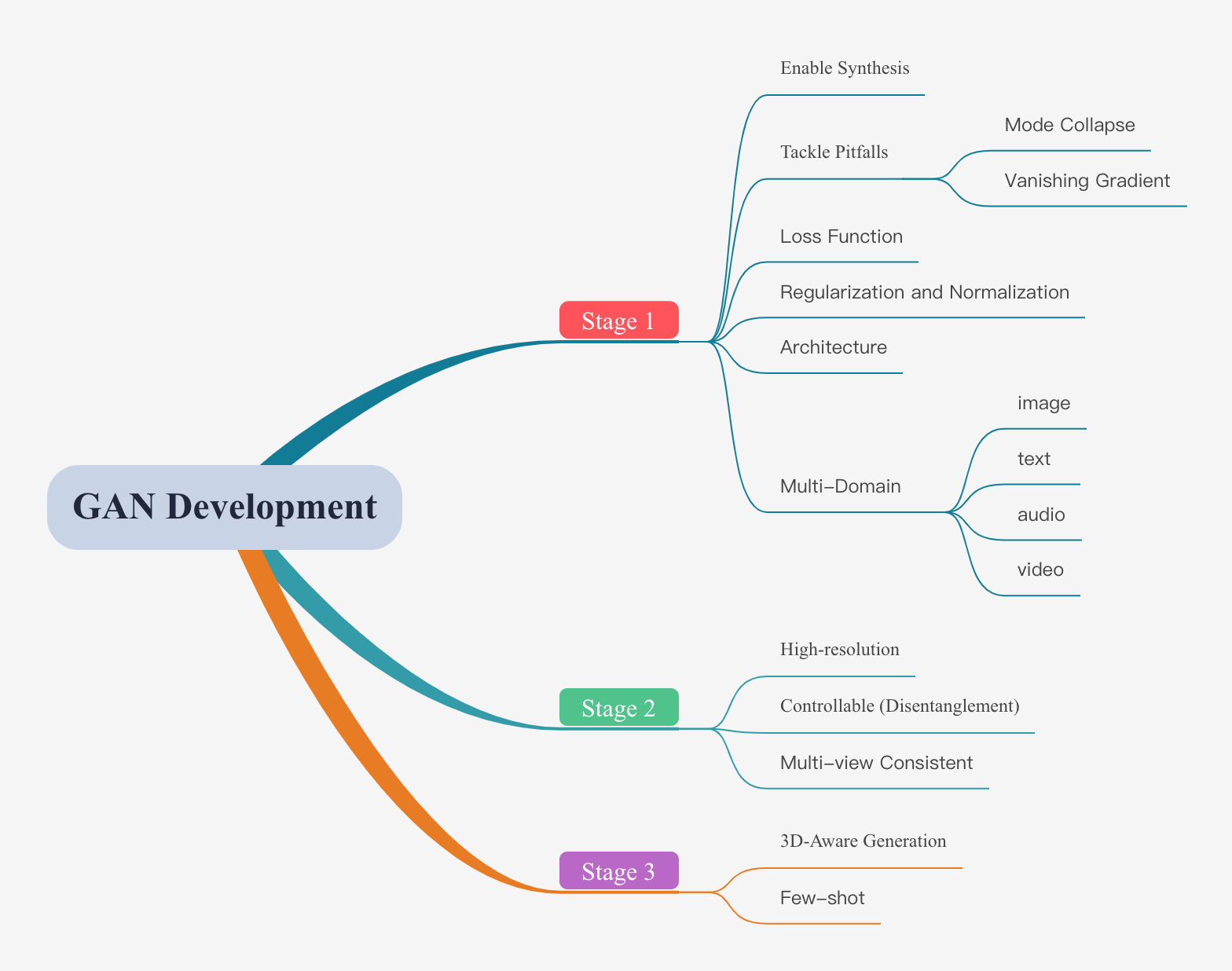
A collection of resources on Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs).
The purpose of GAN is to generate/synthesize fake but photo-real images (synthesize high-resolution portraits that are often indistinguishable from real faces). GANs are popular partly because they tackle the important unsolved challenge of unsupervised learning. It represents a zero-sum game between two machine players, a generator and a discriminator, designed to learn the distribution of data. Using an adversarial methods, bypass the need of computing densities, at the expense of a good density estimation.
If intelligence was a cake, unsupervised learning would be the cake, supervised learning would be the icing on the cake, and reinforcement learning would be the cherry on the cake. We know how to make the icing and the cherry, but we don’t know how to make the cake. – Yann LeCun, 2016.
To quickly touch GAN: Stylegan Online Demo
To read some related survey: 2019 2020
SOTA Benchmark: Image Generation
Open Questions about Generative Adversarial Networks: https://distill.pub/2019/gan-open-problems/
-
mode collapse: diversity the generator can only learn some limited patterns from the large-scale target datasets, or assigns all of its probability mass to a small region in the space.
-
vanishing gradient: the gradient of generator vanishes at the begining of training process.
See more details in the subfolders.
| Branch | |
|---|---|
| Controllable-GAN | Inverion. We can find a common latent code, and we can also find a seperate code for each layer of the generator. It is easy and better to manipulate a given image in the latent feature space. |
| Few-Shot & Limited Data | |
| Pretrained GANs | |
| Style Transfer & Image2Image | |
| Other Applications | In&Out painting, Text2image, High&Super Reselution, Animation, Video Generation |
都是最小化Loss
| Name (paper link) | Loss Function |
|---|---|
| Vanilla GAN | |
| non-saturated GAN | |
| LSGAN | |
| WGAN | |
| WGAN-GP | |
| DRAGAN |
inspired by hwalsuklee