Documentation: https://blinjrm.github.io/detection-datasets/
Source Code: https://github.com/blinjrm/detection-datasets
Datasets on Hugging Face Hub: https://huggingface.co/detection-datasets
detection_datasets aims to make it easier to work with detection datasets.
This library works alongside the Detection dataset organisation on the 🤗 Hub, where some detection datasets have been uploaded in the format expected by the library, and are ready to use.
The main features are:
- Read the dataset :
- From disk if it has already been downloaded.
- Directly from the Hugging Face Hub if it already exist.
- Transform the dataset:
- Select a subset of data.
- Remap categories.
- Create new train-val-test splits.
- Visualize the annotations and images.
- Write the dataset:
- To disk, selecting the target detection format:
COCO,YOLOand more to come. - To the Hugging Face Hub for easy reuse in a different environment and share with the community.
- To disk, selecting the target detection format:
Read the quick start bellow, or directly jump to the tutorials:
| Goal | Tutorial | Colab |
|---|---|---|
| Load from disk and upload to the Hub | Open in the docs | |
| Load from the Hub and transform | Open in the docs |
Python 3.8.1+
detection_datasets is upon the great work of:
- Pandas for manipulating data.
- Hugging Face Datasets to store and load datasets from the Hub.
$ pip install detection_datasetsfrom detection_datasets import DetectionDatasetconfig = {
'dataset_format': 'coco', # the format of the dataset on disk
'path': 'path/do/data/on/disk', # where the dataset is located
'splits': { # how to read the files
'train': ('train.json', 'train'), # name of the split (annotation file, images directory)
'test': ('test.json', 'test'),
},
}
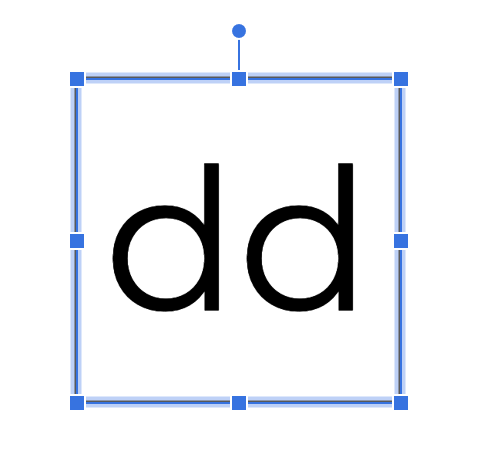
dd = DetectionDataset()
dd.from_disk(**config)
# note that you can use method cascading as well:
# dd = DetectionDataset().from_disk(**config)The detection_dataset library works alongside the Detection dataset organisation on the Hugging Face Hub, where some detection datasets have been uploaded in the format expected by the library, and are ready to use.
dd = DetectionDataset().from_hub(name='fashionpedia')Currently supported format for reading datasets are:
- COCO
- more to come
The list of datasets available from the Hub is given by:
# Search in the "detection-datasets" repository on the Hub.
DetectionDataset().available_in_hub()
# Search in another repository on the Hub.
DetectionDataset().available_in_hub(repo_name=MY_REPO_OR_ORGANISATION)The supported transformations are:
# Select a subset of images, perserving the splits and their proportions
dd.select(n_images=1000)
# Shuffle the dataset, perserving the splits and their proportions
dd.shuffle(seed=42)
# Create new train-val-test splits, overwritting the splits from the original dataset
dd.split(splits=[0.8, 0.1, 0.1])
# Map existing categories to new categories.
# The annotations with a category absent from the mapping are dropped.
dd.map_categories(mapping={'existing_category': 'new_category'})These transformations can be chained; for example here we select a subset of 10.000 images and create new train-val-test splits:
dd = DetectionDataset()\
.from_hub(name='fashionpedia')\
.select(n_images=10000)\
.split(splits=[0.8, 0.1, 0.1])The DetectionDataset objects contains several properties to analyze your data:
dd.data # This is equivlent to calling `dd.get_data('image')`,
# and returns a DataFrame with 1 row per image
dd.get_data('bbox') # Returns a DataFrame with 1 row per annotation
dd.n_images # Number of images
dd.n_bbox # Number of annotations
dd.splits # List of split names
dd.split_proportions # DataFrame with the % of iamges in each split
dd.categories # DataFrame with the categories and thei ids
dd.category_names # List of categories
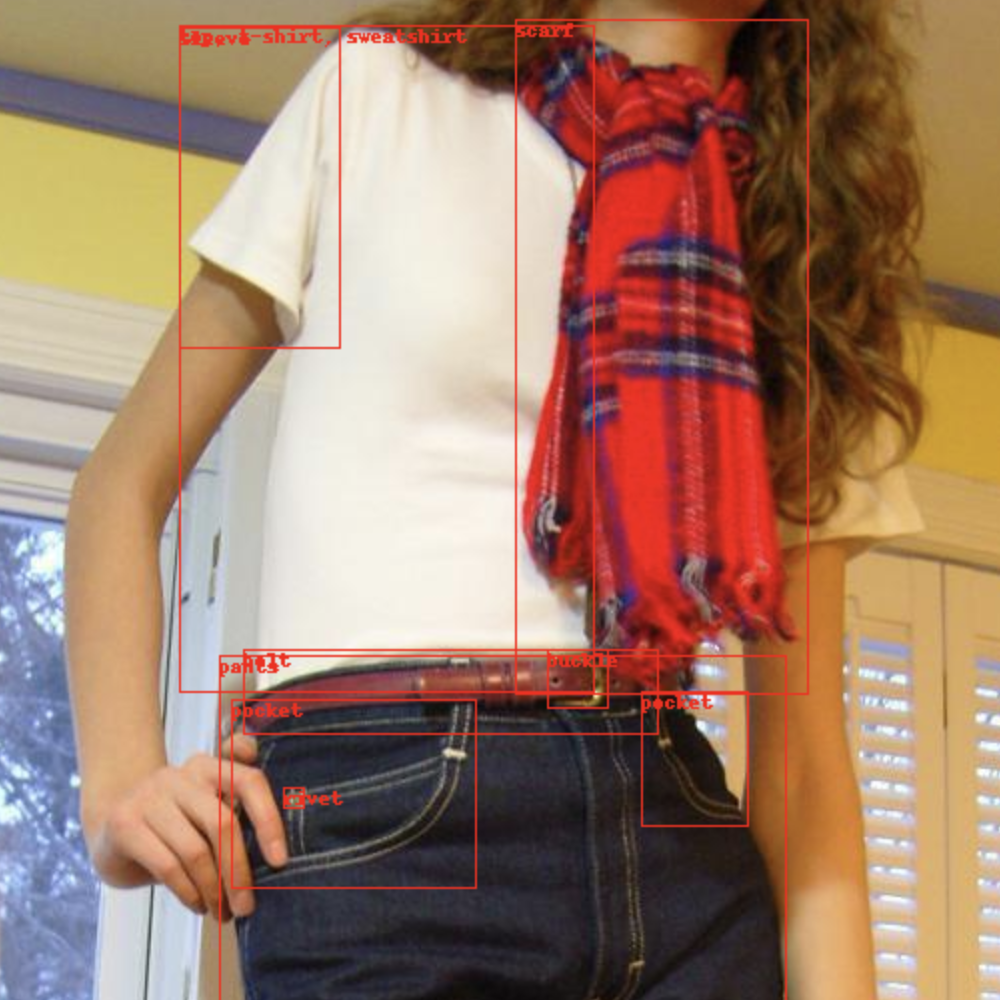
dd.n_categories # Number of categoriesYou can also visualize a image with its annotations in a notebook:
dd.show() # Shows a random image from the dataset
dd.show(image_id=42) # Shows the select image based on image_idOnce the dataset is ready, you can write it to the local filesystem in a given format:
dd.to_disk(
dataset_format='yolo',
name='MY_DATASET_NAME',
path='DIRECTORY_TO_WRITE_TO',
)Currently supported format for writing datasets are:
- YOLO
- COCO
- MMDET
- more to come
The dataset can also be easily uploaded to the Hugging Face Hub, for reuse later on or in a different environment:
dd.to_hub(
dataset_name='MY_DATASET_NAME',
repo_name='MY_REPO_OR_ORGANISATION'
)The dataset viewer on the Hub will work out of the box, and we encourage you to update the README in your new repo to make it easier for the comminuty to use the dataset.