Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA, 2FA) for Django using the Web Authentication API.
This alpha stage software is not production ready and requires further hardening before it can be safely deployed into the wild.
A live demo is available at https://django-webauth.azurewebsites.net/
You may create an account to try it out at https://django-webauth.azurewebsites.net/register/
-
Install
django-webauthusing pip$ pip install django-webauth
-
Add
webauthto INSTALLED_APPS# settings.py INSTALLED_APPS = [ ... "webauth", ]
-
Add django-webauth URLs
# urls.py urlpatterns = [ ... path("webauth/", include("webauth.urls")), ]
-
Add Web Authentication protection to your views. How you do this depends on whether you're protecting function views or class based views:
-
To protect view functions:
Add the
@webauth_requireddecorator to disallow users that have not authenticated with webauth.# views.py from webauth.decorators import webauth_required @webauth_required def private_view(request): ...
-
To protect class based views:
Add
WebAuthRequiredMixinto the inheritance list on your view classes.# views.py from webauth.mixins import WebAuthRequiredMixin class YourClassBasedView(WebAuthRequiredMixin, View): ...
-
-
Set some required
django-webauthsettings# settings.py WEBAUTH_RP_ID = "localhost" WEBAUTH_RP_NAME = "Example Site" WEBAUTH_ORIGIN = "http://localhost:8000" WEBAUTH_VERIFY_URL = "/webauth/verify/"
-
Run migrations to create the table for storing authenticator data
$ python manage.py migrate
-
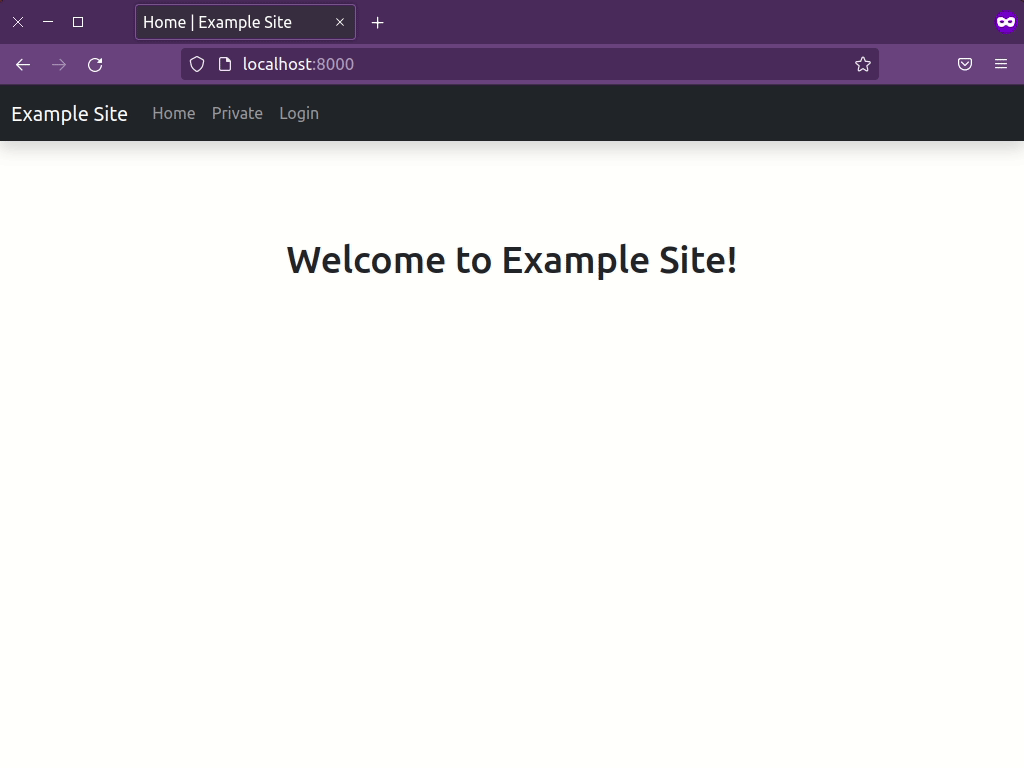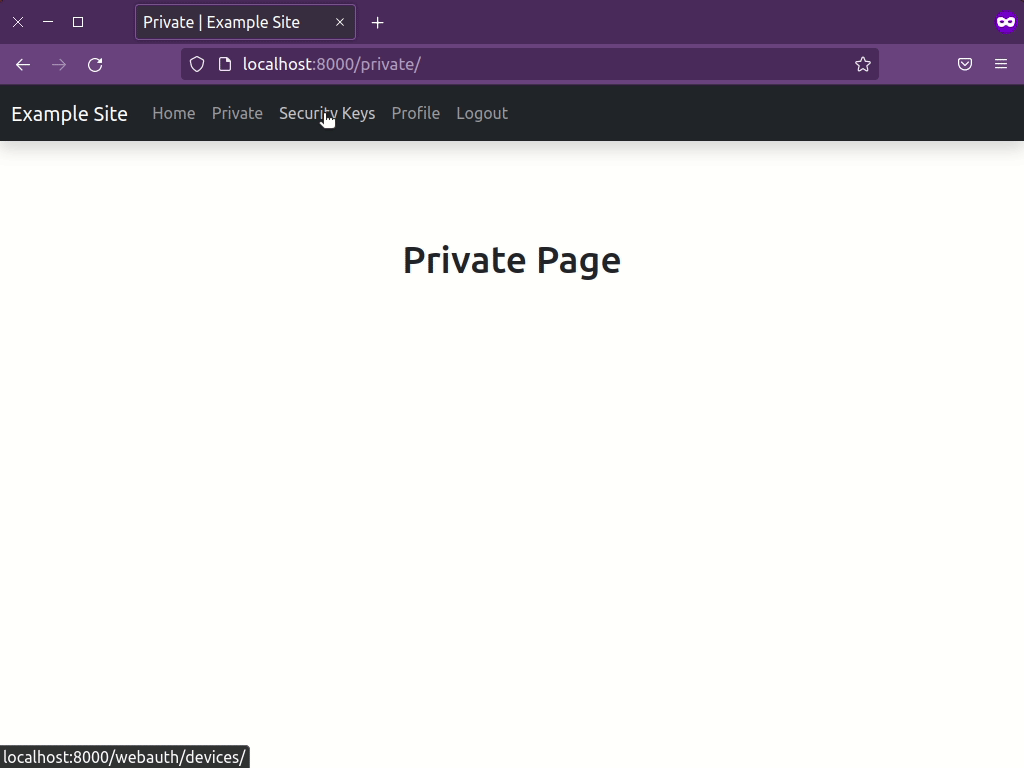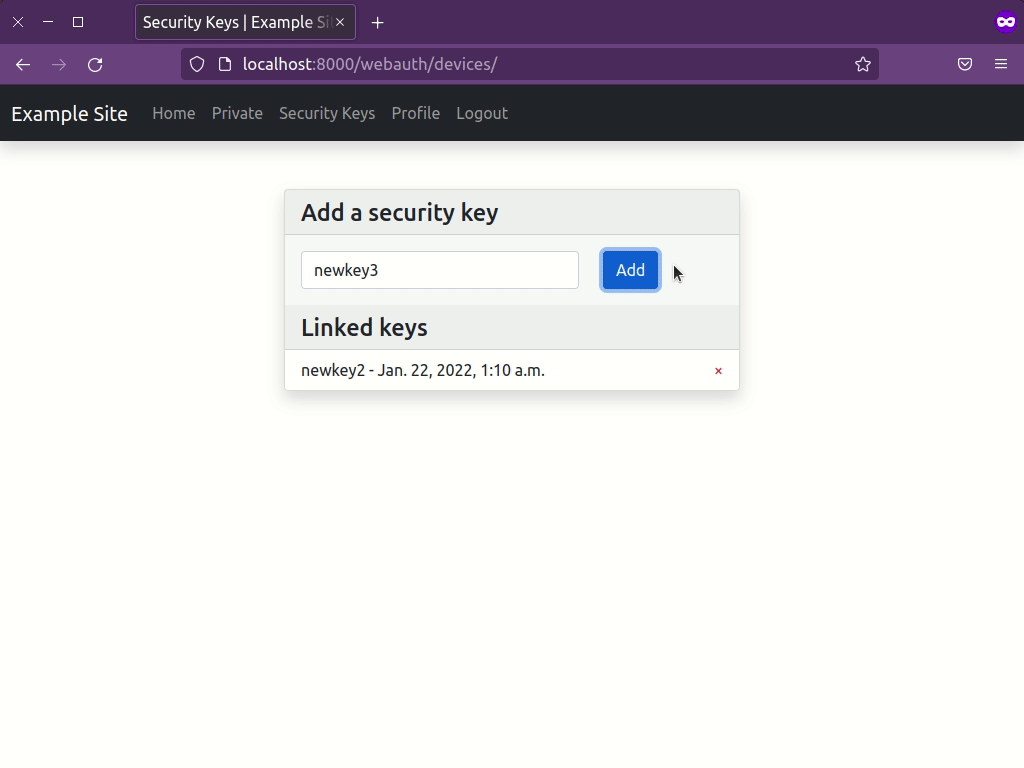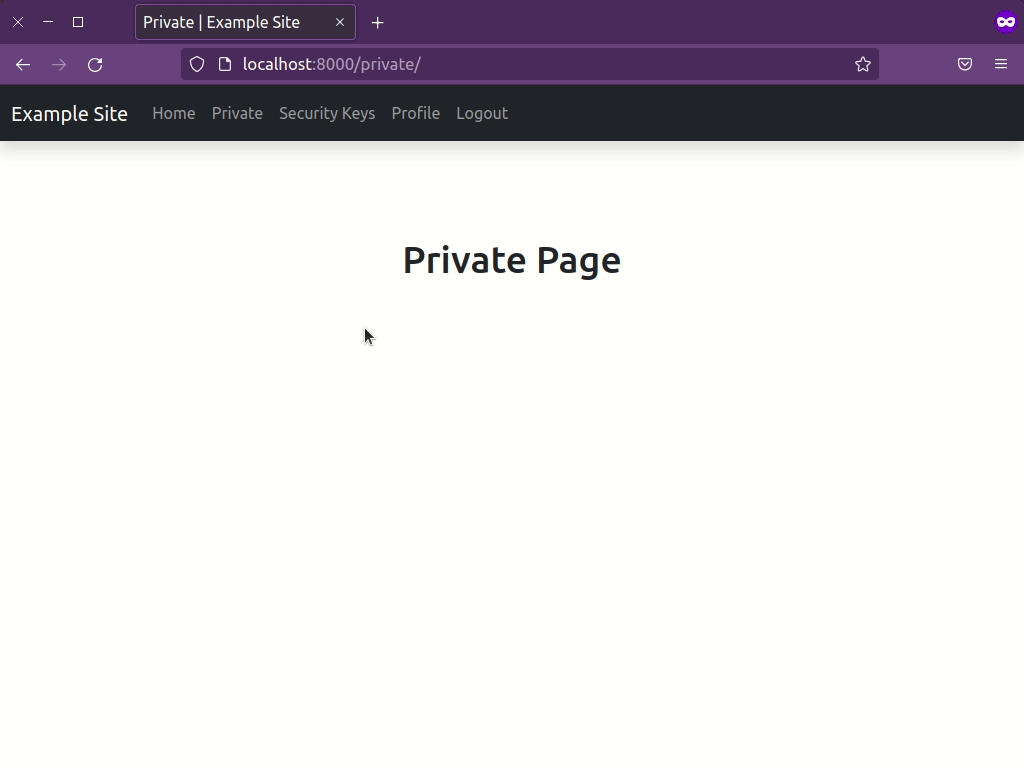
Run your Django app and register a new security key at http://localhost:8000/webauth/register/
-
Navigate to a view you protected in step 4.
django-webauthwill redirect you to a page that will attempt to authenticate using your newly created key. If successful, you will be redirected to the protected view.
django-webauth includes templates out of the box to get you up and running.
The templates extend webauth/base.html, which you will likely want to replace
with your own base template.
Replace the built-in base template simply by creating a new webauth/base.html
in your app's templates folder. See How to override templates
from the Django documentation for more info.
You are also welcome, and encouraged, to replace the other included templates with your own using the same method.
WEBAUTH_RP_ID: the hostname (minus scheme and port) of the server
running your Django app
WEBAUTH_RP_NAME: human readable name of your server intended only
for display
WEBAUTH_ORIGIN: used for verifying assertions. Only authentication
ceremonies occurring in this origin will validate
WEBAUTH_VERIFY_URL: Users not authenticated with django-webauth will
redirect users here when they request a protected view. This "login" page
completes the multi-factor authentication flow.