- querySelector
- querySelectorAll
模拟 jquery 封装两个查询方法:
function $(selector) {
return document.querySelector(selector);
}
function $$(selector) {
return document.querySelectorAll(selector);
}模板字符串使用反引号 (`` ) 来代替普通字符串中的用双引号和单引号。模板字符串可以包含特定语法(${expression})的占位符。
var name = "xiejie";
console.log(`Hello,${name}`);以前使用字符串拼接:
var chessPoint = {
c : 'white',
x : 2,
y : 3
}
var newChess = "<div style='' class='chess " + chessPoint.c + "' data-row='" + chessPoint.y + "' data-line='" + chessPoint.x + "'></div>";
// <div class='chess white' data-row='3' data-line='2'></div>现在使用字符串模板:
var chessPoint = {
c : 'white',
x : 2,
y : 3
}
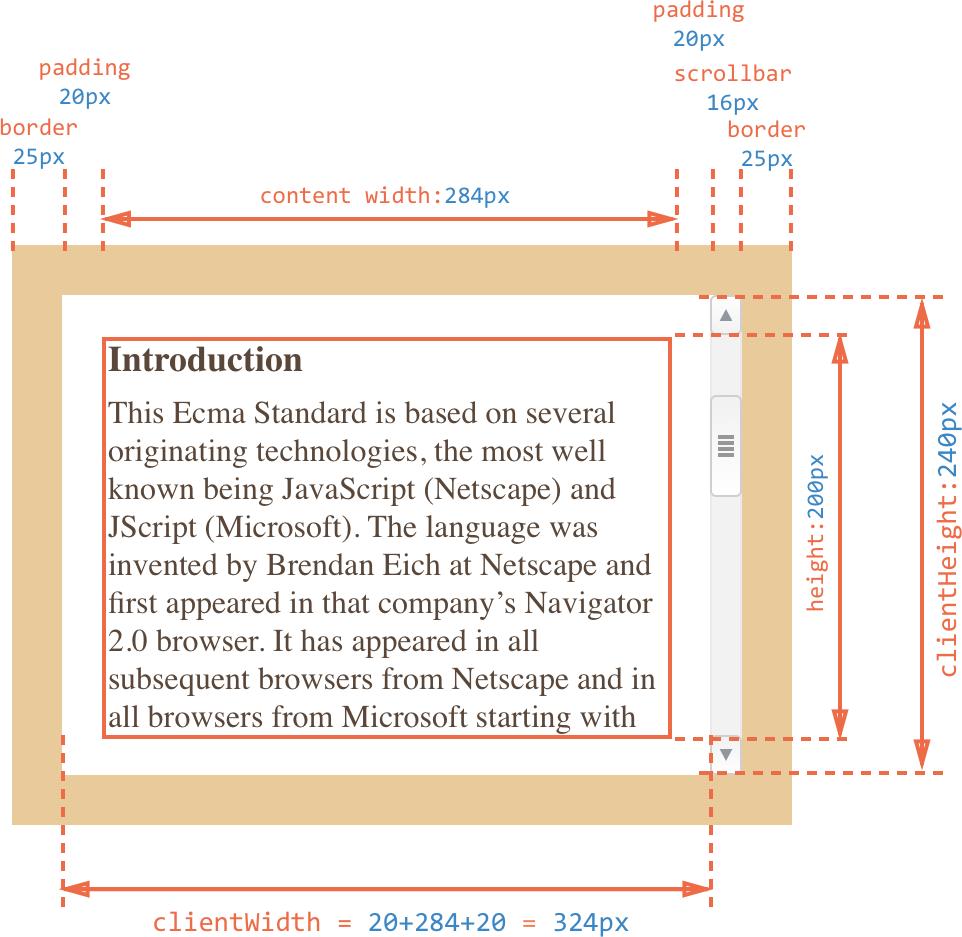
var newChess = `<div class='chess ${chessPoint.c}' data-row='${chessPoint.y}' data-line='${chessPoint.x}'></div>`Element.clientWidth 属性表示元素的内部宽度,以像素计。该属性包括内边距 padding,但不包括边框 border、外边距 margin 和垂直滚动条(如果有的话)。
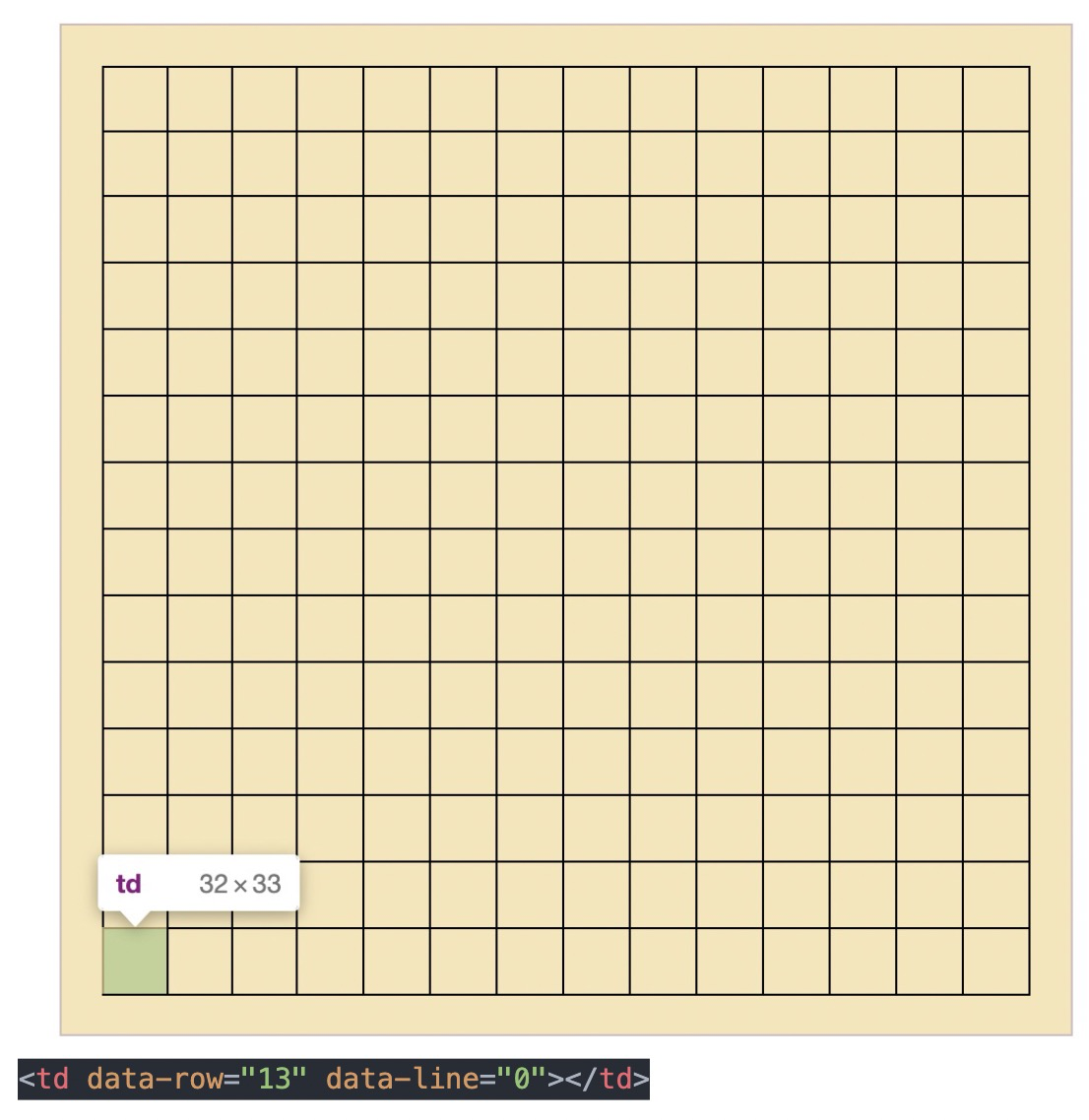
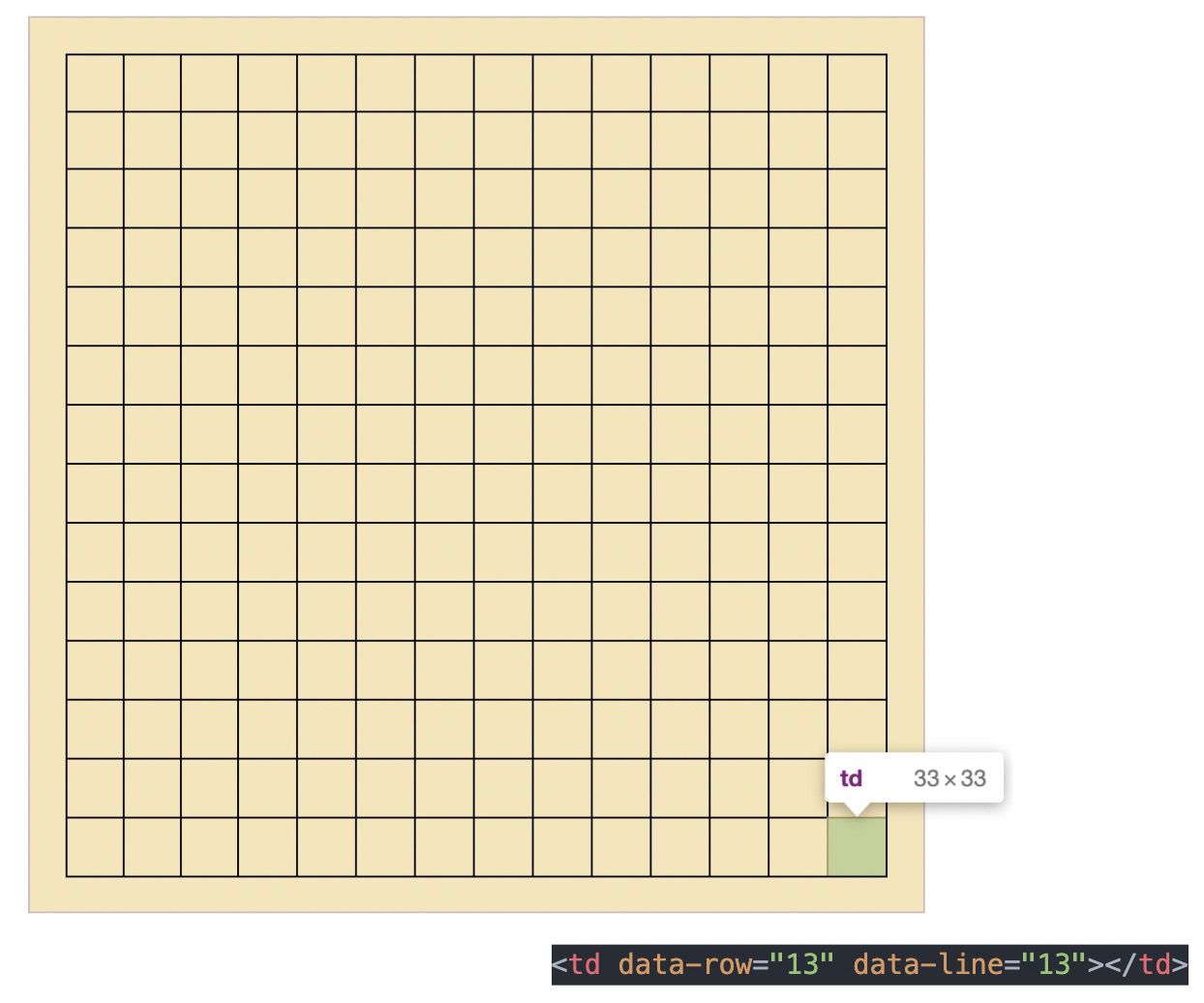
绘制棋盘,其实就是一个 14 行 x 14 列 的 table 表格。
每个 td 会记录当前的格子是第几行第几列,我们通过自定义属性来进行记录。
data-row 记录行,data-line 记录列。
例如:
第一行第一列
第一行最后一列
最后一行第一列
最后一行最后一列
接下来,当用户在棋盘上点击鼠标时,我们需要落下一颗棋子,那么如何确定这颗棋子的坐标呢?
首先,通过 e.target.dataset,能够获取到用户点击的是哪一个 td,这个倒是很简单,获取大的是一个对象
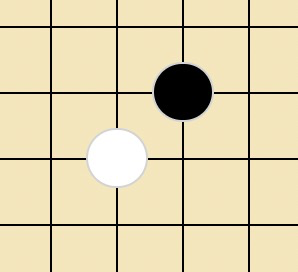
{row: "0", line: "0"}但是接下来有一个很重要的事情,就是在知道用户点击了哪一个 td 后,我们还需要判断落子应该在什么位置?
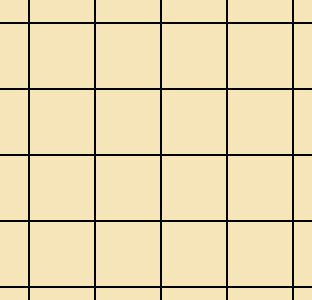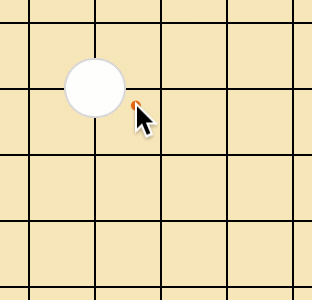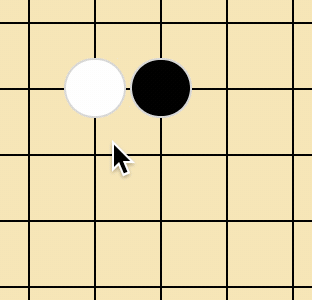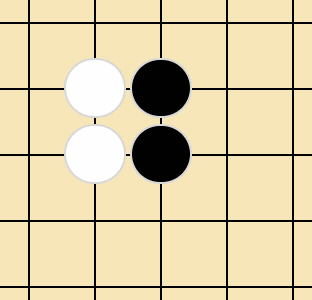
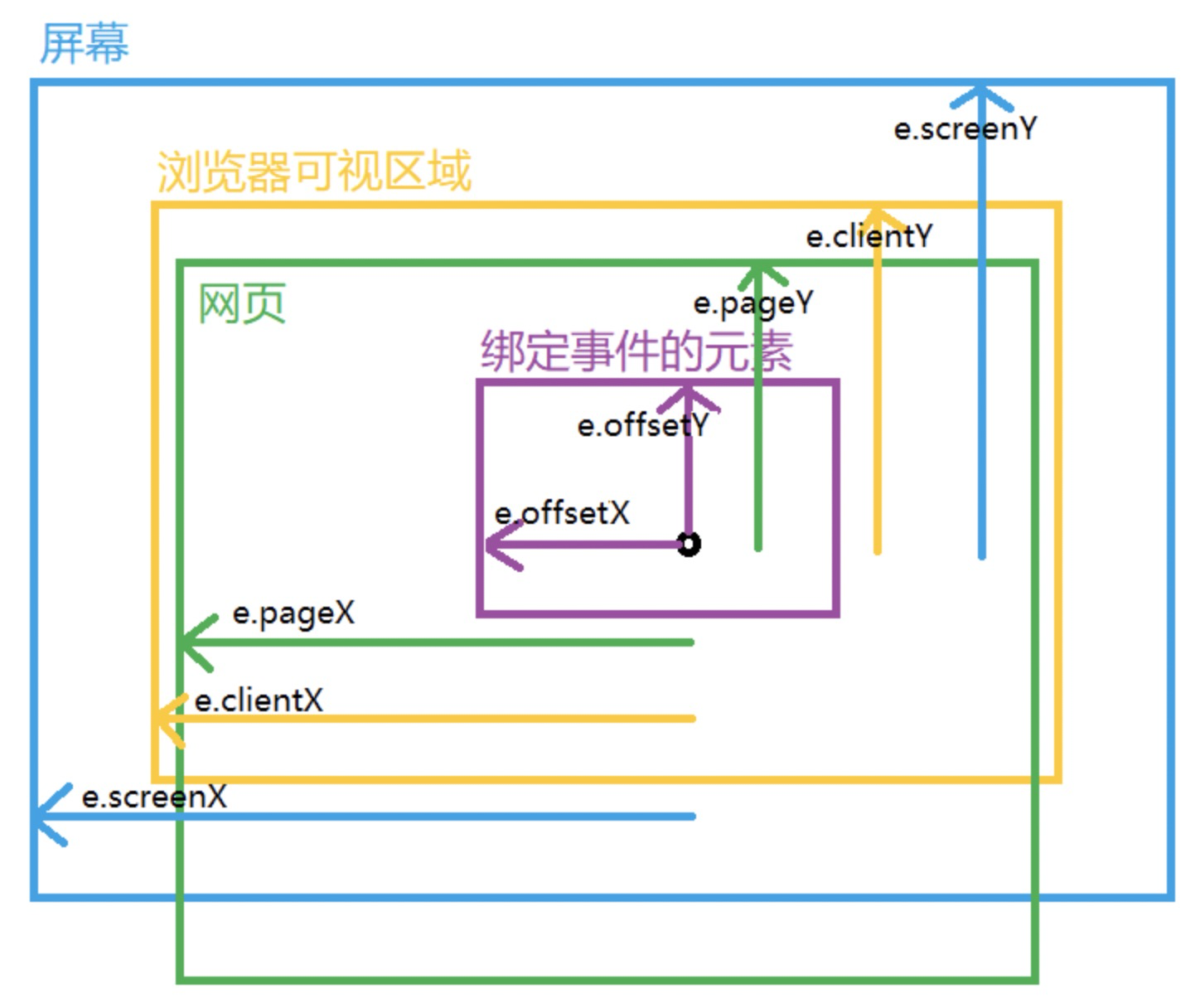
什么意思?看上面的图,我们落子是落在两条线的交叉处的,而不是格子中央,这意味着同样一个 td 格子,用户点击的位置不同,则棋子的位置也不同。
那么如何判定成为了关键!
首先,通过 e.offsetX、e.offsetY,我们就可以获取到事件发生时鼠标相对于事件源元素的坐标,所谓事件源元素就是绑定事件的那个元素。
看下图:
那么,我们就可以采用下面的方式来进行评判。
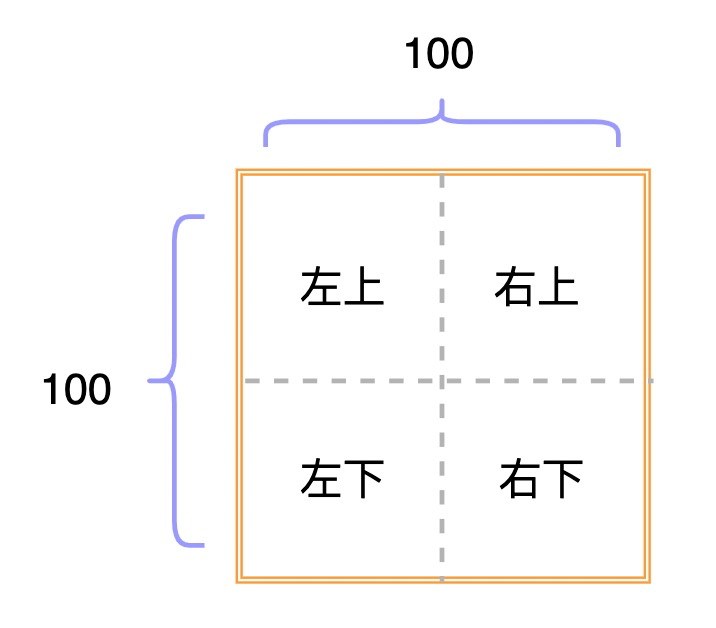
首先计算出一个格子的宽高,然后用户点击的 e.offsetX 小于格子宽度的一半,e.offsetY 小于格子高度的一半,则是左上区域。 e.offsetX 小于格子宽度的一半但是 e.offsetY 大于格子高度的一半,则是左下,依此类推。
//定位落子的位置是在四个角的哪一个
var positionX = e.offsetX > tdw / 2;
var positionY = e.offsetY > tdw / 2;
// 生成点击的坐标点,包含 3 个属性
// x 坐标、y 坐标和 c 落子方
var chessPoint = {
x: positionX ? parseInt(temp.line) + 1 : parseInt(temp.line),
y: positionY ? parseInt(temp.row) + 1 : parseInt(temp.row),
c: whichOne
}这里我们就重新组装了格子信息,得到类似于下面的对象。
{x: 0, y: 0, c: "white"} // 第一个格子左上
{x: 1, y: 0, c: "black"} // 第一个格子右上
{x: 0, y: 1, c: "white"} // 第一个格子左下
{x: 1, y: 1, c: "white"} // 第一个格子右下棋子的坐标已经确定后,接下来要做的工作就是绘制棋子了。
绘制棋子其实就是在 td 单元格里面添加一个 div,例如第一行第一个棋子:
<td data-row="0" data-line="0">
<div style="" class="white" data-row="0" data-line="0"></div>
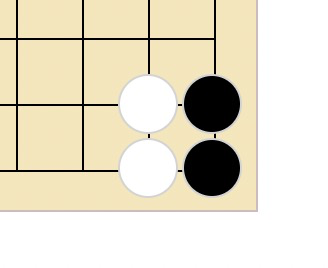
</td>需要注意的是每一行和每一列的最后两个棋子共用一个单元格,例如第一行最后两个棋子:
<td data-row="0" data-line="13">
<!-- 最后一个棋子 -->
<div style="left: 50%;" class="black" data-row="0" data-line="14"></div>
<!-- 倒数第二个棋子 -->
<div style="" class="white" data-row="0" data-line="13"></div>
</td>所以最右下角的格子,会放 4 个 div,如下:
<td data-row="13" data-line="13">
<div style="" class="white" data-row="13" data-line="13"></div>
<div style="left: 50%;" class="black" data-row="13" data-line="14"></div>
<div style="top: 50%;" class="white" data-row="14" data-line="13"></div>
<div style="top: 50%; left: 50%;" class="black" data-row="14" data-line="14"></div>
</td>如何判定胜负呢?那就是每一次落子都需要判断。
具体的方案就是每一次落子都将这个棋子的坐标对象存储入数组,然后每次落子遍历数组进行判断即可。
核心代码块:
// 检查横着有没有连着的 5 个
chess2 = chessArr.find(function (item) {
return curChess.x === item.x + 1 && item.y === curChess.y && item.c === curChess.c;
})
chess3 = chessArr.find(function (item) {
return curChess.x === item.x + 2 && item.y === curChess.y && item.c === curChess.c;
})
chess4 = chessArr.find(function (item) {
return curChess.x === item.x + 3 && item.y === curChess.y && item.c === curChess.c;
})
chess5 = chessArr.find(function (item) {
return curChess.x === item.x + 4 && item.y === curChess.y && item.c === curChess.c;
})
if (chess2 && chess3 && chess4 && chess5) {
end(curChess, chess2, chess3, chess4, chess5);
}
// 检查竖着有没有连着的 5 个
chess2 = chessArr.find(function (item) {
return curChess.x === item.x && item.y + 1 === curChess.y && item.c === curChess.c;
})
chess3 = chessArr.find(function (item) {
return curChess.x === item.x && item.y + 2 === curChess.y && item.c === curChess.c;
})
chess4 = chessArr.find(function (item) {
return curChess.x === item.x && item.y + 3 === curChess.y && item.c === curChess.c;
})
chess5 = chessArr.find(function (item) {
return curChess.x === item.x && item.y + 4 === curChess.y && item.c === curChess.c;
})
if (chess2 && chess3 && chess4 && chess5) {
end(curChess, chess2, chess3, chess4, chess5);
}
// 检查斜线 1 有没有连着的 5 个
chess2 = chessArr.find(function (item) {
return curChess.x === item.x + 1 && item.y + 1 === curChess.y && item.c === curChess.c;
})
chess3 = chessArr.find(function (item) {
return curChess.x === item.x + 2 && item.y + 2 === curChess.y && item.c === curChess.c;
})
chess4 = chessArr.find(function (item) {
return curChess.x === item.x + 3 && item.y + 3 === curChess.y && item.c === curChess.c;
})
chess5 = chessArr.find(function (item) {
return curChess.x === item.x + 4 && item.y + 4 === curChess.y && item.c === curChess.c;
})
if (chess2 && chess3 && chess4 && chess5) {
end(curChess, chess2, chess3, chess4, chess5);
}
// 检查斜线 2 有没有连着的 5 个
chess2 = chessArr.find(function (item) {
return curChess.x === item.x - 1 && item.y + 1 === curChess.y && item.c === curChess.c;
})
chess3 = chessArr.find(function (item) {
return curChess.x === item.x - 2 && item.y + 2 === curChess.y && item.c === curChess.c;
})
chess4 = chessArr.find(function (item) {
return curChess.x === item.x - 3 && item.y + 3 === curChess.y && item.c === curChess.c;
})
chess5 = chessArr.find(function (item) {
return curChess.x === item.x - 4 && item.y + 4 === curChess.y && item.c === curChess.c;
})
if (chess2 && chess3 && chess4 && chess5) {
end(curChess, chess2, chess3, chess4, chess5);
}