给你一个数组 nums 和一个值 val,你需要 原地 移除所有数值等于 val 的元素,并返回移除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须仅使用 O(1) 额外空间并 原地 修改输入数组。
元素的顺序可以改变。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
说明:
为什么返回数值是整数,但输出的答案是数组呢?
请注意,输入数组是以「引用」方式传递的,这意味着在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
你可以想象内部操作如下:
// nums 是以“引用”方式传递的。也就是说,不对实参作任何拷贝
int len = removeElement(nums, val);
// 在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
// 根据你的函数返回的长度, 它会打印出数组中 该长度范围内 的所有元素。
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
print(nums[i]);
}
示例 1:
输入:nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3 输出:2, nums = [2,2] 解释:函数应该返回新的长度 2, 并且 nums 中的前两个元素均为 2。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。例如,函数返回的新长度为 2 ,而 nums = [2,2,3,3] 或 nums = [2,2,0,0],也会被视作正确答案。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2 输出:5, nums = [0,1,4,0,3] 解释:函数应该返回新的长度5, 并且 nums 中的前五个元素为0,1,3,0, 4。注意这五个元素可为任意顺序。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
提示:
0 <= nums.length <= 1000 <= nums[i] <= 500 <= val <= 100
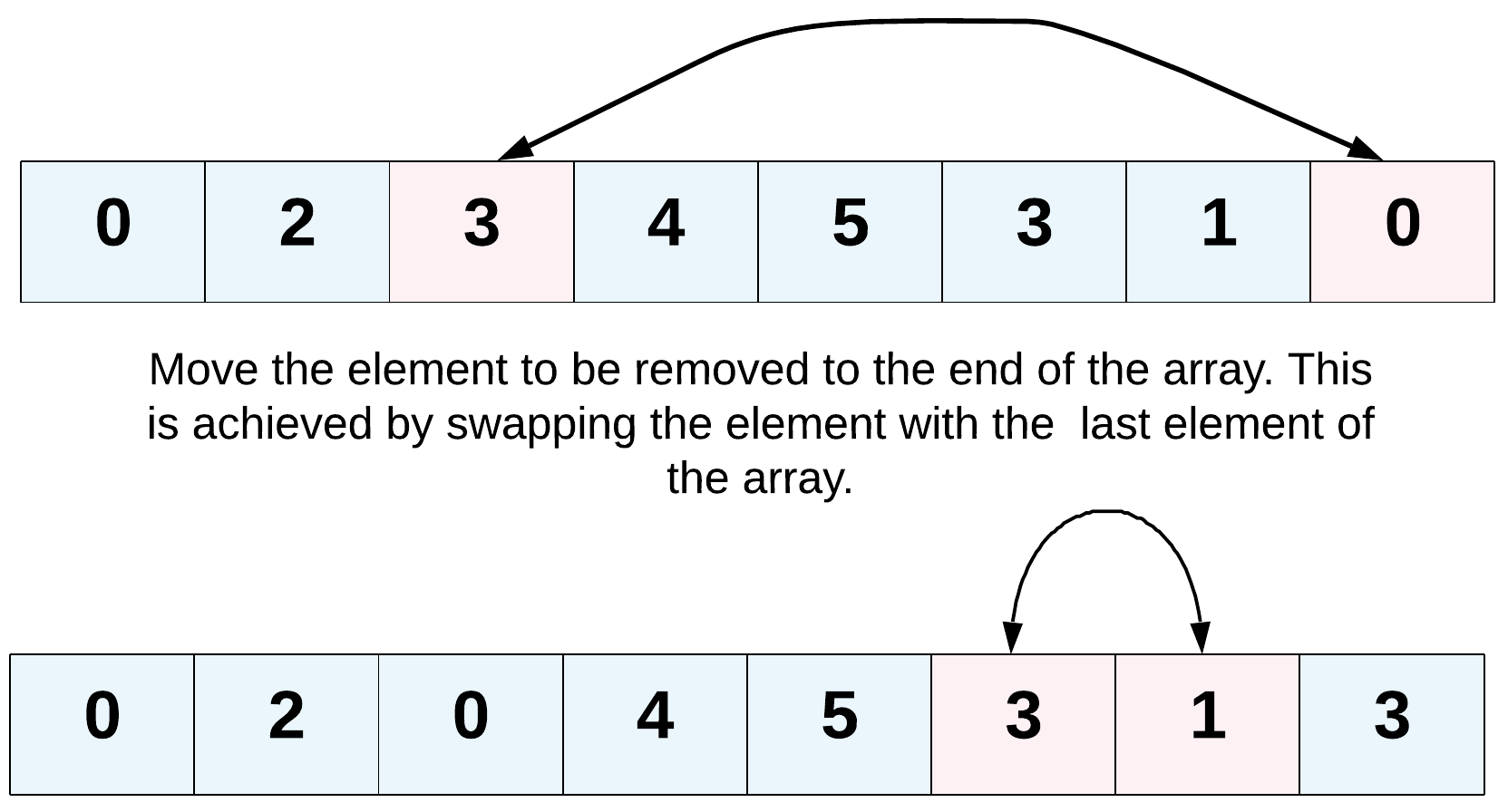
- The problem statement clearly asks us to modify the array in-place and it also says that the element beyond the new length of the array can be anything. Given an element, we need to remove all the occurrences of it from the array. We don't technically need to remove that element per-say, right?
- We can move all the occurrences of this element to the end of the array. Use two pointers!
- Yet another direction of thought is to consider the elements to be removed as non-existent. In a single pass, if we keep copying the visible elements in-place, that should also solve this problem for us.