 |
Sound Control is free software that can be used by anyone to create new musical instruments using their choice of movements, sensed with a variety of off-the-shelf devices (including webcam, Leap Motion, micro:bit, mouse, microphone, etc.). Sound Control uses machine learning to enable users to create new musical instruments by demonstrating examples of motions and sounds, so no programming or musical expertise is necessary! These new instruments can be used to play and manipulate musical material, which can be either new material recorded by users or taken from third-party sample libraries.
Sound Control was created in collaboration with youth with special educational needs and disabilities, as well as their music teachers and therapists. Together, we have aimed to create software that makes it easy to create bespoke digital musical instruments that are tailored to individuals’ abilities and preferences, as well as to create new musical interactions for music therapy and fun.
Sound Control is supported by a Paul Hamlyn Foundation “Widening Access and Participation in the Arts” grant. The project is led by the Northamptonshire Music and Performing Arts Trust. The software development and design research were conducted at Goldsmiths University of London.
- The current version of Sound Control is built with Max/MSP 8.
- On opening the patch in Max, some standard settings may be disabled. This is so that the guts of the patch are hidden from the user in the standalone. However, if you want to edit the source code, you'll probably want to do the following:
- To access full Max menus: File > Max Menus
- To enable scrolling and window enlarging: put the patch in edit mode, then use APPLE + F (or CTRL + F on windows) to search for "window flags". This should scope to a message box:[window flags nogrow, window exec]. Disconnect this object from the loadbang object above it (the one on the right), save the patcher, and re-open it.
- Operating system: There is a flag for building for MacOS or Windows. The toggle for this flag can be found at the top of the patch (underneath "BUILDING: Mac/Win Flag"). This affects which sensorlist.json is loaded, the gametrak code, and the running of the CBMicroBit executable (used for Bluetooth micro:bit connectivity on Mac).
- Saving: For the purpose of testing the save function within the Max environment, there is a block of code in the [subpatch-construction.js] starting at line 113. It inserts a bang object into the instrument subpatch (the instrument subpatch is the popup patch that is created by the subpatch-construction.js). This bang object is connected to a send, which is received by the save handler in the main patch. What this allows you to do is test the saving function, which ONLY WORKS if the instrument subpatch is active, i.e. at the front of all your windows. This bang should only be present during development, and therefore the block of code in the [subpatch-construction.js] which creates it should be commented out when building the standalone.
RapidMax is used for the machine learning component of Sound Control. You can get it here:
- Mac https://github.com/samparkewolfe/RapidMax
- Windows https://github.com/MartinTownley/RapidMax_Windows
https://github.com/Louismac/CBMicroBit
- This is required only on Mac and it enables the use of Micro:Bit via Bluetooth.
- In order to use the CBMicrobit executable with Sound Control running as code in the Max/MSP environment instead of as a Standalone, the CBMicrobit executable must be at the directory /Library/Application Support/Sound_Control/CBMicroBit. (The Sound Control .pkg downloader puts it there for you, so if you've already run the Sound Control installer, you probably have it in the right place already.)
- See "MacOS Package Creation" instructions in this file for how to create the .pkg
- This handles the running of the CBMicroBit software (see above) https://cycling74.com/forums/chess-for-max/replies/1#reply-596a3e15d5b2a4159a6c7d04
http://expr-i0.net/shell_170717.zip
- In order to use the Micro:Bit, you must first flash it with a .hex file. A range of .hex files are located inside "resources/MB Hex Files"
- The .hex file you will want to select depends on two things: the connection you wish to make (USB or Bluetooth), and the version of your Micro:Bit hardware (v1.0 or v1.5).
- Instructions about how to flash your micro:bit with the correct hex file can be found at http://soundcontrolsoftware.com/tutorial/#Setting_up_microbit_optional
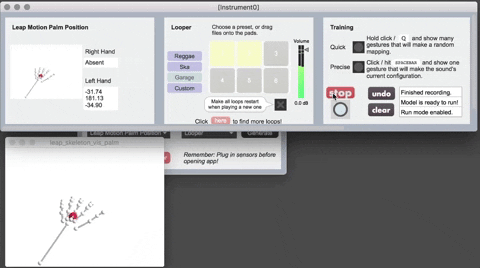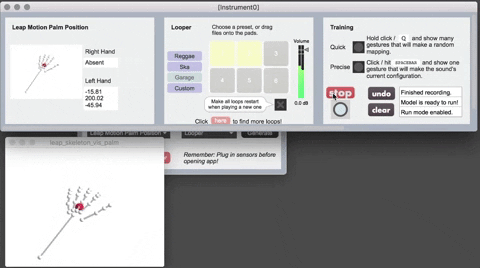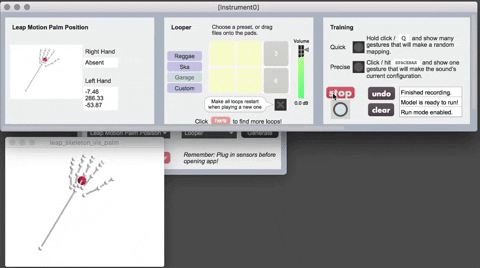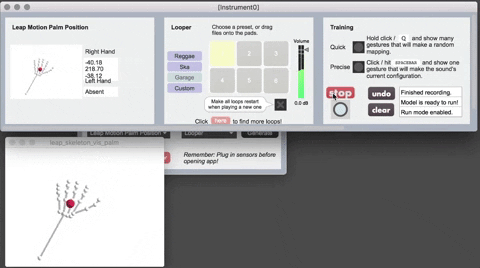
The Leap Motion is a hardware device that senses hand position (of one hand at a time, in this implementation of Sound Control). Currently it is only supported on the Mac version of Sound Control. If you want to use Leap Motion, you'll need to download the following:
- The Leap SDK at https://developer-archive.leapmotion.com/downloads/external/skeletal-beta/osx?version=2.3.1.31549
- Leap Motion for Max: https://github.com/JulesFrancoise/leapmotion-for-max/releases
loopMIDI is required to enable MIDI routing on Windows. The MIDI Mapper instrument within Sound Control has the capability of communicating with an external DAW. This relies on virtual MIDI ports, which are not available by default on Windows operating systems. The loopMIDI software allows you to create these ports manually: https://www.tobias-erichsen.de/software/loopmidi.html
Sound Control's colour tracking uses https://cycling74.com/forums/colour-tracking-with-a-webcam-in-jitter/
The Looper instrument has been known to crash on some Windows machines.
The app automatically sets it’s audio I/O to whatever the I/O settings of the Max.app are. If you want to change these you must close the Sound Control app, set the desired audio I/O settings in the Max.app and then reopen Sound Control. However you can then change the audio I/O settings for the Max.app and not change the Sound Control audio I/O settings after the Sound Control app has been opened.
- Make sure the correct operating system flag is enabled (1 for Mac, 2 for Windows)
- Re-connect the loadbang object to the [window flags nogrow, window exec] message at the top of the patch. This will inhibit scrolling and window re-sizing in the standalone. If you wish to keep these enabled to make testing easier, you can do so.
- Ensure each patch in the project is saved in Presentation mode before building.
- Click File> Build Collective/Application (if this option is not available, click File> Max Menus).
- Click "Include Folder..." and select Sound Control/src folder
- (Optional): Sound Control has a custom icon, the .icns file being located at "resources/icon/sc_icon.icns". To enable the app to have this icon, you must add the following instruction to the build script: "appicon /path/to/icon file" (where your specific path will be something like "Users/username/Sound_Control/resources/sc_icon.icns")
- Click "Build" and select a location. You may want to create a builds folder in your repo that is ignored by git.
- Make sure to select "Application" from the File Format Menu, and click Save.
- In order to include the saving functionality when building a standalone from source, read the info.txt file inside resources/Custom Saving Scripts. This process happens after building the standalone so one cannot save instruments by just using the scripts.
NOTE: You must first build the Sound Control app using the instructions above before creating a package (.pkg) file.
In order for Sound Control's Micro:Bit Bluetooth functionality to work on MacOS, the CBMicrobit executable must be in the following directory of the user's machine: /Library/Application Support/Sound_Control/CBMicroBit. By creating a .pkg installer, you can bundle the Sound Control app and the CBMicroBit into a package, which will automatically place the CBMicroBit in the correct location on the user's machine when the .pkg is run.
- Download the Packages application here: http://s.sudre.free.fr/Software/Packages/about.html
- Once installed, open Packages and select the "Raw Package" template.
- Enter "Sound Control" in the Project Name field, and hit "Create".
- Navigate to the Payload tab, and with the Applications folder highlighted, click the "+" button.
- This will open a dialog box. Locate the Sound Control build you want to package, and click "Add".
- Once the app is added, staying in the Payload tab, navigate to Library/Application support.
- Right-click on Application support and add a new folder. Name this "Sound_Control".
- Place the CBMicroBit inside this Sound_Control by highlighting the folder, clicking "+" and navigating to the CBMicroBit exe.
- In the Packages menu bar, click Build > Build and Run. You can now test if your package puts the CBMicroBit in the right place on your machine, and if the Sound Control app runs as expected.


