This document walks you through the most common use cases for React Native WebView. It doesn't cover the full API, but after reading it and looking at the sample code snippets you should have a good sense for how the WebView works and common patterns for using the WebView.
This guide is currently a work in progress.
- Basic Inline HTML
- Basic URL Source
- Controlling navigation state changes
- Add support for File Upload
- Multiple files upload
- Add support for File Download
- Communicating between JS and Native
The simplest way to use the WebView is to simply pipe in the HTML you want to display. Note that setting an html source requires the originWhiteList property to be set to ['*'].
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { WebView } from 'react-native-webview';
class MyInlineWeb extends Component {
render() {
return (
<WebView
originWhitelist={['*']}
source={{ html: '<h1>This is a static HTML source!</h1>' }}
/>
);
}
}Passing a new static html source will cause the WebView to rerender.
This is the most common use-case for WebView.
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { WebView } from 'react-native-webview';
class MyWeb extends Component {
render() {
return (
<WebView
source={{uri: 'https://facebook.github.io/react-native/'}}
/>
);
}
}Sometimes you want to intercept a user tapping on a link in your webview and do something different than navigating there in the webview. Here's some example code on how you might do that using the onNavigationStateChange function.
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { WebView } from 'react-native-webview';
class MyWeb extends Component {
webview = null;
render() {
return (
<WebView
ref={ref => (this.webview = ref)}
source={{uri: 'https://facebook.github.io/react-native/'}}
onNavigationStateChange={this.handleWebViewNavigationStateChange}
/>
);
}
handleWebViewNavigationStateChange = newNavState => {
// newNavState looks something like this:
// {
// url?: string;
// title?: string;
// loading?: boolean;
// canGoBack?: boolean;
// canGoForward?: boolean;
// }
const { url } = newNavState;
if (!url) return
// handle certain doctypes
if (url.includes('.pdf')) {
this.webview.stopLoading();
// open a modal with the PDF viewer
}
// one way to handle a successful form submit is via query strings
if (url.includes('?message=success')) {
this.webview.stopLoading();
// maybe close this view?
}
// one way to handle errors is via query string
if (url.includes('?errors=true')) {
this.webview.stopLoading();
}
// redirect somewhere else
if (url.includes('google.com')) {
const newURL = 'https://facebook.github.io/react-native/';
const redirectTo = 'window.location = "' + newURL + '"';
this.webview.injectJavaScript(redirectTo);
}
}
}For iOS, all you need to do is specify the permissions in your ios/[project]/Info.plist file:
Photo capture:
<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key>
<string>Take pictures for certain activities</string>
Gallery selection:
<key>NSPhotoLibraryUsageDescription</key>
<string>Select pictures for certain activities</string>
Video recording:
<key>NSMicrophoneUsageDescription</key>
<string>Need microphone access for recording videos</string>
Add permission in AndroidManifest.xml:
<manifest ...>
......
<!-- this is required only for Android 4.1-5.1 (api 16-22) -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
......
</manifest>File Upload using <input type="file" /> is not supported for Android 4.4 KitKat (see details):
import { WebView } from "react-native-webview";
WebView.isFileUploadSupported().then(res => {
if (res === true) {
// file upload is supported
} else {
// not file upload support
}
});
You can control single or multiple file selection by specifing the multiple attribute on your input element:
// multiple file selection
<input type="file" multiple />
// single file selection
<input type="file" />
For iOS, all you need to do is specify the permissions in your ios/[project]/Info.plist file:
Save to gallery:
<key>NSPhotoLibraryAddUsageDescription</key>
<string>Save pictures for certain activities.</string>
Add permission in AndroidManifest.xml:
<manifest ...>
......
<!-- this is required to save files on Android -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
......
</manifest>You will often find yourself wanting to send messages to the web pages loaded by your webviews and also receiving messages back from those web pages.
To accomplish this, React Native WebView exposes three different options:
- React Native -> Web: The
injectedJavaScriptprop - React Native -> Web: The
injectJavaScriptmethod - Web -> React Native: The
postMessagemethod andonMessageprop
This is a script that runs immediately after the web page loads for the first time. It only runs once, even if the page is reloaded or navigated away.
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { View } from "react-native";
import { WebView } from "react-native-webview";
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
const runFirst = `
document.body.style.backgroundColor = 'red';
setTimeout(function() { window.alert('hi') }, 2000);
true; // note: this is required, or you'll sometimes get silent failures
`;
return (
<View style={{ flex: 1 }}>
<WebView
source={{
uri:
"https://github.com/react-native-community/react-native-webview"
}}
injectedJavaScript={runFirst}
/>
</View>
);
}
}This runs the JavaScript in the runFirst string once the page is loaded. In this case, you can see that both the body style was changed to red and the alert showed up after 2 seconds.
Under the hood
On iOS,
injectedJavaScriptruns a method on WKWebView calledevaluateJavaScript:completionHandler:On Android,injectedJavaScriptruns a method on the Android WebView calledevaluateJavascriptWithFallback
While convenient, the downside to the previously mentioned injectedJavaScript prop is that it only runs once. That's why we also expose a method on the webview ref called injectJavaScript (note the slightly different name!).
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { View } from "react-native";
import { WebView } from "react-native-webview";
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
const run = `
document.body.style.backgroundColor = 'blue';
true;
`;
setTimeout(() => {
this.webref.injectJavaScript(run);
}, 3000);
return (
<View style={{ flex: 1 }}>
<WebView
ref={r => (this.webref = r)}
source={{
uri:
"https://github.com/react-native-community/react-native-webview"
}}
/>
</View>
);
}
}After 3 seconds, this code turns the background blue:
Under the hood
On iOS,
injectJavaScriptcalls WKWebView'sevaluateJS:andThen:On Android,injectJavaScriptcalls Android WebView'sevaluateJavascriptWithFallbackmethod
Being able to send JavaScript to the web page is great, but what about when the web page wants to communicate back to your React Native code? This where window.ReactNativeWebView.postMessage and the onMessage prop come in.
You must set onMessage or the window.ReactNativeWebView.postMessage method will not be injected into the web page.
window.ReactNativeWebView.postMessage only accepts one argument which must be a string.
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { View } from "react-native";
import { WebView } from "react-native-webview";
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
const html = `
<html>
<head></head>
<body>
<script>
setTimeout(function () {
window.ReactNativeWebView.postMessage("Hello!")
}, 2000)
</script>
</body>
</html>
`;
return (
<View style={{ flex: 1 }}>
<WebView
source={{ html }}
onMessage={event => {
alert(event.nativeEvent.data);
}}
/>
</View>
);
}
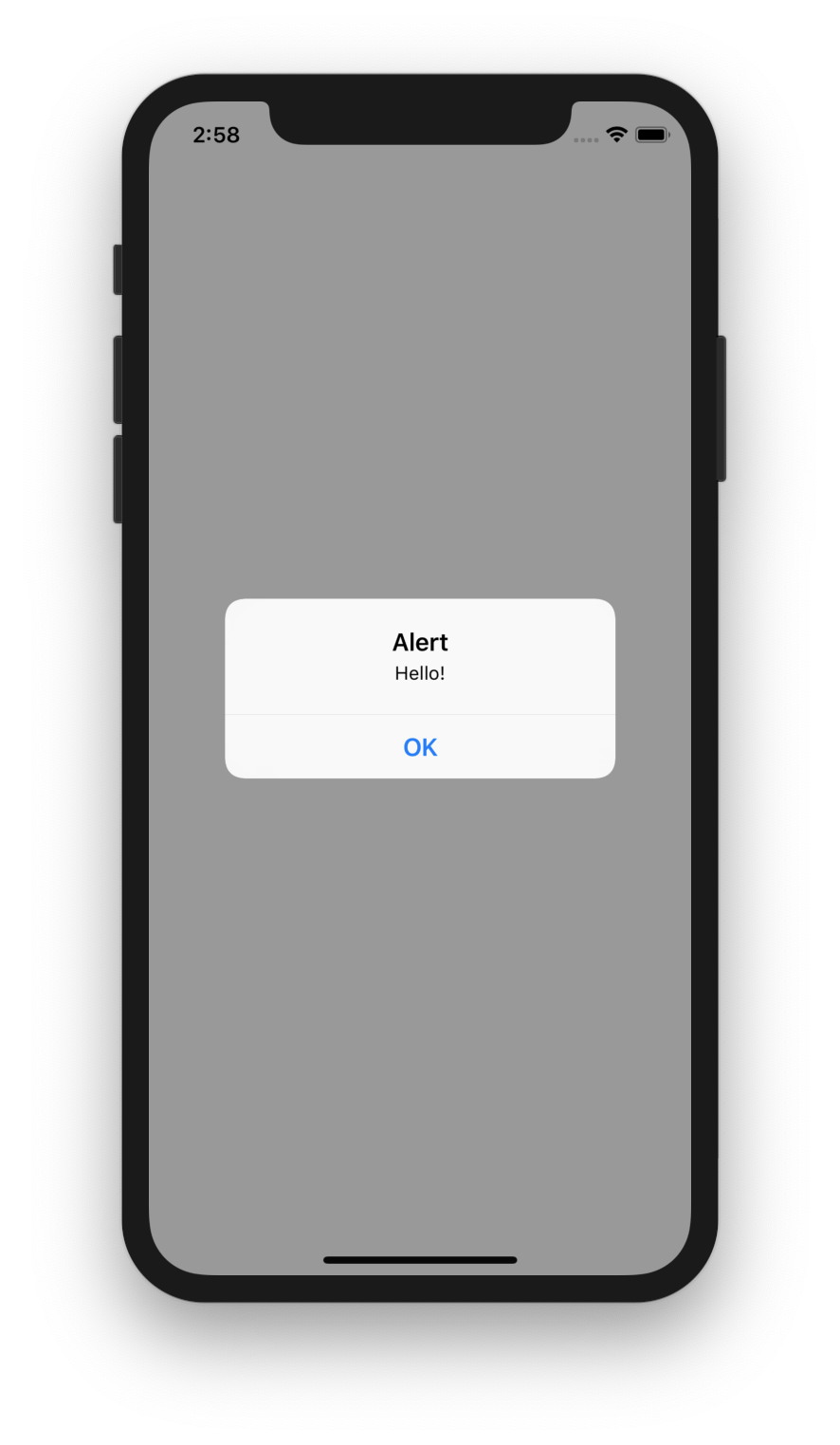
}This code will result in this alert: