Reimagine the way your users fill in their information with BlinkID iOS SDK. Fast, accurate and secure identity document scanning of more than 180 countries worldwide.
BlinkID is:
- Fast. Real-time data extraction in less than 400ms. Way better than minutes-long form-filling.
- Secure. Privacy first, always. Scanning works even if the user’s iPhone is in airplane mode, meaning personal information never touches a third-party server.
- Intelligent. Machine learning models, optimized to read and parse virtually any identity document in the world, be it a Malaysian MyTentera or a Californian driver license.
- Lightweight. Designed to increase your app’s usability, not weight.
- What you make of it. Customize and rebrand the default UI or leave it as it is. It’s up to you.
- More than just a powerful ID scanner. Powerful data extraction, coupled with powerful perks. Get a cropped document image back, spot printed identity documents or data match both sides of the ID for parity.
To see all of these features at work, download our free demo app:
Feeling ready to get going with the integration? First, make sure we support your document type ➡️ full list. And then carefully follow the guidelines below.
Updating to a newer version of the SDK? Go to our 📚 release notes to see what’s changed.
- Requirements
- Quick Start
- Advanced BlinkID integration instructions
MBRecognizerand available recognizers- List of available recognizers
- Localization
- Troubleshooting
- Size Report
- Additional info
SDK package contains Microblink framework and one or more sample apps which demonstrate framework integration. The framework can be deployed in iOS 11.0 or later.
SDK performs significantly better when the images obtained from the camera are focused. Because of that, the SDK can have lower performance on iPad 2 and iPod Touch 4th gen devices, which don't have camera with autofocus.
This Quick Start guide will get you up and performing OCR scanning as quickly as possible. All steps described in this guide are required for the integration.
This guide closely follows the BlinkID-Sample app in the Samples folder of this repository. We highly recommend you try to run the sample app. The sample app should compile and run on your device, and in the iOS Simulator.
The source code of the sample app can be used as the reference during the integration.
- Download and install/update Cocopods version 1.10.0 or newer
- Since the libraries are stored on Git Large File Storage, you need to install git-lfs by running these commands:
brew install git-lfs
git lfs install-
Be sure to restart your console after installing Git LFS
-
Note: if you already did try adding SDK using cocoapods and it's not working, first install the git-lfs and then clear you cocoapods cache. This should be sufficient to force cocoapods to clone BlinkID SDK, if it still doesn't work, try deinitializing your pods and installing them again.
-
Project dependencies to be managed by CocoaPods are specified in a file called
Podfile. Create this file in the same directory as your Xcode project (.xcodeproj) file. -
If you don't have podfile initialized run the following in your project directory.
pod init
- Copy and paste the following lines into the TextEdit window:
platform :ios, '11.0'
target 'Your-App-Name' do
pod 'PPBlinkID', '~> 5.19.1'
end- Install the dependencies in your project:
$ pod install- From now on, be sure to always open the generated Xcode workspace (
.xcworkspace) instead of the project file when building your project:
open <YourProjectName>.xcworkspaceMicroblink SDK is available via Carthage. Please check out Carthage documentation if you are new to Carthage.
- Install Carthage. Check out Installing Carthage guide. Please make sure you have Carthage version >= 0.35.0 installed.
- Create a Cartfile in the same directory where your .xcodeproj or .xcworkspace is.
- Add Microblink as a dependency to this Cartfile:
binary "https://github.com/BlinkID/blinkid-ios/blob/master/blinkid-ios.json"- Run
carthage update. - If successful, a Cartfile.resolved file and a Carthage directory will appear in the same directory as your Xcode project.
- Drag the binaries from
Carthage/Build/<platform>into your application’s Xcode project.
Microblink SDK is available as Swift Package. Please check out Swift Package Manager documentation if you are new to Swift Package Manager.
We provide a URL to the public package repository that you can add in Xcode:
https://github.com/BlinkID/blinkid-swift-package-
Choose Swift package version
NOTE: There is a known issue in Xcode 12 that could cause crash running on real iOS device. Please follow instructions below for the workaround:
- Add a new copy files phase in your application’s Build Phase
- Change the copy files phase’s destination to Frameworks
- Add a new run script phase script to your app’s target
- Add the following script to force deep sign the frameworks with your own signing identity:
find "${CODESIGNING_FOLDER_PATH}" -name '*.framework' -print0 | while read -d $'\0' framework
do
codesign --force --deep --sign "${EXPANDED_CODE_SIGN_IDENTITY}" --preserve-metadata=identifier,entitlements --timestamp=none "${framework}"
done-Download latest release (Download .zip or .tar.gz file starting with BlinkID. DO NOT download Source Code as GitHub does not fully support Git LFS)
OR
Clone this git repository:
- Since the libraries are stored on Git Large File Storage, you need to install git-lfs by running these commands:
brew install git-lfs
git lfs install-
Be sure to restart your console after installing Git LFS
-
To clone, run the following shell command:
git clone [email protected]:BlinkID/blinkid-ios.git-
Copy Microblink.xcframework to your project folder.
-
In your Xcode project, open the Project navigator. Drag the Microblink.xcframework file to your project, ideally in the Frameworks group, together with other frameworks you're using. When asked, choose "Create groups", instead of the "Create folder references" option.
- Since Microblink.xcframework is a dynamic framework, you also need to add it to embedded binaries section in General settings of your target and choose option
Embed & Sign.
-
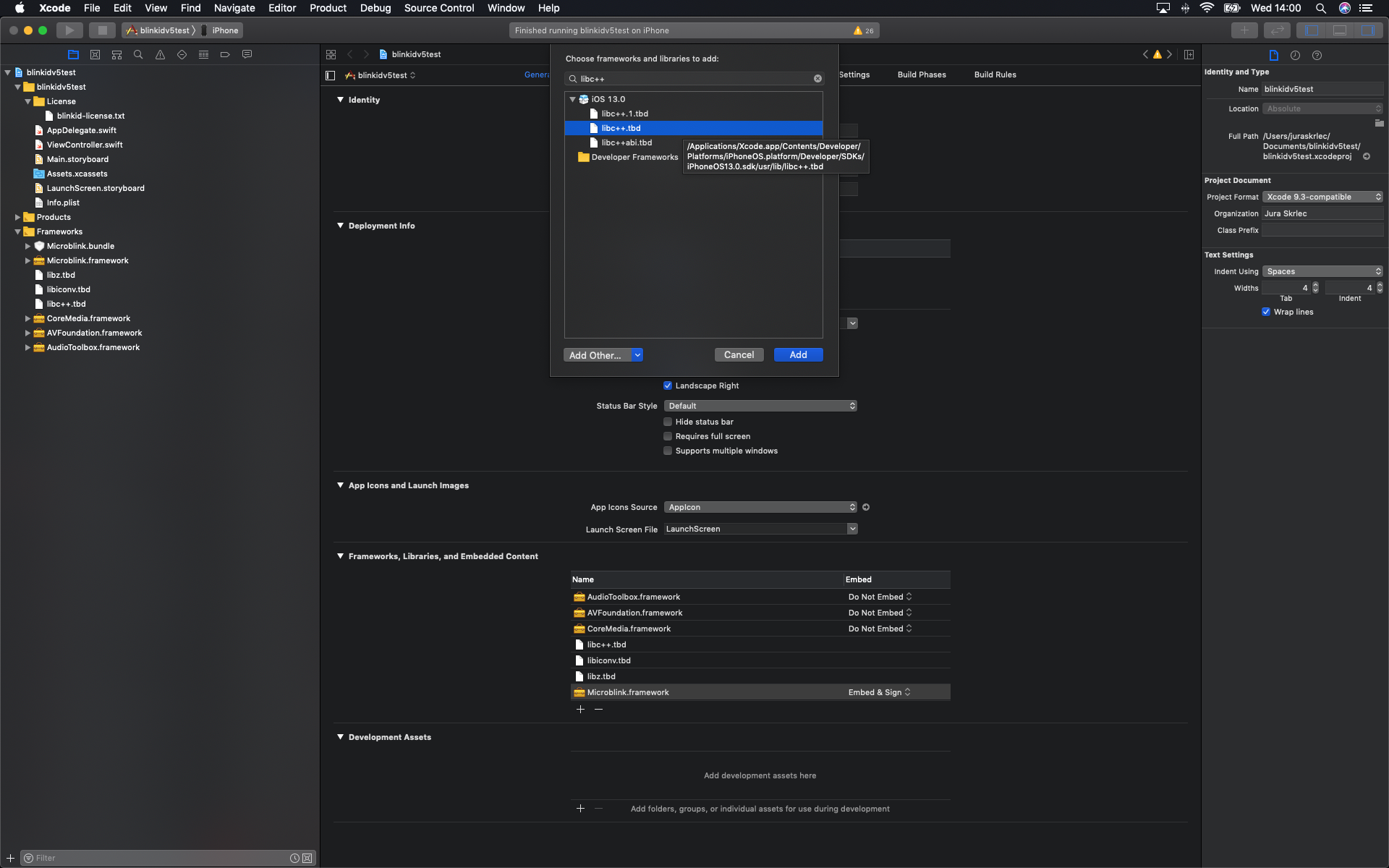
Include the additional frameworks and libraries into your project in the "Linked frameworks and libraries" section of your target settings.
- libc++.tbd
- libiconv.tbd
- libz.tbd
In files in which you want to use scanning functionality place import directive.
Swift
import MicroblinkObjective-C
#import <Microblink/Microblink.h>To initiate the scanning process, first decide where in your app you want to add scanning functionality. Usually, users of the scanning library have a button which, when tapped, starts the scanning process. Initialization code is then placed in touch handler for that button. Here we're listing the initialization code as it looks in a touch handler method.
Swift
class ViewController: UIViewController, MBBlinkIdOverlayViewControllerDelegate {
var blinkIdRecognizer : MBBlinkIdRecognizer?
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
MBMicroblinkSDK.shared().setLicenseResource("blinkid-license", withExtension: "txt", inSubdirectory: "", for: Bundle.main, errorCallback: block)
}
@IBAction func didTapScan(_ sender: AnyObject) {
/** Create BlinkID recognizer */
self.blinkIdRecognizer = MBBlinkIdRecognizer()
/** Create BlinkID settings */
let settings : MBBlinkIdOverlaySettings = MBBlinkIdOverlaySettings()
/** Crate recognizer collection */
let recognizerList = [self.blinkIdRecognizer!]
let recognizerCollection : MBRecognizerCollection = MBRecognizerCollection(recognizers: recognizerList)
/** Create your overlay view controller */
let blinkIdOverlayViewController : MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController = MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController(settings: settings, recognizerCollection: recognizerCollection, delegate: self)
/** Create recognizer view controller with wanted overlay view controller */
let recognizerRunneViewController : UIViewController = MBViewControllerFactory.recognizerRunnerViewController(withOverlayViewController: blinkIdOverlayViewController)
/** Present the recognizer runner view controller. You can use other presentation methods as well (instead of presentViewController) */
self.present(recognizerRunneViewController, animated: true, completion: nil)
}
}Objective-C
@interface ViewController () <MBBlinkIdOverlayViewControllerDelegate>
@property (nonatomic, strong) MBBlinkIdRecognizer *blinkIdRecognizer;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
[MBMicroblinkSDK.sharedInstance setLicenseResource:@"blinkid-license" withExtension:@"txt" inSubdirectory:@"" for:Bundle.main errorCallback:block];
}
- (IBAction)didTapScan:(id)sender {
/** Create BlinkID recognizer */
self.blinkIdRecognizer = [[MBBlinkIdRecognizer alloc] init];
/** Create BlinkID settings */
MBBlinkIdOverlaySettings* settings = [[MBBlinkIdOverlaySettings alloc] init];
/** Create recognizer collection */
MBRecognizerCollection *recognizerCollection = [[MBRecognizerCollection alloc] initWithRecognizers:@[self.blinkIdRecognizer]];
/** Create your overlay view controller */
MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController *blinkIdOverlayViewController = [[MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController alloc] initWithSettings:settings recognizerCollection:recognizerCollection delegate:self];
/** Create recognizer view controller with wanted overlay view controller */
UIViewController<MBRecognizerRunnerViewController>* recognizerRunnerViewController = [MBViewControllerFactory recognizerRunnerViewControllerWithOverlayViewController:blinkIdOverlayViewController];
/** Present the recognizer runner view controller. You can use other presentation methods as well (instead of presentViewController) */
[self presentViewController:recognizerRunnerViewController animated:YES completion:nil];
}
@endA valid license key is required to initialize scanning. You can request a free trial license key, after you register, at Microblink Developer Hub.
You can include the license key in your app by passing a string or a file with license key.
Note that you need to set the license key before intializing scanning. Ideally in AppDelegate or viewDidLoad before initializing any recognizers.
You can pass the license key as a string, the following way:
Swift
MBMicroblinkSDK.shared().setLicenseKey("LICENSE-KEY", errorCallback: block)Objective-C
[[MBMicroblinkSDK sharedInstance] setLicenseKey:@"LICENSE-KEY" errorCallback:block];Or you can include the license key, with the code below. Please make sure that the file that contains the license key is included in your project and is copied during Copy Bundle Resources build phase.
Swift
MBMicroblinkSDK.shared().setLicenseResource("license-key-file", withExtension: "txt", inSubdirectory: "directory-to-license-key", for: Bundle.main, errorCallback: block)Objective-C
[[MBMicroblinkSDK sharedInstance] setLicenseResource:@"license-key-file" withExtension:@"txt" inSubdirectory:@"" forBundle:[NSBundle mainBundle] errorCallback:block];If the licence is invalid or expired then the methods above will throw an exception.
In the previous step, you instantiated MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController object with a delegate object. This object gets notified on certain events in scanning lifecycle. In this example we set it to self. The protocol which the delegate has to implement is MBBlinkIdOverlayViewControllerDelegate protocol. It is necessary to conform to that protocol. We will discuss more about protocols in Advanced integration section. You can use the following default implementation of the protocol to get you started.
Swift
func blinkIdOverlayViewControllerDidFinishScanning(_ blinkIdOverlayViewController: MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController, state: MBRecognizerResultState) {
// this is done on background thread
// check for valid state
if state == .valid {
// first, pause scanning until we process all the results
blinkIdOverlayViewController.recognizerRunnerViewController?.pauseScanning()
DispatchQueue.main.async(execute: {() -> Void in
// All UI interaction needs to be done on main thread
})
}
}
func blinkIdOverlayViewControllerDidTapClose(_ blinkIdOverlayViewController: MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController) {
// Your action on cancel
}Objective-C
- (void)blinkIdOverlayViewControllerDidFinishScanning:(MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController *)blinkIdOverlayViewController state:(MBRecognizerResultState)state {
// this is done on background thread
// check for valid state
if (state == MBRecognizerResultStateValid) {
// first, pause scanning until we process all the results
[blinkIdOverlayViewController.recognizerRunnerViewController pauseScanning];
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
// All UI interaction needs to be done on main thread
});
}
}
- (void)blinkIdOverlayViewControllerDidTapClose:(nonnull MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController *)blinkIdOverlayViewController {
// Your action on cancel
}This section covers more advanced details of BlinkID integration.
- First part will cover the possible customizations when using UI provided by the SDK.
- Second part will describe how to embed
MBRecognizerRunnerViewController's delegatesinto yourUIViewControllerwith the goal of creating a custom UI for scanning, while still using camera management capabilites of the SDK. - Third part will describe how to use the
MBRecognizerRunner(Direct API) for recognition directly fromUIImagewithout the need of camera or to recognize camera frames that are obtained by custom camera management. - Fourth part will describe recognizer concept and available recognizers.
Within BlinkID SDK there are several built-in overlay view controllers and scanning subview overlays that you can use to perform scanning.
MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController implements new UI for scanning identity documents, which is optimally designed to be used with new MBBlinkIdRecognizer and MBBlinkIdCombinedRecognizer. The new MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController implements several new features:
- clear indication for searching phase, when BlinkID is searching for an ID document
- clear progress indication, when BlinkID is busy with OCR and data extraction
- clear message when the document is not supported
- visual indications when the user needs to place the document closer to the camera
- when
MBBlinkIdCombinedRecognizeris used, visual indication that the data from the front side of the document doesn't match the data on the back side of the document.
The new UI allows the user to scan the document at an any angle, in any orientation. We recommend forcing landscape orientation if you scan barcodes on the back side, because in that orientation success rate will be higher. To force the UI in landscape mode, use the following instructions:
Swift
let settings = MBBlinkIdOverlaySettings()
settings.autorotateOverlay = true
settings.supportedOrientations = UIInterfaceOrientationMask.landscapeObjective-C
MBBlinkIdOverlaySettings *settings = [[MBBlinkIdOverlaySettings alloc] init];
settings.autorotateOverlay = YES;
settings.supportedOrientations = UIInterfaceOrientationMaskLandscape;It has MBBlinkIdOverlayViewControllerDelegate delegate which can be used out-of-the-box to perform scanning using the default UI. Here is an example how to use and initialize MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController:
Swift
/** Create your overlay view controller */
let blinkIdOverlayViewController : MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController = MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController(settings: blinkIdSettings, recognizerCollection: recognizerCollection, delegate: self)
/** Create recognizer view controller with wanted overlay view controller */
let recognizerRunneViewController : UIViewController = MBViewControllerFactory.recognizerRunnerViewController(withOverlayViewController: blinkIdOverlayViewController)
/** Present the recognizer runner view controller. You can use other presentation methods as well (instead of presentViewController) */
self.present(recognizerRunneViewController, animated: true, completion: nil)Objective-C
MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController *overlayVC = [[MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController alloc] initWithSettings:settings recognizerCollection: recognizerCollection delegate:self];
UIViewController<MBRecognizerRunnerViewController>* recognizerRunnerViewController = [MBViewControllerFactory recognizerRunnerViewControllerWithOverlayViewController:overlayVC];
/** Present the recognizer runner view controller. You can use other presentation methods as well (instead of presentViewController) */
[self presentViewController:recognizerRunnerViewController animated:YES completion:nil];As you can see, when initializing MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController, we are sending delegate property as self. To get results, we need to conform to MBBlinkIdOverlayViewControllerDelegate protocol.
The SDK comes with the ability to customize some aspects of the UI by using the UI theming. The screens can be customized to fit your app’s look and feel by defining themes in your application that override themes from the SDK. Each theme must extend the corresponding base theme from the SDK, as described in the following sections.
To customize MBBlinkIdOverlayViewController, use MBBlinkIdOverlayTheme class to customize your look. You can customise elements labeled on the screenshot above by providing wanted properties to MBBlinkIdOverlayTheme:
-
reticle
- reticleErrorColor - change custom error UIColor
-
instructions
- instructionsFont - set custom UIFont
- instructionsTextColor - set custom UIColor
- instructionsCornerRadius - set custom corner radius
-
flashlightWarning
- flashlightWarningFont - set custom UIFont
- flashlightWarningBackgroundColor - set custom background UIColor
- flashlightWarningTextColor - set custom text UIColor
- flashlightWarningCornerRadius - set custom corner radius
-
cardIcon
- frontCardImage - change front card image on flip
- backCardImage - change back card image on flip
-
successIcon
- successScanningImage - change success scan image
- successFlashColor - change flash color on success scanning
Please check our Samples for custom implementation of overlay view controller.
Overlay View Controller is an abstract class for all overlay views.
It's responsibility is to provide meaningful and useful interface for the user to interact with.
Typical actions which need to be allowed to the user are:
- intuitive and meaniningful way to guide the user through scanning process. This is usually done by presenting a "viewfinder" in which the user need to place the scanned object
- a way to cancel the scanning, typically with a "cancel" or "back" button
- a way to power on and off the light (i.e. "torch") button
BlinkID SDK always provides it's own default implementation of the Overlay View Controller for every specific use. Your implementation should closely mimic the default implementation as it's the result of thorough testing with end users. Also, it closely matches the underlying scanning technology.
For example, the scanning technology usually gives results very fast after the user places the device's camera in the expected way above the scanned object. This means a progress bar for the scan is not particularly useful to the user. The majority of time the user spends on positioning the device's camera correctly. That's just an example which demonstrates careful decision making behind default camera overlay view.
To use your custom overlay with Microblink's camera view, you must first subclass MBCustomOverlayViewController and implement the overlay behaviour conforming wanted protocols.
There are seven MBRecognizerRunnerViewController protocols.
Seven RecognizerRunnerViewController protocols are:
MBScanningRecognizerRunnerViewControllerDelegateMBDetectionRecognizerRunnerViewControllerDelegateMBOcrRecognizerRunnerViewControllerDelegateMBGlareRecognizerRunnerViewControllerDelegateMBFirstSideFinishedRecognizerRunnerViewControllerDelegateMBDebugRecognizerRunnerViewControllerDelegateMBRecognizerRunnerViewControllerDelegate
In viewDidLoad, other protocol conformation can be done and it's done on recognizerRunnerViewController property of MBOverlayViewController, for example:
Swift and Objective-C
self.scanningRecognizerRunnerViewControllerDelegate = self;In Quick Start guide it is shown how to use a default overlay view controller. You can now swap default view controller with your implementation of CustomOverlayViewController
Swift
let recognizerRunnerViewController : UIViewController = MBViewControllerFactory.recognizerRunnerViewController(withOverlayViewController: CustomOverlayViewController)Objective-C
UIViewController<MBRecognizerRunnerViewController>* recognizerRunnerViewController = [MBViewControllerFactory recognizerRunnerViewControllerWithOverlayViewController:CustomOverlayViewController];This guide will in short present you how to process UIImage objects with BlinkID SDK, without starting the camera video capture.
With this feature you can solve various use cases like: - recognizing text on images in Camera roll - taking full resolution photo and sending it to processing - scanning barcodes on images in e-mail etc.
DirectAPI-sample demo app here will present UIImagePickerController for taking full resolution photos, and then process it with BlinkID SDK to get scanning results using Direct processing API.
Direct processing API is handled with MBRecognizerRunner. That is a class that handles processing of images. It also has protocols as MBRecognizerRunnerViewController.
Developer can choose which protocol to conform:
MBScanningRecognizerRunnerDelegateMBDetectionRecognizerRunnerDelegateMBDebugRecognizerRunnerDelegateMBOcrRecognizerRunnerDelegate
In example, we are conforming to MBScanningRecognizerRunnerDelegate protocol.
To initiate the scanning process, first decide where in your app you want to add scanning functionality. Usually, users of the scanning library have a button which, when tapped, starts the scanning process. Initialization code is then placed in touch handler for that button. Here we're listing the initialization code as it looks in a touch handler method.
Swift
func setupRecognizerRunner() {
var recognizers = [MBRecognizer]()
recognizer = MBBlinkIdCombinedRecognizer()
recognizers.append(recognizer!)
let recognizerCollection = MBRecognizerCollection(recognizers: recognizers)
recognizerRunner = MBRecognizerRunner(recognizerCollection: recognizerCollection)
recognizerRunner?.scanningRecognizerRunnerDelegate = self
}
func processImageRunner(_ originalImage: UIImage) {
var image: MBImage? = nil
if let anImage = originalImage {
image = MBImage(uiImage: anImage)
}
image?.cameraFrame = true
image?.orientation = MBProcessingOrientation.left
let _serialQueue = DispatchQueue(label: "com.microblink.DirectAPI-sample-swift")
_serialQueue.async(execute: {() -> Void in
self.recognizerRunner?.processImage(image!)
})
}
func recognizerRunner(_ recognizerRunner: MBRecognizerRunner, didFinishScanningWith state: MBRecognizerResultState) {
if blinkInputRecognizer.result.resultState == MBRecognizerResultStateValid {
// Handle result
}
}Objective-C
- (void)setupRecognizerRunner {
NSMutableArray<MBRecognizer *> *recognizers = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
self.recognizer = [[MBBlinkIdCombinedRecognizer alloc] init];
[recognizers addObject: self.recognizer];
MBRecognizerCollection *recognizerCollection = [[MBRecognizerCollection alloc] initWithRecognizers:recognizers];
self.recognizerRunner = [[MBRecognizerRunner alloc] initWithRecognizerCollection:recognizerCollection];
self.recognizerRunner.scanningRecognizerRunnerDelegate = self;
}
- (void)processImageRunner:(UIImage *)originalImage {
MBImage *image = [MBImage imageWithUIImage:originalImage];
image.cameraFrame = YES;
image.orientation = MBProcessingOrientationLeft;
dispatch_queue_t _serialQueue = dispatch_queue_create("com.microblink.DirectAPI-sample", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL);
dispatch_async(_serialQueue, ^{
[self.recognizerRunner processImage:image];
});
}
- (void)recognizerRunner:(nonnull MBRecognizerRunner *)recognizerRunner didFinishScanningWithState:(MBRecognizerResultState)state {
if (self.blinkInputRecognizer.result.resultState == MBRecognizerResultStateValid) {
// Handle result
}
}Now you've seen how to implement the Direct processing API.
In essence, this API consists of two steps:
- Initialization of the scanner.
- Call of
- (void)processImage:(MBImage *)image;method for each UIImage or CMSampleBufferRef you have.
Some recognizers support recognition from NSString. They can be used through Direct API to parse given NSString and return data just like when they are used on an input image. When recognition is performed on NSString, there is no need for the OCR. Input NSString is used in the same way as the OCR output is used when image is being recognized.
Recognition from String can be performed in the same way as recognition from image.
The only difference is that user should call - (void)processString:(NSString *)string; on MBRecognizerRunner.
DirectAPI's RecognizerRunner singleton is a state machine that can be in one of 3 states: OFFLINE, READY and WORKING.
- When you obtain the reference to
RecognizerRunnersingleton, it will be inOFFLINEstate. - You can initialize
RecognizerRunnerby callinginitmethod. If you callinitializemethod whileRecognizerRunneris not inOFFLINEstate, you will getIllegalStateException. - After successful initialization,
RecognizerRunnerwill move toREADYstate. Now you can call any of therecognize*methods. - When starting recognition with any of the
recognize*methods,RecognizerRunnerwill move toWORKINGstate. If you attempt to call these methods whileRecognizerRunneris not inREADYstate, you will getIllegalStateException - Recognition is performed on background thread so it is safe to call all
RecognizerRunner'smethods from UI thread - When recognition is finished,
RecognizerRunnerfirst moves back toREADYstate and then calls therecognizerRunner(_ :, didFinishScanningWith:)method of the providedMBScanningRecognizerRunnerDelegate. - Please note that
MBScanningRecognizerRunnerDelegate'srecognizerRunner(_ :, didFinishScanningWith:)method will be called on background processing thread, so make sure you do not perform UI operations in this callback. Also note that until therecognizerRunner(_ :, didFinishScanningWith:)method completes,RecognizerRunnerwill not perform recognition of another image or string, even if any of therecognize*methods have been called just after transitioning toREADYstate. This is to ensure that results of the recognizers associated withRecognizerRunnerare not modified while possibly being used withinrecognizerRunner(_ :, didFinishScanningWith:)method. - By calling
resetStatemethod,RecognizerRunnersingleton will release all its internal resources. Note that even after callingresetStateyou might receiverecognizerRunner(_ :, didFinishScanningWith:)event if there was work in progress whenresetStatewas called. resetStatemethod can be called from anyRecognizerRunnersingleton's state
Both RecognizerRunnerView and RecognizerRunner use the same internal singleton that manages native code. This singleton handles initialization and termination of native library and propagating recognizers to native library. It is possible to use RecognizerRunnerView and RecognizerRunner together, as internal singleton will make sure correct synchronization and correct recognition settings are used. If you run into problems while using RecognizerRunner in combination with RecognizerRunnerView, let us know!
When you are using combined recognizer and images of both document sides are required, you need to call RecognizerRunner.recognize* multiple times. Call it first with the images of the first side of the document, until it is read, and then with the images of the second side. The combined recognizer automatically switches to second side scanning, after it has successfully read the first side. To be notified when the first side scanning is completed, you have to set the MBFirstSideFinishedRecognizerRunnerDelegate through MBRecognizerRunnerMetadataDelegates. If you don't need that information, e.g. when you have only one image for each document side, don't set the MBFirstSideFinishedRecognizerRunnerDelegate and check the RecognitionSuccessType in MBScanningRecognizerRunnerDelegate.recognizerRunner(_ :, didFinishScanningWith:), after the second side image has been processed.
The MBRecognizer is the basic unit of processing within the SDK. Its main purpose is to process the image and extract meaningful information from it. As you will see later, the SDK has lots of different MBRecognizer objects that have various purposes.
Each MBRecognizer has a MBRecognizerResult object, which contains the data that was extracted from the image. The MBRecognizerResult object is a member of corresponding MBRecognizer object its lifetime is bound to the lifetime of its parent MBRecognizer object. If you need your MBRecognizerResult object to outlive its parent MBRecognizer object, you must make a copy of it by calling its method copy.
While MBRecognizer object works, it changes its internal state and its result. The MBRecognizer object's MBRecognizerResult always starts in Empty state. When corresponding MBRecognizer object performs the recognition of given image, its MBRecognizerResult can either stay in Empty state (in case MBRecognizerfailed to perform recognition), move to Uncertain state (in case MBRecognizer performed the recognition, but not all mandatory information was extracted) or move to Valid state (in case MBRecognizer performed recognition and all mandatory information was successfully extracted from the image).
As soon as one MBRecognizer object's MBRecognizerResult within MBRecognizerCollection given to MBRecognizerRunner or MBRecognizerRunnerViewController changes to Valid state, the onScanningFinished callback will be invoked on same thread that performs the background processing and you will have the opportunity to inspect each of your MBRecognizer objects' MBRecognizerResult to see which one has moved to Valid state.
As soon as onScanningFinished method ends, the MBRecognizerRunnerViewController will continue processing new camera frames with same MBRecognizer objects, unless paused. Continuation of processing or reset recognition will modify or reset all MBRecognizer objects's MBRecognizerResult. When using built-in activities, as soon as onScanningFinished is invoked, built-in activity pauses the MBRecognizerRunnerViewController and starts finishing the activity, while saving the MBRecognizerCollection with active MBRecognizer.
The MBRecognizerCollection is is wrapper around MBRecognizer objects that has array of MBRecognizer objects that can be used to give MBRecognizer objects to MBRecognizerRunner or MBRecognizerRunnerViewController for processing.
The MBRecognizerCollection is always constructed with array [[MBRecognizerCollection alloc] initWithRecognizers:recognizers] of MBRecognizer objects that need to be prepared for recognition (i.e. their properties must be tweaked already).
The MBRecognizerCollection manages a chain of MBRecognizer objects within the recognition process. When a new image arrives, it is processed by the first MBRecognizer in chain, then by the second and so on, iterating until a MBRecognizer object's MBRecognizerResult changes its state to Valid or all of the MBRecognizer objects in chain were invoked (none getting a Valid result state).
You cannot change the order of the MBRecognizer objects within the chain - no matter the order in which you give MBRecognizer objects to MBRecognizerCollection, they are internally ordered in a way that provides best possible performance and accuracy. Also, in order for SDK to be able to order MBRecognizer objects in recognition chain in a best way possible, it is not allowed to have multiple instances of MBRecognizer objects of the same type within the chain. Attempting to do so will crash your application.
This section will give a list of all MBRecognizer objects that are available within BlinkID SDK, their purpose and recommendations how they should be used to get best performance and user experience.
The MBFrameGrabberRecognizer is the simplest recognizer in SDK, as it does not perform any processing on the given image, instead it just returns that image back to its onFrameAvailable. Its result never changes state from empty.
This recognizer is best for easy capturing of camera frames with MBRecognizerRunnerViewController. Note that MBImage sent to onFrameAvailable are temporary and their internal buffers all valid only until the onFrameAvailable method is executing - as soon as method ends, all internal buffers of MBImage object are disposed. If you need to store MBImage object for later use, you must create a copy of it by calling copy.
The MBSuccessFrameGrabberRecognizer is a special MBecognizer that wraps some other MBRecognizer and impersonates it while processing the image. However, when the MBRecognizer being impersonated changes its MBRecognizerResult into Valid state, the MBSuccessFrameGrabberRecognizer captures the image and saves it into its own MBSuccessFrameGrabberRecognizerResult object.
Since MBSuccessFrameGrabberRecognizer impersonates its slave MBRecognizer object, it is not possible to give both concrete MBRecognizer object and MBSuccessFrameGrabberRecognizer that wraps it to same MBRecognizerCollection - doing so will have the same result as if you have given two instances of same MBRecognizer type to the MBRecognizerCollection - it will crash your application.
This recognizer is best for use cases when you need to capture the exact image that was being processed by some other MBRecognizer object at the time its MBRecognizerResult became Valid. When that happens, MBSuccessFrameGrabberRecognizer's MBSuccessFrameGrabberRecognizerResult will also become Valid and will contain described image.
Unless stated otherwise for concrete recognizer, single side BlinkID recognizes from this list can be used in any context, but they work best with the MBDocumentOverlayViewController, which has UI best suited for document scanning.
Combined recognizers should be used with MBDocumentVerificationOverlayViewController which manages scanning of multiple document sides in the single camera opening and guides the user through the scanning process. Some combined recognizers support scanning of multiple document types, but only one document type can be scanned at a time.
The MBMrtdRecognizer is used for scanning and data extraction from the Machine Readable Zone (MRZ) of the various Machine Readable Travel Documents (MRTDs) like ID cards and passports. This recognizer is not bound to the specific country, but it can be configured to only return data that match some criteria defined by the MBMrzFilter.
You can find information about usage context at the beginning of this section.
The MBMrtdCombinedRecognizer scans Machine Readable Zone (MRZ) after scanning the full document image and face image (usually MRZ is on the back side and face image is on the front side of the document). Internally, it uses MBDocumentFaceRecognizer for obtaining full document image and face image as the first step and then MBMrtdRecognizer for scanning the MRZ.
You can find information about usage context at the beginning of this section.
The MBPassportRecognizer is used for scanning and data extraction from the Machine Readable Zone (MRZ) of the various passport documents. This recognizer also returns face image from the passport.
You can find information about usage context at the beginning of this section.
The MBVisaRecognizer is used for scanning and data extraction from the Machine Readable Zone (MRZ) of the various visa documents. This recognizer also returns face image from the visa document.
You can find information about usage context at the beginning of this section.
The MBIdBarcodeRecognizer is used for scanning barcodes from various ID cards. Check this document to see the list of supported document types.
You can find information about usage context at the beginning of this section.
The MBDocumentFaceRecognizer is a special type of recognizer that only returns face image and full document image of the scanned document. It does not extract document fields like first name, last name, etc. This generic recognizer can be used to obtain document images in cases when specific support for some document type is not available.
You can find information about usage context at the beginning of this section.
The MBBlinkIdRecognizer scans and extracts data from the front side of the supported document.
You can find the list of the currently supported documents here.
We will continue expanding this recognizer by adding support for new document types in the future. Star this repo to stay updated.
Use MBBlinkIdCombinedRecognizer for scanning both sides of the supported document. First, it scans and extracts data from the front, then scans and extracts data from the barcode on the back, and finally, combines results from both sides. The BlinkIDCombinedRecognizer also performs data matching and returns a flag if the extracted data captured from the front side matches the data from the barcode on the back.
You can find the list of the currently supported documents here.
We will continue expanding this recognizer by adding support for new document types in the future. Star this repo to stay updated.
The SDK is localized on following languages: Arabic, Chinese simplified, Chinese traditional, Croatian, Czech, Dutch, Filipino, French, German, Hebrew, Hungarian, Indonesian, Italian, Malay, Portuguese, Romanian, Slovak, Slovenian, Spanish, Thai, Vietnamese.
If you would like us to support additional languages or report incorrect translation, please contact us at help.microblink.com.
If you want to add additional languages yourself or change existing translations, you need to set customLocalizationFileName property on MBMicroblinkApp object to your strings file name.
For example, let's say that we want to change text "Scan the front side of a document" to "Scan the front side" in BlinkID sample project. This would be the steps:
- Find the translation key in en.strings file inside Microblink.framework
- Add a new file MyTranslations.strings to the project by using "Strings File" template
- With MyTranslations.string open, in File inspector tap "Localize..." button and select English
- Add the translation key "blinkid_generic_message" and the value "Scan the front side" to MyTranslations.strings
- Finally in AppDelegate.swift in method
application(_:, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:)addMBMicroblinkApp.instance()?.customLocalizationFileName = "MyTranslations"
In case of problems with integration of the SDK, first make sure that you have tried integrating it into Xcode by following integration instructions.
If you have followed Xcode integration instructions and are still having integration problems, please contact us at help.microblink.com.
In case of problems with using the SDK, you should do as follows:
If you are getting "invalid licence key" error or having other licence-related problems (e.g. some feature is not enabled that should be or there is a watermark on top of camera), first check the console. All licence-related problems are logged to error log so it is easy to determine what went wrong.
When you have determine what is the licence-relate problem or you simply do not understand the log, you should contact us help.microblink.com. When contacting us, please make sure you provide following information:
- exact Bundle ID of your app (from your
info.plistfile) - licence that is causing problems
- please stress out that you are reporting problem related to iOS version of BlinkID SDK
- if unsure about the problem, you should also provide excerpt from console containing licence error
If you are having problems with scanning certain items, undesired behaviour on specific device(s), crashes inside BlinkID SDK or anything unmentioned, please do as follows:
- Contact us at help.microblink.com describing your problem and provide following information:
- log file obtained in previous step
- high resolution scan/photo of the item that you are trying to scan
- information about device that you are using
- please stress out that you are reporting problem related to iOS version of BlinkID SDK
Here is a list of frequently asked questions and solutions for them and also a list of known problems in the SDK and how to work around them.
In demo everything worked, but after switching to production license I get NSError with MBMicroblinkSDKRecognizerErrorDomain and MBRecognizerFailedToInitalize code as soon as I construct specific MBRecognizer object
Each license key contains information about which features are allowed to use and which are not. This NSError indicates that your production license does not allow using of specific MBRecognizer object. You should contact support to check if provided licence is OK and that it really contains all features that you have purchased.
I get NSError with MBMicroblinkSDKRecognizerErrorDomain and MBRecognizerFailedToInitalize code with trial license key
Whenever you construct any MBRecognizer object or, a check whether license allows using that object will be performed. If license is not set prior constructing that object, you will get NSError with MBMicroblinkSDKRecognizerErrorDomain and MBRecognizerFailedToInitalize code. We recommend setting license as early as possible in your app.
Make sure you link your app with iconv and Accelerate frameworks as shown in Quick start.
If you are using Cocoapods, please be sure that you've installed git-lfs prior to installing pods. If you are still getting this error, go to project folder and execute command git-lfs pull.
SDK crashes on armv7 devices if bitcode is enabled. We are working on it.
In my didFinish callback I have the result inside my MBRecognizer, but when scanning activity finishes, the result is gone
This usually happens when using MBRecognizerRunnerViewController and forgetting to pause the MBRecognizerRunnerViewController in your didFinish callback. Then, as soon as didFinish happens, the result is mutated or reset by additional processing that MBRecognizer performs in the time between end of your didFinish callback and actual finishing of the scanning activity. For more information about statefulness of the MBRecognizer objects, check this section.
Microblink.framework is a dynamic framework which contains slices for all architectures - device and simulator. If you intend to extract .ipa file for ad hoc distribution, you'll need to preprocess the framework to remove simulator architectures.
Ideal solution is to add a build phase after embed frameworks build phase, which strips unused slices from embedded frameworks.
Build step is based on the one provided here: http://ikennd.ac/blog/2015/02/stripping-unwanted-architectures-from-dynamic-libraries-in-xcode/
APP_PATH="${TARGET_BUILD_DIR}/${WRAPPER_NAME}"
# This script loops through the frameworks embedded in the application and
# removes unused architectures.
find "$APP_PATH" -name '*.framework' -type d | while read -r FRAMEWORK
do
FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_NAME=$(defaults read "$FRAMEWORK/Info.plist" CFBundleExecutable)
FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH="$FRAMEWORK/$FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_NAME"
echo "Executable is $FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH"
EXTRACTED_ARCHS=()
for ARCH in $ARCHS
do
echo "Extracting $ARCH from $FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_NAME"
lipo -extract "$ARCH" "$FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH" -o "$FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH-$ARCH"
EXTRACTED_ARCHS+=("$FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH-$ARCH")
done
echo "Merging extracted architectures: ${ARCHS}"
lipo -o "$FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH-merged" -create "${EXTRACTED_ARCHS[@]}"
rm "${EXTRACTED_ARCHS[@]}"
echo "Replacing original executable with thinned version"
rm "$FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH"
mv "$FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH-merged" "$FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH"
doneLogging can be disabled by calling disableMicroblinkLogging method on MBLogger instance.
We are delivering complete size report of our BlinkID SDK based on our BlinkID-sample-Swift sample project. You can check that here.
Complete API reference can be found here.
For any other questions, feel free to contact us at help.microblink.com.