internet Even Work?
+
+When you visit a URL like https://www.vcahospitals.com/, what happens?
+
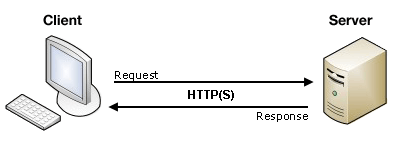
+Here is a simplified diagram of the client-server model:
+
+
+
+Source: Mozilla.org
+
+
+When a User enters in a website name (web address), a request is made to the Server for that company. That server stores all the data for that company and will return the data which was requested. The Client (browser), will then display that data and allow the user to view and interact with the requested data.
+
+## What is the Front End?
+
+The **Front End** is the part of the application that users see, touch, and interact with.
+
+When we're talking about web development, the Front End is the part of the code base that takes care of rendering the user interface in the web browser.
+
+The Front End will prompt users in various ways to collect information which can be used to customize the user's experience within an application.
+
+## What technologies are used on the Front End?
+
+The three main technologies used on the Front End are:
+
+- CSS (styling of the webpage)
+- HTML
+- JavaScript
+
+Other frameworks are build on top of JavaScript such as React, Vue, or Angular.
+
+## What is the Back End?
+
+Back End engineering is concerned with managing and manipulating data (aka information).
+
+When we talk about Back End engineering, we're often thinking of the programming tasks involved in making this possible:
+
+- Storing data and accessing it later
+- Verifying that data is accurate
+- Manipulating, analyzing, and/or calculating data
+- Making sure data can be retrieved quickly and easily
+
+## What technologies are used on the Back End?
+
+There are numerous technologies that can be used for Back End programming. Here are a few of them:
+
+- **Languages and frameworks**: Ruby/Rails, Python/Django, Elixir/Phoenix, Java/Spring, and more.
+- **Databases**: PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle Database, MongoDB, etc.
+
+## Both Front End and Back End work with a lot of data and logic.
+
+Most of the work you will do as a developer is data manipulation.
+
+- How will you get the data?
+- What parts of it will you use?
+- Do you need to reformat any of the data?
+- How will you display the data to the user?
+- What does this data mean?
+
+Both Front End and Back End deal with taking in data (input), and then giving back or _returning_ new data based on that input. Today we're going to look at how we might work with some of this data in both Ruby, our Back End language, and JavaScript, our Front End language.
+
+### Interested in learning more about FE vs BE?
+
+:arrow_right: Come to a **What is Front End, Back End, and Full Stack Development? workshop**! You can see a list of upcoming events here!
+
+## Up Next
+
+- [JavaScript Introduction](../js-intro)
diff --git a/try-coding-fe/wrap-up/index.md b/try-coding-fe/wrap-up/index.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..581d374
--- /dev/null
+++ b/try-coding-fe/wrap-up/index.md
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+---
+layout: lesson
+---
+
+### Go Back
+
+- [Welcome and Introductions](../)
+- [Ruby Number Guesser](../rb-number-guesser)
+
+# Next Steps
+
+## Feedback
+
+At Turing, we rely on constant feedback from our students to improve the Turing experience. Please take two minutes at this time to fill out this survey to give us feedback on this Try Coding session today.
+
+## Attend Other Events
+
+We are always creating new, exciting events for prospective students. Check out our upcoming events here!
+
+## Talk to Us
+
+We know everyone has different barriers or concerns as they start this process. Our team is here to help you find solutions to each barrier and ease your concerns from how to pay for Turing to what is the job support like.
+
+Reach out if you have any questions at all - from _Can I afford this?_ to _Should I do frontend or backend?_ to _What is a typical day like as a Turing student?_ - we're here for you! Email **admissions@turing.edu** with your questions and we'll schedule a one on one call with you!
+
+## Apply!
+
+Let's do it! Start your application today at apply.turing.edu.
diff --git a/try-coding-general/index.md b/try-coding-general/index.md
index f780490..dccedc8 100644
--- a/try-coding-general/index.md
+++ b/try-coding-general/index.md
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
layout: lesson
---
-# Try Coding
+# Try Coding - Ruby Focus
Please sign up for a free replit.com account before beginning this workshop.
diff --git a/workshop-curriculum/index.html b/workshop-curriculum/index.html
index 2d30275..8fce7b6 100644
--- a/workshop-curriculum/index.html
+++ b/workshop-curriculum/index.html
@@ -16,7 +16,8 @@
Information Sessions
Try Coding
These workshops will get you some hands-on experience with code. You'll get a glimpse at Front End and Back End code!