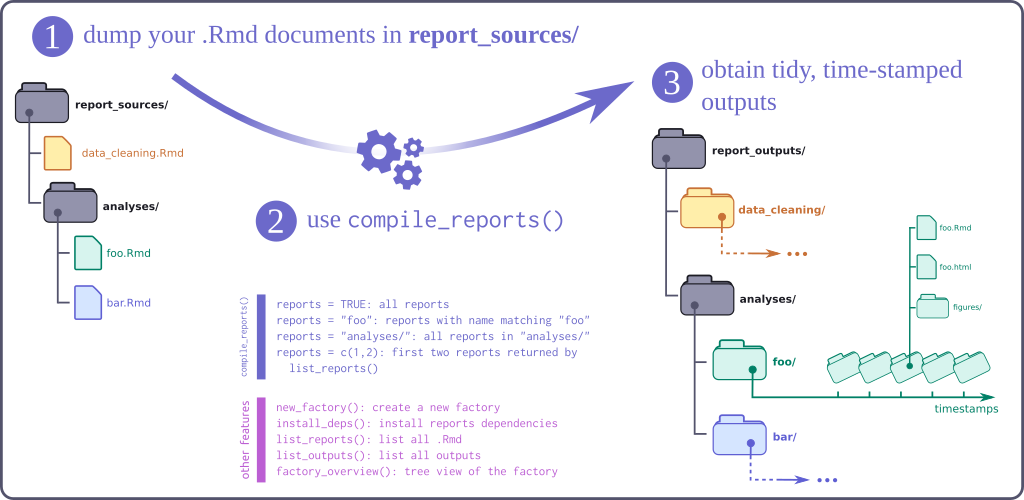
The report factory is an R package providing a lightweight infrastructure for
compiling multiple .Rmd reports stored in a dedicated folder, with naming
conventions enforcing the date of the report to be part of the file name. Each
compiled report is rendered using rmarkdown::render(), and newly created files
are stored into a dedicated, time-stamped folder. Several functions facilitate
this workflow, and allow to compile all documents, or only the most recent
reports.
Some projects may require different types of analyses to be run repeatedly over time, for instance due to updates in data and inputs.
While rmkardown::render is becoming a standard for compiling a single analysis
document, a number of issues remain: one needs to keep track of different
version of the data/inputs, of the analysis code itself, and of different
versions of the ouputs.
The report factory aims to facilitate these tasks by:
- defining a report as an explicitely dated
.Rmdfile - providing functions to compile all reports, using by default the most recent versions
- storing each report output in a separate, time-stamped folder
- maintaining compatibility with basic workflows, i.e. all reports can still be
directly compiled using
rmarkdown::render()for testing purposes (although one should make sure to remove the outputs afterwards) - keeping things simple: no configuration files, no handling of potential dependencies between reports, no caching
- git-friendly: the factory is compatible with git-based workflows, with produced outputs being ignored by git
A report factory is a folder with the following structure (see next section for creating new factories):
-
report_sources/: folder storing.Rmdreports (possibly in sub-folders); files must be named using the convention[report_base_name]_[yyyy-mm-dd].Rmd; the date format is very important as it will be used for identifying the latest report version; examples:sitrep_ebola_2018-06-13,incidence_curve_flu_2017-12-23; note this folder should not contain any outputs of the.Rmdfiles! -
report_outputs: outputs of the reports, automatically generated by the factory, in dedicated folders named as[report_base_name]_[yyyy-mm-dd]/compiled_[timestamp]/
To install the development version of the package, use:
devtools::install_github("reconhub/reportfactory")Note that this requires the package devtools installed.
The main features of the package include:
-
new_factory(): will create a new report factory, by default adding examples of reports ready for compilation -
list_reports(): will list available reports -
list_outputs(): will list available outputs -
list_deps(): will list packages needed in the reports; use the optionmissing = TRUEto list only packages that are missing and need to be installed -
install_deps(): will install packages needed in the reports; by default, only install missing packages; useupdate = TRUEto force the install of all packages -
validate_factory(): will check that the factory is valid, that all report names are unique, etc. -
compile_report(): compiles one specific report (name to be matched against the output oflist_reports() -
update_reports(): compiles every report, using by default the latest version of each report; use the optionsall = TRUEto compile all reports (including old ones)
Note that manual compilation of each document can still be done the usual way,
using rmarkdown::render in the source folder; if you do so, make sure you
remove all output files, as they would prevent further updates from the factory.
-
create a new factory using
new_factory()and move into this new folder -
go to
report_sources/, write your.Rmdreport, using the provided examples as inspiration; remove the examples files; make sure you use the naming conventions explained above, e.g.foobar_2018-01-25.Rmd. -
check your report by compiling the
.Rmdmanually if needed, e.g.rmarkdown::render("foobar_2018-01-25.Rmd"); once you are happy with the results, make sure you remove all output files from the source folder -
run
update_reports()to generate all outputs, orcompile_report("foobar_2018-01-25")if you just want to produce time-stamped outputs for this report; check results in the folderreport_outputs
We start by creating a new factory in the temporary folder:
library(reportfactory)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'reportfactory'
#> The following object is masked from 'package:devtools':
#>
#> install_deps
destination <- file.path(tempdir(), "new_factory")
destination
#> [1] "/tmp/RtmpyESa5b/new_factory"
new_factory(destination)
#> [1] "/tmp/RtmpyESa5b/new_factory"
dir()
#> [1] "data" "README.md" "report_sources"By default, examples of reports (using simulated epidemiological data) are added to the factory; these can be listed by:
list_reports()
#> [1] "contacts_2017-10-29.Rmd" "contacts_2017-10-30.Rmd"
#> [3] "contacts_2017-11-01.Rmd" "epicurve_2017-10-27.Rmd"
#> [5] "epicurve_2017-10-28.Rmd" "epicurve_2017-10-30.Rmd"
list_outputs()
#> character(0)
list_deps() # list all needed packages
#> [1] "earlyR" "epicontacts" "ggplot2" "here" "incidence"
#> [6] "knitr" "magrittr" "projections" "readxl"
list_deps(missing = TRUE) # list only missing ones
#> character(0)To compile a single report, one can use:
compile_report("contacts_2017-10-29", quiet = TRUE)
#>
#> /// compiling report: 'contacts_2017-10-29'
#>
#> /// 'contacts_2017-10-29' done!
list_outputs()
#> [1] "contacts_2017-10-29/compiled_2018-06-18_20-50-28/contacts_2017-10-29.html"To compile all reports (only most recent versions), use:
update_reports()
#>
#> /// compiling report: 'contacts_2017-11-01'
#>
#> /// 'contacts_2017-11-01' done!
#>
#> /// compiling report: 'epicurve_2017-10-30'
#>
#> /// 'epicurve_2017-10-30' done!
list_outputs()
#> [1] "contacts_2017-10-29/compiled_2018-06-18_20-50-28/contacts_2017-10-29.html"
#> [2] "contacts_2017-11-01/compiled_2018-06-18_20-50-29/contacts_2017-11-01.html"
#> [3] "epicurve_2017-10-30/compiled_2018-06-18_20-50-32/epicurve_2017-10-30.html"In the Rmd reports, all file paths should be referred to using here(),
assuming a path from the root directory.
We recommend storing all data in a data/ folder in the root directory. When
loading your data in the reports, make sure you use here, e.g.:
my_data <- read.csv(here::here("data/linelist_2018-06-11.csv"))The rationale is the same as for data: store your scripts in a dedicated folder
at the root of the project, e.g. scripts/, and source them from R using
here, e.g.:
source(here::here("script/custom_plot_functions.R"))Follow the same idea as for data and scripts, as long as you do not alter the
minimum infrastructure (report_sources/ and other files).
See details of contributions on:
https://github.com/reconhub/reportfactory/contributors
Contributions are welcome via pull requests.
Please note that this project is released with a Contributor Code of Conduct. By participating in this project you agree to abide by its terms.
Maintainer: Thibaut Jombart ([email protected])