Relayers' Optimistic Verification Game (ROVG) is a module of Darwinia ChainRelay, which is a super-light client with a sub-linear foreign blockchain header stored. Each block header contains a particular pre-calculated field mmr_root of previous block header hashes using the Merkle Mountain Range algorithm. Thus, each block header is "history aware," making it possible to verify whether a lower height block belongs to the chain by checking the header hash and Merkle Proof to the mmr_root. Darwinia ChainRelay also includes difficulty transitions for PoW consensus, and validators set changes for PoS consensus into mmr_rootto detect malicious fork. With this cryptographic enforcement, it's sturdy and economically infeasible for one or a group of adversaries to forge a block header on a fork and be accepted by Darwinia ChainRelay without detection. Please check out Darwinia ChainRelay for more detail.
RROVG is here to provide a mechanism for faster resolution and confirmation of recent block header. It will reward honest relayer while punishing malicious relayer. False block header submission will be eventually detected via rounds of challenges if necessary. The result is deterministic that the adversary will fail and be slashed; therefore, the process is optimistic.
There're some essential prerequisites and assumptions:
- At least one honest relayer can monitor the latest state on both chains, detect malicious data submission, and react by submitting objectively observed data within a reasonable timeframe.
- There's enough incentive for an honest relayer to perform.
- It is permissionless for anyone to act as a relayer and participate in the verification game; there's no entry barrier except some bonding capital.
Darwinia ChainRelay is a sub-linear light client, which means it does not store every block header of the blockchain it monitors. When initialized, it contains only one block, which is the genesis block. When a relayer submits a new block header, it might be the block header of height 10,000 or even higher. There are huge blanks in-between. If another relayer does not agree and submits a different block header claiming that's the block header data at the height of 10,000. How does ChainRelay resolve this conflict, and who is going to be the judge?
ROVG is a commit-reveal process. Once a block header is submitted, it provides block header hash and its mmr_root of all previous block header hashes till genesis block. Therefore, if a block header submission is in question, ChainRelay will challenge the relayer for a prior block header data or more specified by a sampling function. That block header hashes must be a leaf or leaves of previously submitted mmr_root. In this way, if an adversary tries to fool ChainRelay, he must prepare the whole chain, while each block must comply with consensus rule. The attack difficulty equals attacking the original blockchain network.
To reduce spam and faster resolution, each data submission shall include some pledge specified by bond_function, which takes challenging rounds as a parameter and may be variable. If data is honest and taken as confirmed, the pledge is returned in full, and the relayer is entitled to additional rewards coming from verification fees. If failed in the challenge, the pledge is confiscated and goes to those who challenge and win. This incentive model greatly discourages malicious relayers and encourages honest relayers to actively participate and guard the ChainRelay.
In the chapters below, we discuss the different game modes and how we choose the one we believe to be most efficient.
There are several tools in this project, and also a lot of thought of relayer verification game as different mode.
It is very helpful to know there are more possibilities to do relayer games through this document.
-
refitis a relayer fee inference tool to simulate and optimized the game for relayers in Darwinia Network.Parameters are organized in scenario config files. You can fine-tune three important equations and load these scenario config files to simulate the verification game. You can evaluate the efficiency of the parameter setting. If you are only interesting in this part, please go to Refit section
-
The
chain,relayer,challengerin/scenario/<model>folder can read the scenario file and simulate with more detail.
In this tool we assume the target chain is Ethereum, however you can simulate different chain by changing parameters. All the behavior of relayers, and the parameters are described a in a yaml file. You can easily load the scenario file to simulate the result. There are some example scenario files listed in scenario.
There are six different game mode: relayers-only, relayer-challenger, relayer-challengers, relayers-extend, proposal, and proposal-only. We have analysized each mode, their pros and cons. The winning mode is proposal-only which will be implemented in Darwinia ChainRelay and deployed to Darwinia testnet, aka Crab Network first.
You can quickly jump to Proposal-Only mode section for conclusion otherwise you can read on and see how the solution evolves along the way.
In relayers-only, relayers-extend and proposal mode, when someone doesn't agree with the block submitted by other relayer, he should submit the correct block to express his opinion, while in relayer-challenger mode and relayer-challengers mode, he signals simply by send a yes or no flag.
Following table shows the main different between these mode.
| Rule \Mode | Relayers-Only | Relayer-Challenger | Relayer-Challengers | Relayers-Extend | Proposal/Proposal-Only |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Only 1 relayer submit blocks | ✔️ | ✔️ | |||
| Allow extend from challenger | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ||
| Allow extend from initial relayer | ✔️ | ||||
| Once in participate all | ✔️ | ✔️ | |||
| Once lie drop all | ✔️ | ||||
| Ensure correct 1st block overall | ✔️ | ✅ | ✅ | ||
| Versus mode | 1 vs many | 1 vs 1 | 1 vs many | 1 vs many | many vs many |
| Possible results | slash/reward | slash/reward | slash/reward/return | slash/reward/return | slash/reward/return |
Note: In most cases, return will no happend.
| Label | Meaning |
|---|---|
| ✔️ | in any condition |
| ✅ | in most condition (Optimistic) |
In all mode, the sampling function will point out the next one or many blocks, the relayer(s) should submit on it.
The sampling function is subtle, and should different when the target chain using different consensus mechanism.
There is a discussion sampling function section, but we will explain these modes with a general half sampling equation.
There is still a little possibility that the initial submit in from a valid branch chain, so there is a stage two in the game, after that the blocks from the initial relayer are verified on chain. There is a discussion in Stage two section.
If there is only one [[challengers]] in scenario file, the scenario will run in relayer-challenger mode.
The scenario/challenger.yml is a scenario for one relayer and one challenger, you may run it with -v option to know more about this.
If there is more than one [[challengers]] in scenario file, the scenario will run in relayer-challengers mode.
The scenario/challengers.yml is a scenario for one relayer with multiple challengers, you may run it with -v option to know more about this.
There are 3 rules in relayers-only mode.
- Anyone can relay a ethereum header on the darwinia chain
- Confirmed or open a round of game
- if there is only one block (or same blocks) over the challenge time, this block is confirmed. (2-1)
- else (there are different blocks in the same block height) the game is starts
- everyone in the game should submit the block based on the
sampling functionuntil closed (2-2-1)- Once the a block according sampling function submit the next round of gamae is started, and become recursive in 2
- everyone in the game should submit the block based on the
- anyone can get in the game in any round but need to participate until the game closed
- Close game
- In following two condition, that all of the submission in the game from a relayer are ignored. (3-1)
- if someone in the game did not keep submit the blocks in following rounds in the game
- if the block of someone in the game is verified fail by hash
- Because some submission are ignored, if all blocks in each round become the only or the same, this block is confirmed, and game is closed. (3-2)
- In following two condition, that all of the submission in the game from a relayer are ignored. (3-1)
Here is some visualized example with two relayer Evil and Honest, Evil is a bad guy some times relay incorrect header, Honest is always relay a correct header.
This is a plot to show Ethereum, G is the genesis block or a block already confirmed on Darwinia chain before the game start.
G==========================================>
Here is the first submit, Evil relay a block with lie(L), and Honest find out this and relay a truth block with the same ehereum block height,
so the game starts. In the meanwhile, the chain can not determine which block is truth or lied, all the information on chain is that there are two different blocks with same block height, at least one of the block with incorrect information.
G======================================1===>
Evil L
Honest H
Based on sampling function, the Evil and Honest should submit the header on the position 2 (adopted rule 2-2-1.).
G==================2===================1===>
Evil L
Honest H
- Evil has no response on position 2,
- Evil submit a correct block on position 2 honestly.
- Evil submit a block still with lie on position 2.
the Honest will submit a header on position 2
G==================2===================1===>
Evil L
Honest H H
And waiting the challenge time over, the lie block from Evil will be removed (adopted rule 3-1), and the only block in each round will be confirmed (denote with C) (adopted rule 3-2).
G==================2===================1===>
Evil -
Honest C C
the Honest will submit a header on position 2
G==================2===================1===>
Evil H L
Honest H H
And waiting the challenge time over,
the blocks (the same) in submit round 2 are all confirmed. (adopted rule 2-1)
And Evil and Honest are still in the game and base on sampling_function,
they should submit headers on position 3(adopted rule 2-2-1.).
G==================2=========3=========1===>
Evil C L
Honest C H
the Honest will submit a correct header on position 2.
G==================2===================1===>
Evil L L
Honest H H
And there is nothing confirmed without different opinions,
so base on the sampling_function the position 3 should be submit by Evil and Honest.
G=======3==========2===================1===>
Evil L L
Honest H H
Evil and Honest can start to submit the block on position 3 when they have different opinion on position 2,
but the challenge time of submit round 3 will be star counting after run out the challenge time of submit round 2.
Here is the pseudo code of chain, help you to comprehensive this model with multiple relayers in one game.
The RPC handlers on chain allow anyone to submit headers to challenge blocks still in challenge time, or submit the header according to the sampling function.
The offchain worker keeps updating the next sampling block.
Here is the pseudo code for the client as the initial relayer.
The client first submits the initial header, and than keeps watching the next_sampling_block, and submits header of next_sampling_block.
submit the initial header
whilenext_sampling_block
submitnext_sampling_block
Here is the pseudo code for the client validating submitting block on chain.
The client first finds out a incorrect initial header, and than keeps watching the next_sampling_block, and submits header of next_sampling_block.
while submit headers
if verify fail
submit correct blockwhile next sample block submit changed
if the block not correct
submit new correct block
- In the first scenario, the game is closed.
- In the second and third scenario, the game is still going and will be convergence some where between
Gand1.
Once the Evil goes into contradictory. All of the bond from Evil will be slashed, and the slash to reward can be distributed with different functions.
In the model, no mater there are how many malicious relayers, one honest relayer always response correct information will win the game.
For a honest relayer, the optimistic bond entry barrier is log2(first submit block - blocks_from_last_comfirm) * bond and the max game round is first submit block - blocks_from_last_comfirm.
However, in the worst case, the bond entry barrier may up to O(n), please refer this issue.
In relayer-challenger mode, when someone is not accepted the block submitted by other relayers, he just puts a challenge on chain to express his opinion. And currently, we do not consider the scenario that the challenger do evil. However, there is still a bond for the challenger to challenge.
- Any relayer can relay a ethereum header on the darwinia chain
- Any challenger can challenge the relayer and open the game
- challenger needs to bond some value for each challenge before the half challenge time over
- relayer needs to submit the next specified block by
sampling function
- Close game
- The challenger stops challenging, the relayer wins and challenger will be slashed
- The relayer can not provided the next sampling block block pass the validation before the next half challenge time over
Here is some visualized example with Evil relayer and Challenger challenger, Evil is a bad guy some times relay incorrect header, Challenger is honest challenger challenge with the correct opinion.
This is a plot to show Ethereum, G is the genesis block or a block already confirmed on Darwinia chain before the game start.
G==========================================>
Here is the first submission, Evil relays a block with lie(L), and Challenger finds out this block is not correct and challenge it with 0, so the game starts.
In the meanwhile, the chain still can not determine which block is truth or lied, all the information on chain is that there is a block with dispute.
G======================================1===>
Evil L
Challenger 0
Based on sampling function, the Evil should submit the block on position 2.
G=================2====================1===>
Evil L
Challenger 0
- Evil has no response on position 2,
- Evil submit a block on position 2 honestly.
- Evil submit a block still with lie on position 2.
If Evil is not response before the half challenge time over, the Challenger will win the game and the bond of Evil in position 1 will become the be slashed and become reward for Challenger.
If Evil submit a correct block in position 2, the challenger will challenge with 0 on position 1 and '1' on position 2.
G=================2====================1===>
Evil H L
Challenger 1 0
Such that, based on sampling function, the next sampling block will be between the position 1 and position 2.
G=================2==========3=========1===>
Evil H L
Challenger 1 0
If Evil submit a correct block in position 2, the challenger will challenge with 0 on position 1 and '0' on position 2.
G=================2====================1===>
Evil L L
Challenger 0 0
Such that, based on sampling function, the next sampling block will be between the genesis and position 2.
G=======3=========2====================1===>
Evil L L
Challenger 0 0
Here is the pseudo code, help you to comprehensive this model with one relayer and one challenger. Once challenger determine a block pending on chain is correct or not, he will not change his idea.
The rpc on chain allow relayer to submit headers, and any one to challenge blocks still in challenge time.
The offchain worker keep updating the next sampling tartget.
Here is the pseudo code for the relayer, this code is the same with the initial relayer in relayers-only model
The client first submits the initial header, and than keeps watching the next_sampling_block, and submits header of next_sampling_block.
submit the initial header
whilenext_sampling_block
submitnext_sampling_block
Here is the pseudo code for challenger
The client first finds out a incorrect initial header and submits a challenge info , and than keeps watching the
next_sampling_block, and keeps submitting the challenge info base on the relayer's new submission.while submit headers
if verify fail
challenge
while next sample block submit changed
verify the block
submit new challenge
- In the first scenario, the game is closed.
- In the second and third scenario, the game is still going and will be convergence some where between
Gand1.- Following are the assumption, that challenger will beat the evil relayer
- The fake blocks are not easy to pass validation blocks when near by
- If challenger is not collusion with the evil relayer.
- Following are the assumption, that challenger will beat the evil relayer
Once the Evil goes into contradictory. All of the bond from Evil will be slashed, and the game is closed.
Please note there is no correct block on position 1 after the game closed, so there may be multiple parallel relayer-challenger games on chain to keep the bridge works.
For a honest challenger or relayer, the bond entry barrier is log2(first submit block - blocks_from_last_comfirm) * bond and the max game round is log2(first submit block - blocks_from_last_comfirm).
In this model, there is an assumption that the challenger will be honest to keep the bridge secure, so it is required some legal enforcement or high value staking for challenger,
such that it is not truly decentralized for this model.
In the worst case, the bond entry barrier may up to O(n), please refer this issue.
In relayer-challengers mode, when someone is not accepted the block submitted by other relayer, he just put a challenge on chain to express his opinion. With multiple challengers, the challengers can take over the challenge jobs, and relay is obliged to all the challeenge from relayers.
- Any relayer can relay a ethereum header on the darwinia chain
- Any challenger can challenge the relayer with the challenge info non-exsist
- challenger needs to bond some value for each challenge before the half challenge time over
- relayer needs to submit the sampling headers based on the challenge and the
sampling function
- Close game
- The challengers stop challenging, the relayer wins and all challengers will be slashed
- The relayer can not provided the next sampling block block pass the validation before the next half challenge time over
Here is some visualized example with relayer Evil and challengers Challenger 1, Challenger 2, Challenger 3, Evil is a bad guy some times relay incorrect header, challengers may not be a honest.
This is a plot to show Ethereum, G is the genesis block or a block already confirmed on Darwinia chain before the game start.
G==========================================>
Here is the first submit, Evil submit a block B, and Challenger 1 find out this block is not correct and challenge it with 0, so the game starts.
In the meanwhile, the chain still can not determine which block is truth or lied, all the information on chain is that there is a block with dispute.
G======================================1===>
Evil B
Challenger 1 0
Here in Challenger 1 submit a challenge 0, that the length of challenge is 1, and the game is opened.
Based on sampling function, the Evil should submit the block on position 2.
G=================2====================1===>
Evil B
Challenger 1 0
- Evil has no response on position 2,
- Evil submit a block on position 2.
If Evil dose not submit, Evil will be slashed, than go to reward stage and reward the correct challenger.
When Evil submit a header on position 2, there are also two kind of scenarios.
- challenger confirm with the submission on position 2
- challenger deny with the submission on position 2
The relayer-challengers allows multiple challengers with different opinions.
For example, Challenger 2 and Challenger 3 have different opinions on the block at position 2.
Challenger 2 does not confirm the block on position 2 and submit a new challenge 00, that the length of challenge is two.
And based on Challenger 2's challenge, the relayer should submit the block on position 3a.
G======3a==========2====================1===>
Evil B B
Challenger 1 0
Challenger 2 0 0
Challenger 3 confirms the block on position 2 and submits a new challenge 01, that the length of challenge is two.
And based on Challenger 3's challenge, the relayer should submit the block on position 3b.
G======3a==========2=========3b=========1===>
Evil B B
Challenger 1 0
Challenger 2 0 0
Challenger 3 1 0
If Evil submit a block on position 2, there can be challenge with 00 and 01, and the maximum next sampling blocks can be two,
so the max challenge and the maximum next sampling blocks become a tree and follows the following equation.
challenge for n round = 2 ^ (submit_round - 1)total challenge = 2 ^ submit_round - 1samples for n round = 2 ^ (submit_round - 2)total samples for n round = 2 ^ (submit_round - 1)
When there is no new challenge and all the blocks are over the challenge waiting time, all the bond from challengers will be slashed. If the relayer submit a block can not be validate or contradictory with other submissions, the relayer will be slashed, and than go to reward stage and reward the correct challenger.
The game will be closed when reaching following conditions
- relayer wins
- There is no new challenger and all challenging time are over
- relayer fail
- The block can not be verified
- The relayer has not response over the challenge waiting time
All of the challengers will be slash, and reward the relayer.
The relayer will be slash, all the bond of challenger will be returned, and the leaf of challenge make the relayer fail should be rewarded, also the roots and parents derived from the wining leaf should be rewarded. These reward are based on the slash value of relayer on each submit round. However there may be still some challengers we can not check their behavior, so the value they bond will be returned without rewards.
For example, the block height of position 1 is G+4, and the block on position 3b can not be verified with the block in position 1.
Following chart show the challenge from three challengers.
G 3a 2 3b 1==>
Evil B B B
Challenger 1 0
Challenger 2 1 0
Challenger 3 0 0
Following are the actions for the relayer and challengers
- Evil is slashed
- All bond of challengers are returned
- Challenger 1 is rewarded from the relayer's bond of position 1
- Challenger 2 is rewarded from the relayer's bond of position 2
- There is no reward for Challenger 3.
Another example, the block height of position 1 is G+4, and all the blocks are valid.
Following chart show the challenge from three challengers.
G 3a 2 3b 1==>
Honest B B B B
Challenger 1 0
Challenger 2 1 0
Challenger 3 0 0
Following are the actions for the relayer and challengers
- All bond from Honest relayer is returned
- All challengers are be slashed as reward to relayer
The slash and reward can be related as following:
- The value slashed from Challenger 1 is as reward for the submission of block in position 2
- The value slashed from Challenger 2 is as reward for the submission of block in position 3b
- The value slashed from Challenger 3 is as reward for the submission of block in position 3a
Here is the pseudo code, help you to comprehensive this model with one relayer and one challenger, Once challenger determine a block pending on chain is correct or not, he will not change his idea.
The rpc on chain allow relayer to submit headers, and any one to challenge blocks still in challenge time.
The offchain worker keep updating the next sampling blocks.
Here is the pseudo code for the relayer, this code is the same with the initial relayer in relayers-only model
The client first submit the initial header, and than keep watch the list of
next_sampling_blocks, and submit each header listed innext_sampling_blocks.submit the initial header
whilenext_sampling_blocks
submit each header listed innext_sampling_blocks
Here is the pseudo code for challenger
The client first findout an uncorrect initial header and submit a challenge info , and than keep watch the
next_sampling_blocks, and keep submit the challenge info base on the relayer's new submit.while submit headers
if verify fail
challenge
while submit headers
if next sample block submit
verify the block
submit new challenge
In this model, we are not determine each block in different round is correct or not.
We just make sure we have a solution which can always to challenge a evil relayer and let him to provide more information on chain.
Once the relayer contradictory itself the relay is slashed and the game is close.
On the other hand, the honest relayer can get the corresponding rewards for each block from the corresponding slash of challenge.
For a honest relayer, the bond entry barrier is blocks_from_last_comfirm * bond and the max game round is first submit block - blocks_from_last_comfirm.
For a honest challenger, the bond entry barrier is log2(first submit block - blocks_from_last_comfirm) * bond and the max game round is log2(first submit block - blocks_from_last_comfirm).
In the worst case, the bond entry barrier may up to O(n), please refer this issue.
The challenging time of block may be extended with graceful period for relayer only.
The graceful period will be calculate by graceful_function when implementing.
The relayer-extend mode is similar to the relayer-challengers mode, and the challenger need to provide headers to express the different opinions.
In this mode the challengers should submit header to prevent the evil challengers to mal-response easy and DoS the system.
However, there is still no the rule Once in participate all for Once lie drop all, so there is some rare case without confirm block at all.
The simulation of fee and challegne times of this mode are similar to relayer-challengers mode.
Here in, the plots are converted from the second scenario (Evil submit block on position 2) in relayer-challengers mode,
that relayers submit the blocks a to e, and the Evil decides to quit the game without response on position 3a and position 3b.
G======3a==========2=========3b=========1===>
Evil b a Slash
Challenger 1 c Return
Challenger 2 d c Return (extend from Challenger 1)
Challenger 3 b e Return
The game is closed and c is not confirmed, because of e.
The results are 3 status, following 2 cases help you to know more about this.
Case 1
G======3a==========2=========3b=========1===>
Evil b a
Challenger 1 c
Challenger 2 d c
Challenger 3 e
Only Challenger 2 beat Evil, so we can deem the result from Challenger 3 is correct.
So Challenger 1 and Challenger 2 got the reward, and the c is confirmed as following plot.
G======3a==========2=========3b=========1===>
Evil - - Slash
Challenger 1 C Reward
Challenger 2 - Slash
Challenger 3 C C Reward
Case 2
G======3a==========2=========3b=========1===>
Evil b a Slash
Challenger 1 c Return
Challenger 2 d c Return (extend from Challenger 1)
Challenger 3 e Return
Challenger 4 b e Return (extend from Challenger 3)
Challenger 2 and Challenger 4 beat Evil.
Without Once in participate all and Once lie drop all, the possible blocks in position 1 are C, E.
A is eliminated, because the initial relayer having responsibility to keep relaying the sampling blocks.
There is no rule to eliminate blocks C or E, so there is no confirm block.
And let us using Honest(H) and Lie(L) symbols to show the four possible for Case 2.
Case 2-1
G======3a==========2=========3b=========1===>
Evil H L Slash
Challenger 1 H Return
Challenger 2 L H Return (extend from Challenger 1)
Challenger 3 L Return
Challenger 4 H L Return (extend from Challenger 3)
Case 2-2
G======3a==========2=========3b=========1===>
Evil H L Slash
Challenger 1 L Return
Challenger 2 L L Return (extend from Challenger 1)
Challenger 3 H Return
Challenger 4 H H Return (extend from Challenger 3)
Case 2-3
G======3a==========2=========3b=========1===>
Evil L L Slash
Challenger 1 L Return
Challenger 2 H L Return (extend from Challenger 1)
Challenger 3 H Return
Challenger 4 L H Return (extend from Challenger 3)
Case 2-4
G======3a==========2=========3b=========1===>
Evil L L Slash
Challenger 1 H Return
Challenger 2 H H Return (extend from Challenger 1)
Challenger 3 L Return
Challenger 4 L L Return (extend from Challenger 3)
Therefor, if the game rarely stop as the status show in the Case 2, we just slash Evil and return the bond for challengers as following plot.
G======3a==========2=========3b=========1===>
Evil - - Slash
Challenger 1 - Return
Challenger 2 - - Return (extend from Challenger 1)
Challenger 3 - Return
Challenger 4 - - Return (extend from Challenger 3)
Case 2 is the worst case for this mode, nothing is confirmed, and the good news is there is not bad block relay on chain.
However, in optimistic game, there is always a good guy in each round.
Such that the good guy will return in position 3a or position 3b to beat Challenger 2 or Challenger 4.
In this model, the working affair for challenging is sharing to more than one challengers.
But the affair for the relayer is the same as aforementioned models.
In the relayer-take-over mode, the extend only happened on challengers, but not the initial relayer.
In proposal mode, each submit from relayer is a proposal, anyone can against or take-over each other.
Consider the Case 1 of relayer-extend mode.
G======3a==========2=========3b=========1===>
Initial Relayer b a
Challenger 1 c
Challenger 2 d c
Challenger 3 e
If the Initial Relayer is not evil, but he run into network issues. The extned feature only allow for Challenger is not fair for the Initial Relayer. So the same case in proposal mode it will become following table.
Note:
- following position is block number, the content in brackets is block info help you understand.
- the content in brackets for Proposal is proposing level
- level like round before, but in this mode, the Proposal 5 is allowed. Such that level is more precise for this mode.
Proposal(Level) |Chain Status |**Against**|**Extend From**|Disagree |Agree |Sample Added |Allow Samples
----------------|---------------------------------------------|-----------|---------------|---------------|----------------|----------------|-------------
|G======3a==========2=========3b=========1===>| | | | | |
Proposal 1(1) | a |None |None |None |position 1(self)|None |1
Proposal 2(1) | c |Proposal 1 |None |position 1(a) |position G |Position 2 |1, 2
Proposal 3(2) | b a |Proposal 2 |Proposal 1(1) |position 1(c) |position 2(self)|Position 3b |1, 2, 3b
Proposal 4(2) | d c |Proposal 3 |Proposal 2(1) |position 2(b) |position G |Position 3a |1, 2, 3a, 3b
Proposal 5(1) | e |Proposal 1 |None |position 1(a,c)|position G |reuse Position 2|1, 2, 3a, 3b
When every submit become a proposal, the good guy can extend the honest proposal and again other lie proposals.
The sampling function takes 2 parameters(position 1 and position G) and return the position 2, which is with some random effect.
When Proposal 2 submitting on chain, the position 2 will be calculated.
Because there is no consensus on position 1, he can not say he agree on position 1.
There is only one relay block on position 2, so he can say agree on position 2.
After position 2 is determined, Proposal 5 still get the same position for position 2.
When Proposal 3 submitting on chain the position 3a will be calculated.
Also, when Proposal 4 submitting on chain the position 3a and position 3b will be calculate
Here in, a guy disagree Proposal 4 may submit Proposal 6, and another guy disagree Proposal 6 as following
Proposal(Level) |Chain Status |**Against**|**Extend From**|Disagree |Agree |Sample Added|Allow Samples
----------------|----------------------------------------------|-----------|---------------|--------------|-----------------|------------|--------------------
|G======3a====4b====2=========3b==========1===>| | | | | |
Proposal 6(3) | f b a |Proposal 4 |Proposal 3(2) |position 2(d) |position 3a(self)|Position 4b |1, 2, 3a ,3b, 4b
Proposal(Level) |Chain Status |**Against**|**Extend From**|Disagree |Agree |Sample Added|Allow Samples
----------------|----------------------------------------------|-----------|---------------|--------------|-----------------|------------|--------------------
|G==4a==3a====4b====2=========3b==========1===>| | | | | |
Proposal 6(3) | f b a |Proposal 4 |Proposal 3(2) |position 2(d) |position 3a(self)|Position 4b |1, 2, 3a ,3b, 4b
Proposal 7(3) | g b a |Proposal 6 |Proposal 3(2) |position 3a(f)|position G |Position 4a |1, 2, 3a ,3b, 4a, 4b
On the other hand, a guy disagree Proposal 3 may submit Proposal 6, and another guy disagree Proposal 6 as following
Proposal(Level)|Chain Status |**Against**|**Extend From**|Disagree |Agree |Sample Added|Allow Samples
---------------|----------------------------------------------|-----------|---------------|---------------|-----------------|------------|--------------------
|G======3a==========2=========3b====4d====1===>| | | | | |
Proposal 6(3) | d f c |Proposal 3 |Proposal 4(2) |position 1(a,e)|position 3b(self)|Position 4d |1, 2, 3a ,3b, 4d
Proposal(Level)|Chain Status |**Against**|**Extend From**|Disagree |Agree |Sample Added|Allow Samples
---------------|----------------------------------------------|-----------|---------------|---------------|-----------------|------------|--------------------
|G======3a==========2====4c===3b====4d====1===>| | | | | |
Proposal 6(3) | d f c |Proposal 3 |Proposal 4(2) |position 1(a,e)|position 3b(self)|Position 4d |1, 2, 3a ,3b, 4d
Proposal 7(3) | d g c |Proposal 6 |Proposal 4(2) |position 3b(f) |position 2(d) |Position 4c |1, 2, 3a ,3b, 4c, 4d
If the blocks of proposals in the Allow Samples, the proposals are in the same game, and one proposal submitting only add one or zero sample.
In the proposal mode of relayer game, you can find out there is always against proposal for each proposal excluding the initial proposal. Once the largest level proposal without different opinion and over the challenge time, the proposal chain base on extend from will be confirmed. These comfirmed proposals have different against proposals, so the incentive model is really easy to be calculated based on it's against proposal. The only one proposal may without against propoal is the initial proposal, the already paid by the requesting demand from the user using the token bridge. If you are interesting about the initial proposal, please refer the backing pallet. There maybe some incorrect proposals without other proposal to against on it, the bond value of these proposal will be slash and give to treasury.
The substrate template shows the basic concept of model. Please note that, the term "take over"(legacy used) in the sample code is just the same meaning for "extend".
Here is the basic material for proposing for a initial relayer
- provide a block, not exist on chain and not in list of allow samples
Here is the basic material to propose for a relayer (not initial) find out a evil proposal
- provide a block in allow samples, against proposal,
- if the level of proposal greater than 1, the proposal (level n) should extend from the proposal with level (n-1)
Here is the pseudo code on rpc handler of chain to find out the disagree position and the agree position
- find out the agree position and the disagree position
if self position first on chain
agree self.position
disagree smallest_and_greater_than_self(recursive on positions of against proposal and its extend from proposals)
else
agree biggest_and_smaller_than_self(recursive on positions of extend from proposal and its extend from proposal and G)
disagree against_proposal.position
- add a challenge_time for the proposal
Here is the pseudo code for the offchain worker on chain
If current block is greater the challenge_time of the largest_level_proposal
if largest_level_proposal conflicts with the block confirmed on chain
slash the proposal into treasurylet correct_proposal = largest_level_proposal
while correct_proposal:
confirm correct_proposal.position
slash correct_proposal.against as reward
del correct_proposal.against
next_proposal = correct_proposal.take_over
del correct_proposal
Base on optimistic condition, there is always a good relayer submitting a correct proposal on each round.
So the proposal mode, provide a many-to-many game, it provided a system let honest guys extend from each other.
Besides, one confirm block can slash more than one evil proposals provide a better game for honest relayer.
In this model, the working affair and bond entry barrier share to all the relayers.
Under optimistic condition, the honest relayers are the majority, so the working affair and bond entry barrier is relatively smaller than the evil relayers.
In the proposal mode, the proposal including the against infomation, and the extend from information.
Besides, Proposal 5 of proposal mode is allowed to submit after Proposal 3 of proposal mode.
In the proposal-only mode, there are only serial blocks in submission, and the relayer game becomes in rounds as the same as relayers-only mode.
Such that the Proposal 5 of proposal mode (the Proposal 3 in proposal-only mode) can not submit after Proposal 3 of proposal mode (the Proposal 5 in proposal-only mode).
Besides, the simulation of fee and challegne time of proposal-only mode are also can use refit with two relayer in relayers-only mode.
Proposal(round) |Chain Status |Samples
----------------|---------------------------------------------|-------------
|G==4a==3a====4b====2====4c===3b====4d===1===>|
Proposal 1(1) | a |1
Proposal 2(1) | c |1
Proposal 3(1) | e |1
| |1, 2 (challenge time over next round start)
Proposal 4(2) | b a |1, 2
Proposal 5(2) | d c |1, 2
Proposal 6(2) | f e |1, 2
| |1, 2, 3a, 3b (challenge time over next round start)
Proposal 7(3) | f b g a |1, 2, 3a ,3b,
Proposal 8(3) | h b i a |1, 2, 3a ,3b
| |1, 2, 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b, 4c, 4d (challenge time over next round start)
The samples will be add when each round starts, and the number of samples exponentially increase with game round. For an honest relayer, he just relayer more correct blocks he observed, but the affair of creating an incorrect block for an evil relayer becomes an overwhelming burden. Base on the assumption, there alway a honest guy submit correct block in each round, so there will be at least Proposal 9 in round 4.
The substrate template shows the basic concept of model.
Here is the basic material for proposing for a initial relayer
- provide a block, not exist on chain and not in list of samples
Here is the basic material to propose for a relayer (not initial) find out a evil proposal
- provide a serial blocks in samples
- if the blocks in samples greater than 1, the serial blocks should cover one of the submission in before round
Here is the pseudo code on rpc handler of chain
if submission round greater than 1
check the submisstion follows the samples
check the submisstion cover one of submission in before round
else if sample not set
set the sample of first roundvalidate blocks
if proposal is the first submission of each round
update the challenge time of the round
Here is the pseudo code for the offchain worker on chain
if the last round is over challenge time
if only one submission in the round
close game
else
add new samples for the next round
Here is the pseudo code for the client, this is a POC level client, watching the event and submitting headers.
In production, the offchain worker push samples chaning event will be more efficence.
loop
watch and get info fromSubmitHeaders
if first block heigh unseen
add into the current games
for game in current games
if the samples of game changed and not none
submit headers based on samples
else if the samples of game is none
remove this game from current game
Confirm correct blocks, and there will be a correct relayer in each round. The only correct relayer in each round is winner, others will be slashed. The reward method is simple as winner takes all model.
In this model, the number of samples exponentially increase with game round, and the confrim time is easiliy to be calculated by rounds. The reward method for this model is winner takes all, so it is easy and clear for relayer who participate in.
Sampling function is an equation to provide the block height numbers, that relayer should submit the blocks at that block height. Sampling function is the key part to prevent the attacker, and also determine the total consuming time in relayer game. And it is reasonable for using different sample equation for different target chain with different consensus algorithm. Following listed are the design philosophy.
- Transparent and with ambiguous part
- The sample equation should be clear and transparent for people, and there will be also some ambiguous part provided by random number, such that the attacker need much affair to making fake headers.
- Once the sample calculated, it will reuse at all.
- Take proposal mode for example, if same agree position and same disagree position will get the same sample block number as output
- Sampling the tail at first
- By nature, the PoW consensus mechanism, the branch will occur and not greater than a reasonable length, for example 6. To accelerate the process of relayer verification game, the sampling function will label the position N-6 to position N-1 blocks at the second round, such that the nature branch point can be find out as soon as possible.
- Confirm blocks affinity
- If the sampling block is in the
ConfrimBlockAttractRangerange of confirmed blocks, the sampling blocks will change to the block near by the confirmed blocks - Such that it is easy to find out the counterfeit block which is near by a confirmed block
- If the sampling block is in the
Here is a sample pallet shows to sample a block with the features aforementioned. And the pseudo code for relay pallet, sample pallet listed here help to know more about what is thing going on chain.
relay pallet
The RPC handlers on chain allow anyone to submit headers to challenge blocks still in challenge time, or submit the header according to the sampling function.
The offchain worker keeps updating the next sampling block.
fn
submit
find out the agree position and the disagree position
callgen_sampling_blocksof sample palletfn
offchain_worker
find out the blocks over challenge time
store the block as confirmed and callconfirmof sample pallet
sample pallet
fn
confirm
store the block height of confirmed blocksfn
gen_sampling_blocks
generat the sampling block base on disagree block, agree block,
and also consider the concensuse of target chain, confirmed blocks
In stage two of the relayer verification game, the nature branch will be solved.
When a relayer with dispute on chain but all blocks is correct, the challenger or second relayer can ask to open the stage two of the game.
Here is status when the stage two opening in relayers-only mode.
G==============================nnnn1=====>
Initial Relayer Caaaa
Relayer 2 Cbbbb
C: is the latest confirm block
Only the longest validated chain will be accepted in block chain network. Relayer 2 start to provide the chain as long as possible after the point of first submission to open the stage two.
G==============================nnnn1=====>
Initial Relayer Caaaa
Relayer 2 Cbbbbbbbb
Then, Initial Relayer should provide a longer chain to prove that he is the longest validated chain in the challenge time as following.
G==============================nnnn1=====>
Initial Relayer Caaaaaaaaa
Relayer 2 Cbbbbbbbb
If Relayer 2 can still challenge by providing more headers, and so on.
The stage two of game should be rare, because all relayers should submit a block already finalized. However, Stage Two is designed to solve the branch issue just in case.
title(optional)- The title for this scenario will print on the console
F(optional)- The block producing factor for Darwinia / Ethereum
- For example: 2.0, that means that Darwinia produce 2 blocks and Ethereum produce 1 block.
-
challenge_function- Once a relayer submit a header and challenge the time in blocks after the calculated value from challenge function, Darwinia network will deem this header is valided and become a best header.
- Current support: integer number, linear
- For example:
10, that means a submit block will be deem to relayed and finalized after 10 Darwinia blocks. - For example:
challenge_linear, that means a submit block will wait according the linear function, and the parameters of function need to provide.
-
sample_function- Once there is dispute on any header, the relayer should submit the next Ethereum block sampling as calculated.
- Current support: half
- For example: 'half', that means the next sampling block will be
(submited_ethereum_block_height - relayed_ethereum_block_height) / 2
-
bond_function- The bond function will increase the bond to improve speed of the finality, and the cost of keeping lie will be enormous.
- Current support: float number, linear
- For example:
10.0, that means the bond of each submit is always 10.0.
-
reward_function- The reward from relayers including the treasury and the slash from the lie relayers (attackers)
- It may be reasonable when that the slash part of reward should be the same as bond functions, but both the first round submit and the second round submit are to help to beat the attackers in the first round, so the slash from the first round sumit may split some portion for the honest relayers in the second round.
- And also it may be that the treasury part is only for the last submit rounds, if the slash never split to the next round
- the treasury part is from the fee of redeem action, but it will be a debt without limitation in simulation
suffix d: block difference between last block number relayed on Darwinia, suffix e: block difference between last related block number of Ethereum
Dd(optional)- the block difference between last block number relayed on Darwinia,
De(optional)- the block difference between last related block number of Ethereum
Relays will not always be honest, s/he may some times cheat or not response.
The following parameters are used for relayers
[[relayers]]name(optional)- if name is not provided, the relayer will be name with serial numbers
choice- relayer may be response as
H(Honest),L(Lie),N(No response) - if the length of chose are shorter than other relayers, it will be deem to no response.
- relayer may be response as
We assume there always is a good guy to relay the correct headers, and the guy will name Darwinia,
and this relayer will be automatic add into the scenario when load from configure file,
so please avoid to use this name for the relayer.
The following parameters are used for challenger
[[challengers]]name(optional)- if name is not provided, the relayer will be name with serial numbers
choice- challenger may be response as following
1(agree with relayer, this means relayer is honest at this round)0(disagree with relayer, this means relayer lies at this round)
- challenger may be response as following
The three function can use different equations, base on the function setting, following parameters of function should be filled.
-
[challenge_linear]- the linear equation for challenge function
challengeing block = int(min(Wd * D, Md) + min(We * E, Me)) + C- suffix
d: block difference between last block number relayed on Darwinia, suffixe: block difference between last related block number of Ethereum - D is the distance in Darwinia chain
- E is the distance in Ethereum chain
- W is the weight for that portion
- M is the maximum value for that portion
-
[bond_linear]- the linear equation for bond function
bond = min(W * E, M) + C- W is the weight
- M is the maximum value for the variable part
-
[reward_split]- Split the slash for reward the honest relayers in two rounds
- slash value of submit round will take P as reward in current round, and leave (1-P) for the next round
- P is the portion
- the slash value for this submit round is slash value * P
- the slash value for this next submit round is slash value * (1 - P)
-
[reward_treasury_last]- The slash for reward the honest relayers in the same round
- The treasury will reward the relayers in the last submit round, because there is no attacker(lie relayers) in the last round.
- C is the constant of the reward from treasury
This executable is written in Rust, it can be easily to build and run with cargo command.
cargo build --release
then the binary will be placed in ./target/release, you can run this command with scenario file as following command.
./target/release/refit scenario/basic.yml
Also, you can put -v option to see all status in each round of submit.
./target/release/refit -v scenario/multi-challengers2.yml
following picture is the example what you will see with verbose flag
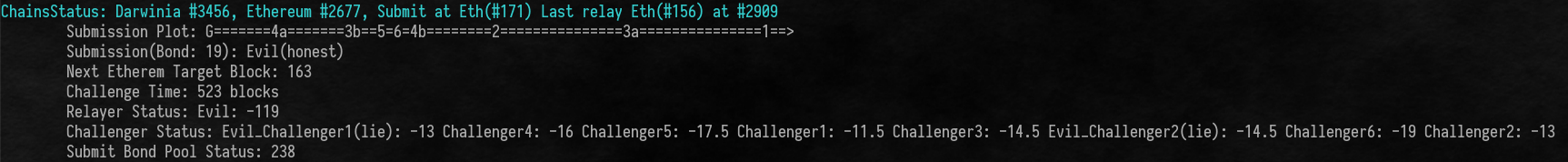
Besides, you can patch some equation parameters with option p, for examples.
./target/release/refit -p challenge_linear.C=9 challenge_linear.Wd=10.0 -- scenario/basic.yml
Currently, all parameters in challenge_linear and bond_linear, and also the values of challenge_function and bond_function can be patched.
The challenge times(in blocks), and the bonds for each round will show as plot help you to modify the equation.
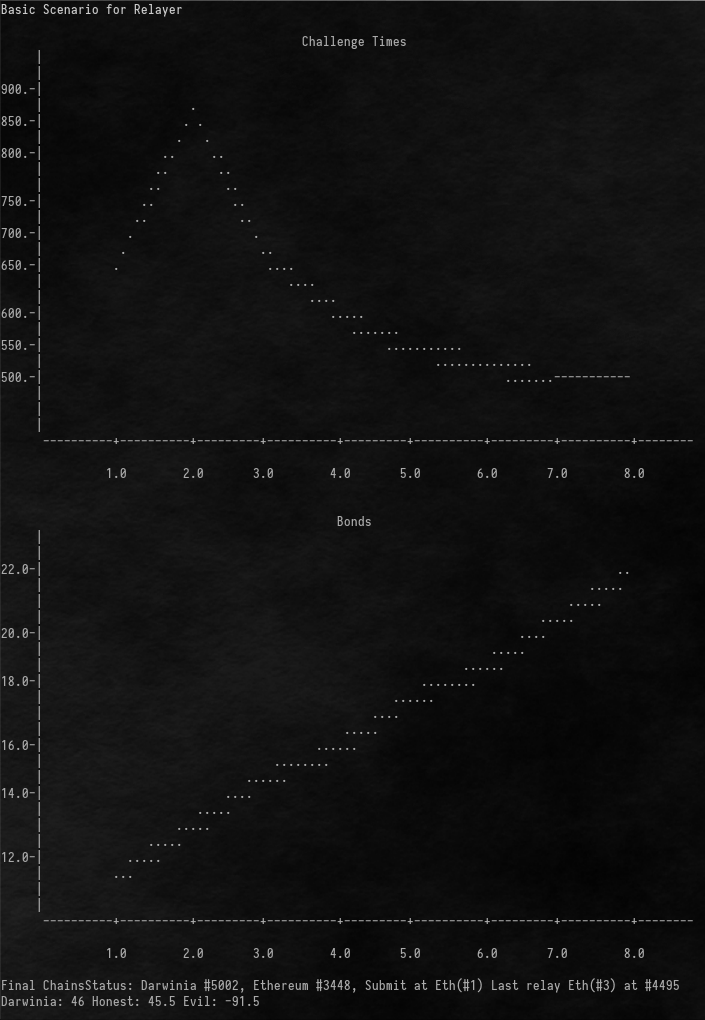
After running this tool, the reward and slash from each relayer will show as following picture.
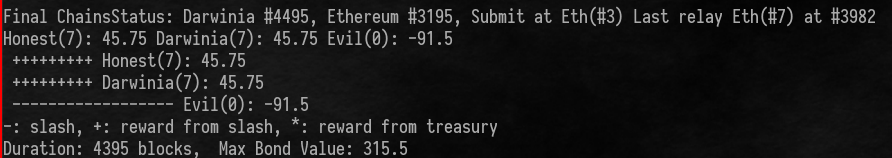
If you want to use this tool without plot with a smaller binary, please use --no-default-features option when building.
cargo build --release --no-default-features
This project has document, you can use this command to show the document on browser.
cargo doc --no-deps --open
If you want to add more equation for different function, you can take a look the trait in bond, challenge, sample.
The Equation trait and ConfigValidate will guild you to add you customized equation.
| Item | Material |
|---|---|
| EMeetup 2020/06/23 | Slides |