The library allows to format user input on the fly according to the provided mask and to extract valueable characters.
Masks consist of blocks of symbols, which may include:
[]— a block for valueable symbols written by user.
Square brackets block may contain any number of special symbols:
0— mandatory digit. For instance,[000]mask will allow user to enter three numbers:123.9— optional digit . For instance,[00099]mask will allow user to enter from three to five numbers.А— mandatory letter.[AAA]mask will allow user to enter three letters:abc.а— optional letter.[АААааа]mask will allow to enter from three to six letters._— mandatory symbol (digit or letter).-— optional symbol (digit or letter).
Other symbols inside square brackets will cause a mask initialization error.
Blocks may contain mixed types of symbols; such that, [000AA] will end up being divided in two groups: [000][AA] (this happens automatically).
Blocks must not contain nested brackets. [[00]000] format will cause a mask initialization error.
Symbols outside the square brackets will take a place in the output.
For instance, +7 ([000]) [000]-[0000] mask will format the input field to the form of +7 (123) 456-7890.
{}— a block for valueable yet fixed symbols, which could not be altered by the user.
Symbols within the square and curly brackets form an extracted value (valueable characters).
In other words, [00]-[00] and [00]{-}[00] will format the input to the same form of 12-34,
but in the first case the value, extracted by the library, will be equal to 1234, and in the second case it will result in 12-34.
Mask format examples:
- [00000000000]
- {401}-[000]-[00]-[00]
- [000999999]
- {818}-[000]-[00]-[00]
- [A][-----------------------------------------------------]
- [A][_______________________________________________________________]
- 8 [0000000000]
- 8([000])[000]-[00]-[00]
- [0000]{-}[00]
- +1 ([000]) [000] [00] [00]
pod 'InputMask'git "https://github.com/RedMadRobot/input-mask-ios.git"Listening to the text change events of UITextField and simultaneously altering the entered text could be a bit tricky as
long as you need to add, remove and replace symbols intelligently preserving the cursor position.
Thus, the library provides corresponding MaskedTextFieldDelegate class.
MaskedTextFieldDelegate conforms to UITextFieldDelegate protocol and encaspulates logic to process text edit events.
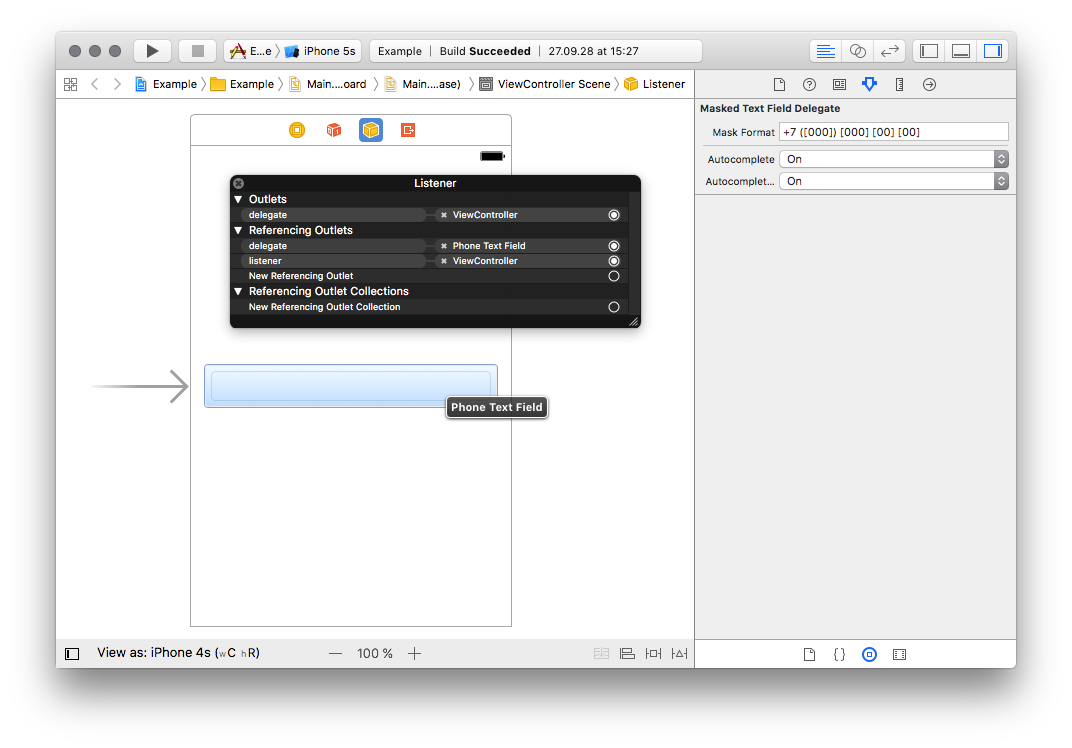
The object might be instantiated via code or might be dropped on the Interface Builder canvas as an NSObject and then
wired with the corresponding UITextField.
MaskedTextFieldDelegate has his own listener MaskedTextFieldDelegateListener, which extends UITextFieldDelegate protocol
with a callback providing actual extracted value. All the UITextFieldDelegate calls from
the client UITextField are forwarded to the MaskedTextFieldDelegateListener object, yet it doesn't allow to override
textField(textField:shouldChangeCharactersIn:replacementString:) result, always returning false.
class ViewController: UIViewController, MaskedTextFieldDelegateListener {
var maskedDelegate: MaskedTextFieldDelegate!
@IBOutlet weak var field: UITextField!
open override func viewDidLoad() {
maskedDelegate = MaskedTextFieldDelegate(format: "{+7} ([000]) [000] [00] [00]")
maskedDelegate.listener = self
field.delegate = maskedDelegate
maskedDelegate.put(text: "+7 123", into: field)
}
open func textField(
_ textField: UITextField,
didFillMandatoryCharacters complete: Bool,
didExtractValue value: String
) {
print(value)
}
}Sample project might be found under Source/Sample
In case you want to format a String somewhere in your applicaiton's code, Mask is the class you are looking for.
Instantiate a Mask instance and feed it with your string, mocking the cursor position:
let mask: Mask = try! Mask(format: "+7 ([000]) [000] [00] [00]")
let input: String = "+71234567890"
let result: Mask.Result = mask.apply(
toText: CaretString(
string: input,
caretPosition: input.endIndex
),
autocomplete: true // you may consider disabling autocompletion for your case
)
let output: String = result.formattedText.stringAn experimental feature. While transforming the text, Mask calculates affinity index, which is basically an Int that shows the absolute rate of similarity between the text and the mask pattern.
This index might be used to choose the most suitable pattern between predefined, and then applied to format the text.
For the implementation, look for the PolyMaskTextFieldDelegate class, which inherits logic from MaskedTextFieldDelegate. It has its primary mask pattern and corresponding list of affine formats.
open class ViewController: UIViewController, MaskedTextFieldDelegateListener {
@IBOutlet weak var listener: PolyMaskTextFieldDelegate!
@IBOutlet weak var field: UITextField!
open override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
listener.affineFormats = [
"8 ([000]) [000] [00] [00]"
]
}
open func textField(
_ textField: UITextField,
didFillMandatoryCharacters complete: Bool,
didExtractValue value: String
) {
print(complete)
print(value)
}
}Sometimes you need to know when text property of UITextField was changed by user. For example, you may want to use NotificationCenter with notification UITextFieldTextDidChange, or func addTarget(_ target: Any?, action: Selector, for controlEvents: UIControlEvents) with event editingChanged. These events are emitting by iOS only if text property was changed by user. But the MaskedTextFieldDelegate, implemented in input-mask always returns false inside method open func textField(_ textField: UITextField, shouldChangeCharactersIn range: NSRange, replacementString string: String) -> Bool, and programmatically modifies text property independently. return false inside this method, suppresses triggering of these events by iOS.
Possible workaround:
class NotifyingMaskedTextFieldDelegate: MaskedTextFieldDelegate {
weak var editingListener: NotifyingMaskedTextFieldDelegateListener?
override func textField(
_ textField: UITextField,
shouldChangeCharactersIn range: NSRange,
replacementString string: String
) -> Bool {
defer {
self.editingListener?.onEditingChanged(inTextField: textField)
}
return super.textField(textField, shouldChangeCharactersIn: range, replacementString: string)
}
}
protocol NotifyingMaskedTextFieldDelegateListener: class {
func onEditingChanged(inTextField: UITextField)
}In 2.0.0 version separate MaskedTextFieldDelegateListener callbacks have been merged into a single method providing an extracted value and input complete flag.
The library is distributed under the MIT LICENSE.