一个vscode 上好用的工具Nand2Tetris tools 可以自动运行后生成.out 文件 并与.cmp 文件对比。以及自动压缩需要提交的文件,打开模拟器等。
运行程序方式可以 cmd + P 打开命令面板,按下>终端命令提示符, 然后才可以nand2tetris 模糊搜索对应命令。
提交文件,熟悉是否能够使用coursera提交作业。
use primitive nand gates to yield a basic chip-set.
pay attention to HDL select two representative Chip's implementation
CHIP Mux8Way16 {
IN a[16], b[16], c[16], d[16],
e[16], f[16], g[16], h[16],
sel[3];
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
// Put your code here:
Mux4Way16(a=a, b=b, c=c, d=d, sel=sel[0..1], out=out1);
Mux4Way16(a=e, b=f, c=g, d=h, sel=sel[0..1], out=out2);
Mux16(a=out1, b=out2, sel=sel[2], out=out);
}
draw the true table and simplify the bool logic
CHIP Mux {
IN a, b, sel;
OUT out;
PARTS:
// Put your code here:
Not(in=sel, out=notsel);
And(a=notsel, b=a, out=out1);
And(a=b, b=sel, out=out2);
Or(a=out1, b=out2, out=out);
}
the main problem is ALU
use Mux16 chip for control bit. zx nx zy ny f no etc.
Mux16(a=x, b=false, sel=zx, out=x1);
Not16(in=x1, out=notx1);
Mux16(a=x1, b=notx1, sel=nx, out=x2);
1bit register -> 16bit register -> 8RAM -> 64RAM -> 512RAM -> 4KRAM -> 16KRAM
use DMUX plus top address bits to load the load to the selected RAM
use behinds bits to load the input
use MUX and the top bits of address to output the selected RAM's output.
the main problem is PC
Inc16(in=state, out=out1);
Mux16(a=state, b=out1, sel=inc, out=out2); //In most cases, the counter has to simply increment itself by 1 in each clock cycle
Mux16(a=out2, b=in, sel=load, out=out3);
Mux16(a=out3, b=false, sel=reset, out=out4);
Register(in=out4, load=true, out=out, out=state);
a new level of abstraction, from machine code to symbolic Programming.
get familiar with the hack assemble Language
Mult assume R0 and R1 >= 0, use loop to resolve this problem.
the main problem is fill.asm use two nested loop to solve this problem.
the outer loop used for check the KBD and the inner loop used the fill the screen
initialize i and use it for counter, use address for pointer use n for the number of pixel (8K)
pay attention to a bug
@address
M = M + 1 //address = address + 1not
@address
M = M + i //address = address + imy memory out of bound and always send error for this reason. I debug ths problem use a lot of time...
0000000000000000
0111111111111111 RAM
1000000000000000
1011111111111111 screen
1100000000000000 keyboard 注意只考虑这三种输入,其他地址输入无效
a[14] determins load to screen or RAM, a[13] determines load to screen
and assume there is only three type input
this part is really cool you need to pay a lot of efforts in this problem
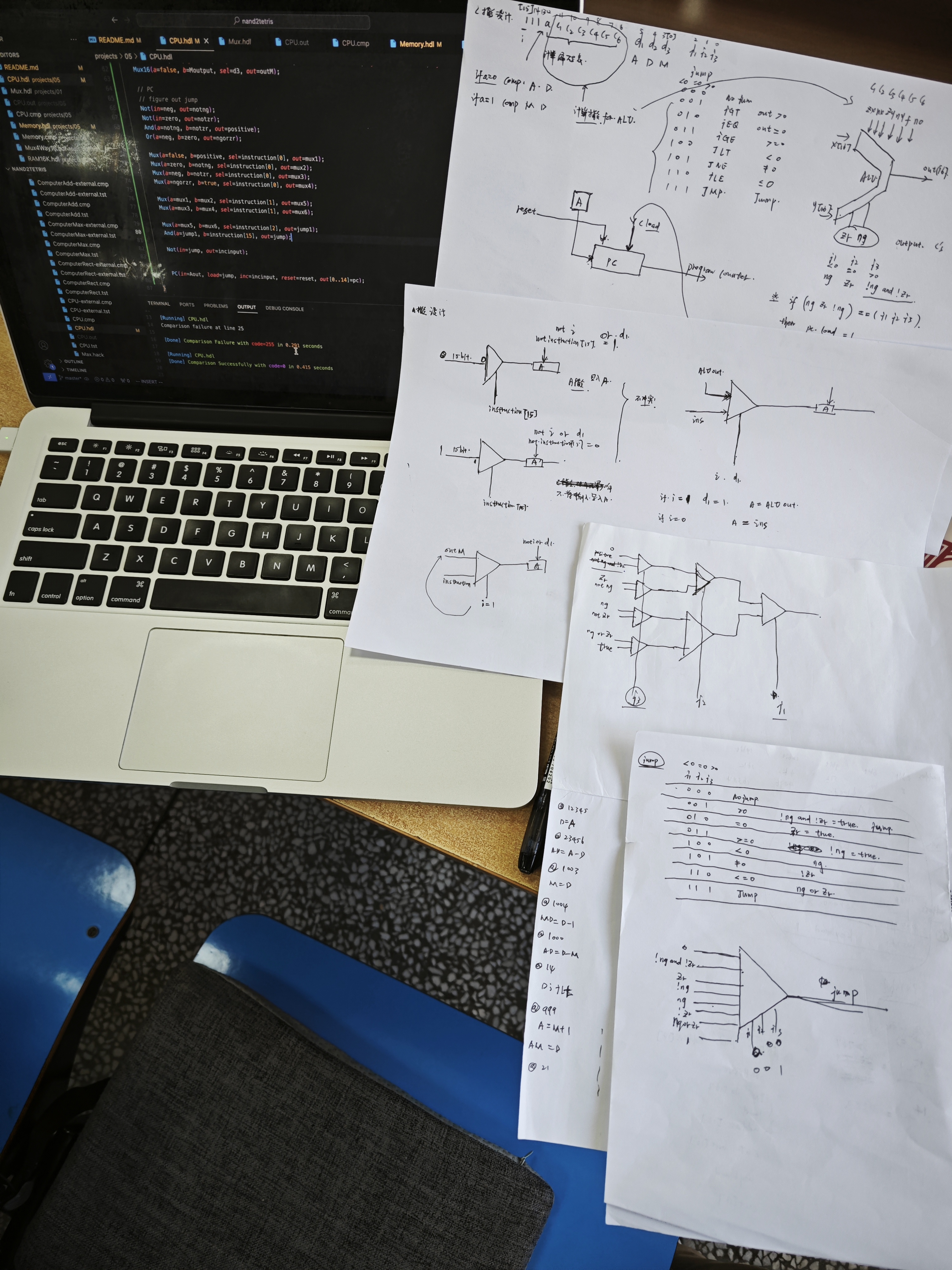
- problem1 consider how to identify A-instruction and C-instruction and how to use the control bit i and d1 put them in the same part of the Architecture without conflict.
- problem2 ALU part (zx nx zy ny f no) = (c1 c2 c3 c4 c5 c6), x[16] = D, y[16] = A/M, and if a == 0 comp A D, if a == 1 comp M D
- probelem3 PC. this is the most hard part in CPU, you need to use the control bits j1 j2 j3 and ALU's output control bit to determine the Program Counter, which corresponds to the address of the instruction in the ROM, which will be executed in the next clock. when load is true, the pc's output will be the address stored in A register. and if no jump, then inc = true.
// PC
// figure out jump
// j1 j2 j3
// 0 0 0 jump = 0
// 0 0 1 !ng and !zr
// 0 1 0 zr
// 0 1 1 !ng
// 1 0 0 ng
// 1 0 1 !zr
// 1 1 0 ng or zr
// 1 1 1 jump = 1
- problem 4 another bug is the the output load to D register only when it is C instruction.
can't pass CPU-externa.txt
use nearly a whole day and debug some problems, rewarding!!!
just connect the ROM RAM and CPU is ok
use python dict and re module
- read original file and store the lines in list
- delete all space and comments
- first scan the list and add label to symbol table(the dict)
- second scan the list and add the variable to the symbol table (take careful not all the value behind the @ are variable)
- remove label and restore it in another list
- iterate though the list if it's A instruction use parsea if it's C instruction use parsec
- use sys re and str.method to read the original file and store the vmcode in the VMTranslator.vmcode attribute
- first handle Arithmetric operation
there is a hard question with
self.arithmetic_dict = { "neg": "-", "not": "!", "add": "+", "sub": "-", "and": "&", "or": "|", "eq": "JEQ", "gt": "JGT", "lt": "JLT" }
eqgtandltyou need to use different label and jump assemble to branchtrue -1andfalse 0, I can't think out a better method to figure out this question, because assemble language can't access the ALU's flag bit. - constant segment it's a virtual segment and there's is no pop operation with this segment, the push constant i just push i into the stack
- static segment
R[16]~R[255]to store the static variable,
for push first get the static value@filename.indexD=Mthen push it into the stack
for pop first get the stack value and store it into D register then@filename.indexM=D - temp pointer segment
temp segment
push addr = 5+ i; *sp = *addr; sp++
pop addr = 5 + i; sp--; *addr = *spR[13] R[14] R[15] is used for variable pointer segment just change the 5 to 3 and plus the index 0/1 is R[3]/R[4] corresponds toTHISandTHAT - local argument this that segment
these four segment has the same push or pop paradigm
addr = LCL + index; *sp = *addr; sp++
this project is very rewarding to practice python

at the beginning i passed all test except the Fibonaccielement
I review all my asm code translation and find no bugs but the RAM[0] = 271 and RAM[1] = 4, always wrong.
then I review my call Main.fibonacci 1 function
I find an important issue to make every call function return address label unique, please make sure that you translated asm code has three different returnaddresslabel
@Main.fibonacci$ret0 ... (Main.fibonacci$ret0)@Main.fibonacci$ret1 ... (Main.fibonacci$ret1)@Main.fibonacci$ret2 ... (Main.fibonacci$ret2)the first and second is translated fromMain.vmand third fromSys.vm
to make your returnaddress alias returnlabel unique
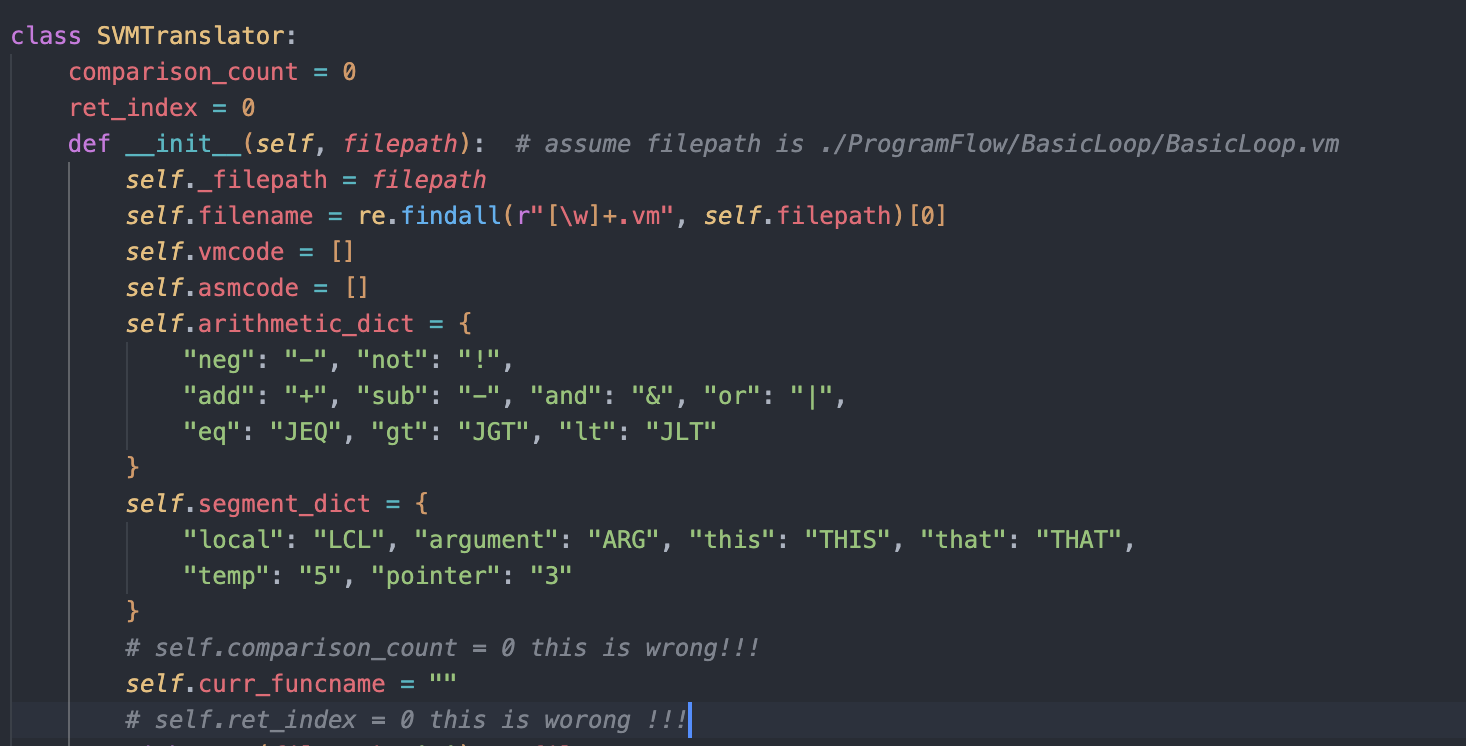
make sure to make your ret_index as a class attribute
then in your instance method
SVMTranslator.ret_index += 1
then every call of the same function in different files will has a unique return address label
first handle string, then add dilimeters to split the line
delimeters = re.findall(r"[\[\]\(\)\{\}\,\.\;\-\~ ]", code)
if delimeters:
for delimeter in delimeters:
first, code = code.split(delimeter, 1)[0], code.split(delimeter,1)[1]
if first:
self.tokens.append(first)
if delimeter == ' ':
continue
else:
self.tokens.append(delimeter)use the given un_terminal_tags to parse the class construct the parse tree
from compileClass() to compileTerm() use Terminal_token and Unterminal_token to express every line in .xml file
pay attention to the descent parsing tree