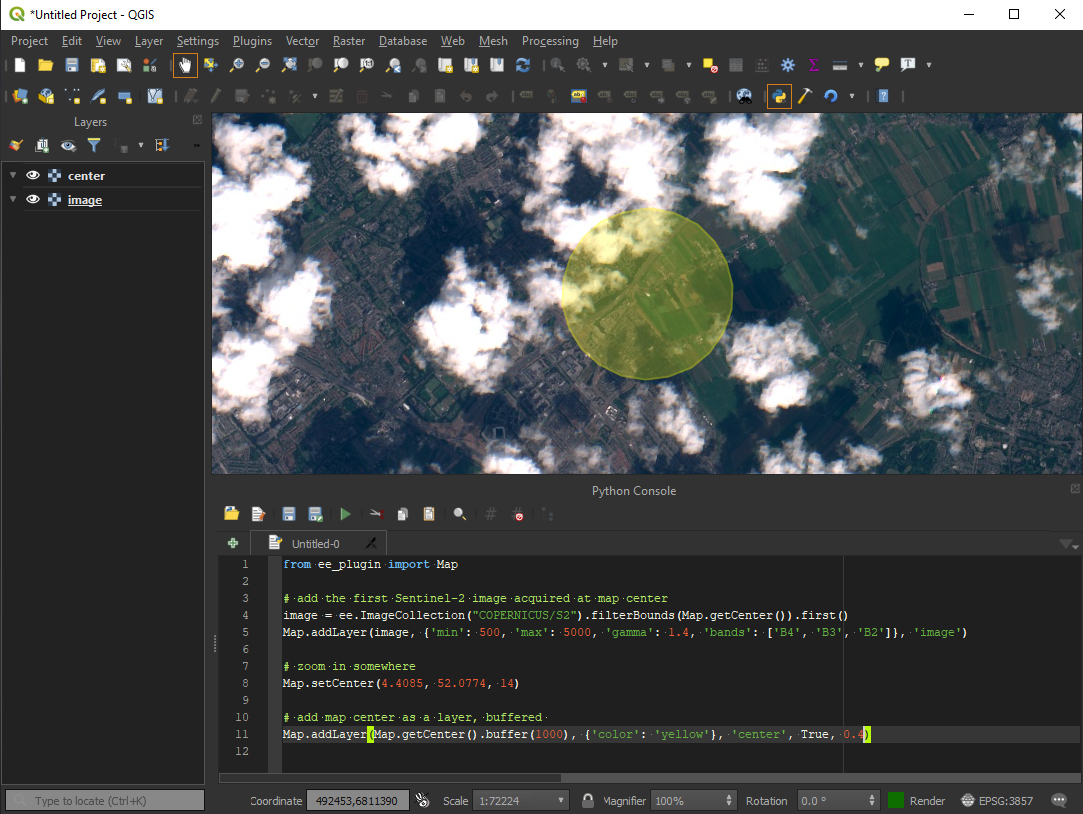
Integrates Google Earth Engine with QGIS using Python API.
Check User Guide to get started.
- Create a new QGIS plugin skeleton
- Migrate to QGIS3
- Embed GEE Python library
- Implement Map.addLayer() for ee.Image
- Implement Map.addLayer() for ee.Geometry, ee.Feature and ee.FeatureCollection
- Implement Map.centerObject()
- Implement Map.getBounds()
- Implement Map.getCenter()
- Implement Map.setCenter()
- Implement Map.getScale()
- Implement Map.getZoom()
- Implement Map.setZoom()
- Upload to QGIS plugin repository: https://plugins.qgis.org/plugins/
- EE layer inspector
- Make print(ee_object) more user-friendly, without requiring getInfo(), maybe async ...
- Add support for map layers in a way similar to EE Code Editor
- Add support for Data Catalog, allowing adding assets without the need to write scripts (select time, styling)
- Custom EE scripts as Processing algorithms, so that users can use it within Graphical Modeller
- Fetch (cache?) raster assets locally (EE > QGIS), for a given rectangle / CRS, as a Processing tool
- Export vector and raster data (QGIS > EE) either via Tasks or some other way
- Use QGIS vector/raster style editors to edit EE layer styles
This section is for developers-only.
The ee_plugin uses paver for packaging. If you do not have paver (https://github.com/paver/paver) installed, install it by typing the following in a console:
pip install paver
Open a console in the folder created in the first step, and type
paver setup
This will get all the dependencies needed by the plugin.
Install into QGIS by running
paver install
This should create a symbolic link to the plugin directory wihin the QGIS plugins deployment directory. Check Settings > User Profiles > Open Active Profile Folder, and then go to python/plugins. To reload any changes made in the plugin into Qgis, it is recommended to use the plugin reloader.
To generate the installable zip package
paver package
- Ujaval Gandhi - QGIS Plugin Builder
- JetBrains - PyCharm