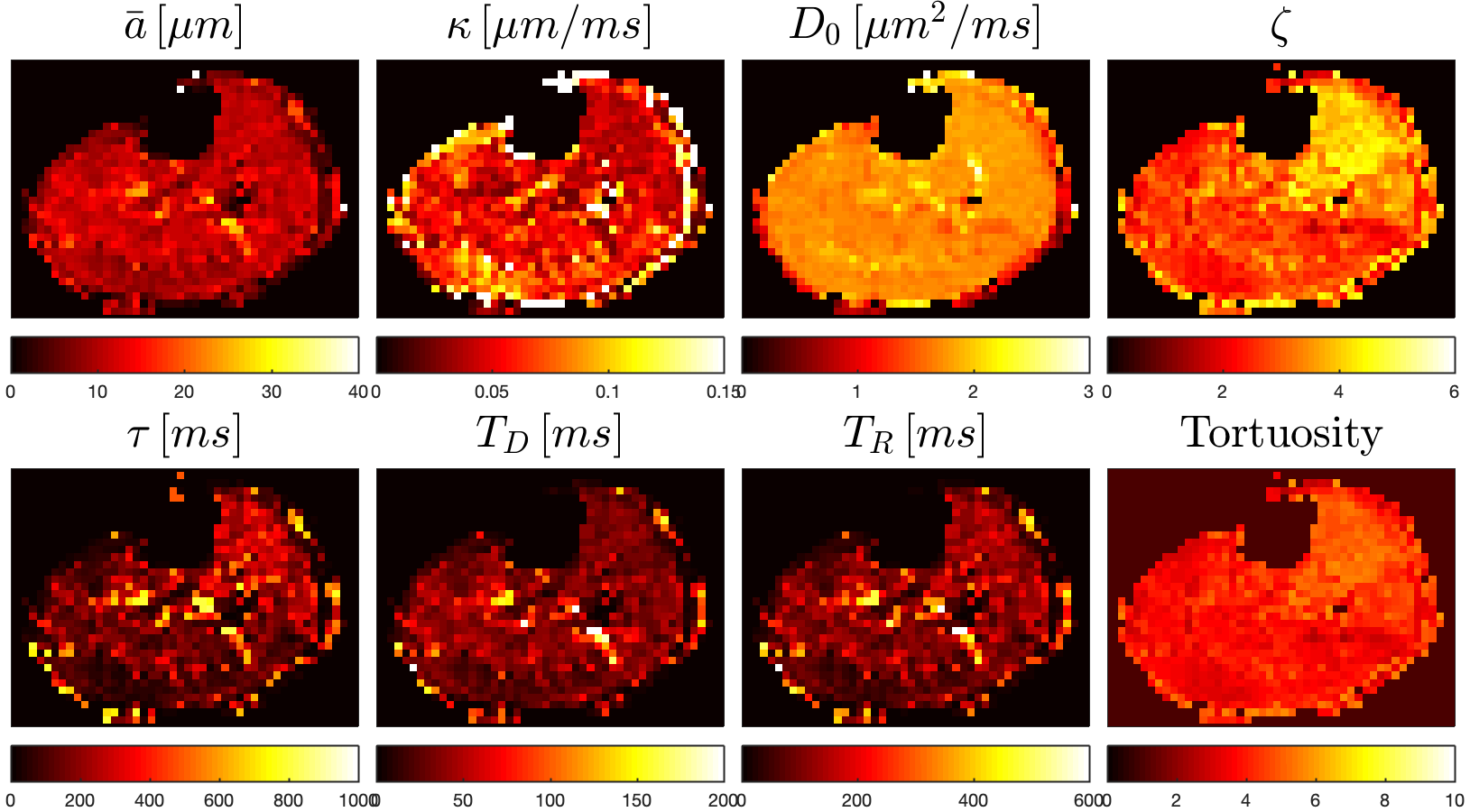
The following scripts are intended for the use in modeling the dependence of diffusion on diffusion time, D(t), within permeable anisotropic microstructure. This model was motivated by the necessessity to characterize "disordered" microstructure. Prior to the publication (1) of this Random Permeable Barrier Model, the only proposed solution to a time-varying diffusion coefficient in biological tissue was derived from periodic boundaries (Tanner et al (1979)).
Moreover, the RPBM has been identified as a powerful model to describe the microstructure of muscle tissue. It has been applied in-vivo for quantifying muscle myofiber diameter and sarcolemma membrane permeability (3,4).
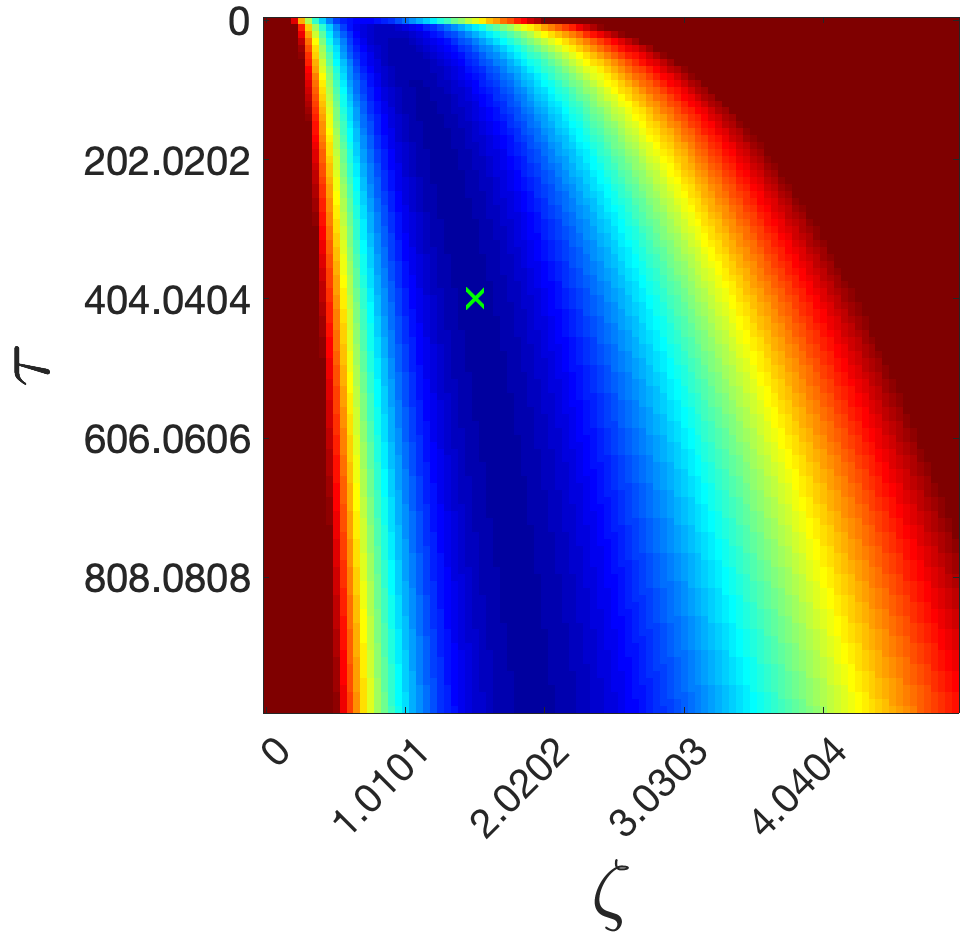
D(t) resembles a power-law decay, which is largely unremarkable. This is problematic in regards to fitting, where standard non-linear approaches such as Levenberg-Marquardt would either be (1) deflected by noise or (2) become stuck in a shallow minimum.
Our solution is to perform Grid-search fitting numerous times with various noise realizations. In doing so, we can rapidly sample the shallow fitting landscape to determine the global minimum.Please cite the following works.
(1)Novikov DS, Fieremans E, Jensen JH, Helpern JA. Random walk with barriers. Nat Phys 2011; 7(6): 508–514. DOI:10.1038/nphys1936.6.
(2)Novikov DS, Jensen JH, Helpern JA, Fieremans E. Revealing mesoscopic structural universality with diffusion. Proc Natl Acad SciU S A 2014; 111(14): 5088–5093. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1316944111.7.
(3)Fieremans, E., Lemberskiy, G., Veraart, J., Sigmund, E. E., Gyftopoulos, S., and Novikov, D. S. (2017) In vivo measurement of membrane permeability and myofiber size in human muscle using time-dependent diffusion tensor imaging and the random permeable barrier model. NMR Biomed., 30: e3612. DOI:10.1002/nbm.3612.
(4)Sigmund EE, Novikov DS, Sui D, Ukpebor O, Baete S, Babb J, Liu K,Feiweier T, Kwon J, McGorty K, Bencardino J, Fieremans E. Time-dependent diffusion in skeletal muscle with the random permeablebarrier model (RPBM): application to normal controls and chronic ex-ertional compartment syndrome patients. NMR Biomed 2014; 27(5):519–528. DOI:10.1002/nbm.3087.