-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 387
Azure AD authentication
Note: This feature is available in Enterprise, AWS, Team editions only.
- Overview
- Enabling Azure AD authentication provider
- Azure Active Directory Configuration
- Cloudbeaver Configuration
- Testing the Azure AD authentication
- Configure SQL Server databases access
CloudBeaver supports authorization through Azure AD.
To do this, you must have:
-
An active Azure account.
-
A configured application in Azure AD.
You will need the following settings for your application from CloudBeaver:Name Description Redirect Url Url to which Azure AD will send you a response about the authorization attempt request which is taken from the identity provider in CloudBeaver. -
Configured Azure AD identity provider in CloudBeaver.
You will need the following settings:Name Description Domain / Tenant ID The organization's domain or Tenant ID in Azure An Application (client) ID The ID of Azure AD application A Secret Key A Secret key from Azure AD application
This step is required for users to be able to use the authorization through Azure AD. However, it might not work immediately as you will need to configure the provider.
- Log into CloudBeaver as an administrator
- Go to the Administration menu and enable Azure in the Server configuration tab.

Tip: For more information, see Server configuration administration
Authorization to the Microsoft platform is only possible using registered applications, so we need to create an application in the Azure AD, if it does not exist, and configure it.
- Register a new Enterprise Application in Azure AD according to the official Microsoft documentation.
- Cloudbeaver uses the OpenId protocol for authorization in Azure Active Directory.
For this it is necessary to configure the application secrets - more information on how to do this can be found at official Microsoft documentation.
Do not forget to record the value of the secret key because it can only be obtained once. If you do not do this you will have to repeat this step.
Cloudbeaver supports the ability to read and display information about the user's first and last name from the OpenID token. If you want to support this feature you need to add the family_name and given_name fields to the response token. More information on how to do this can be found at official Microsoft documentation
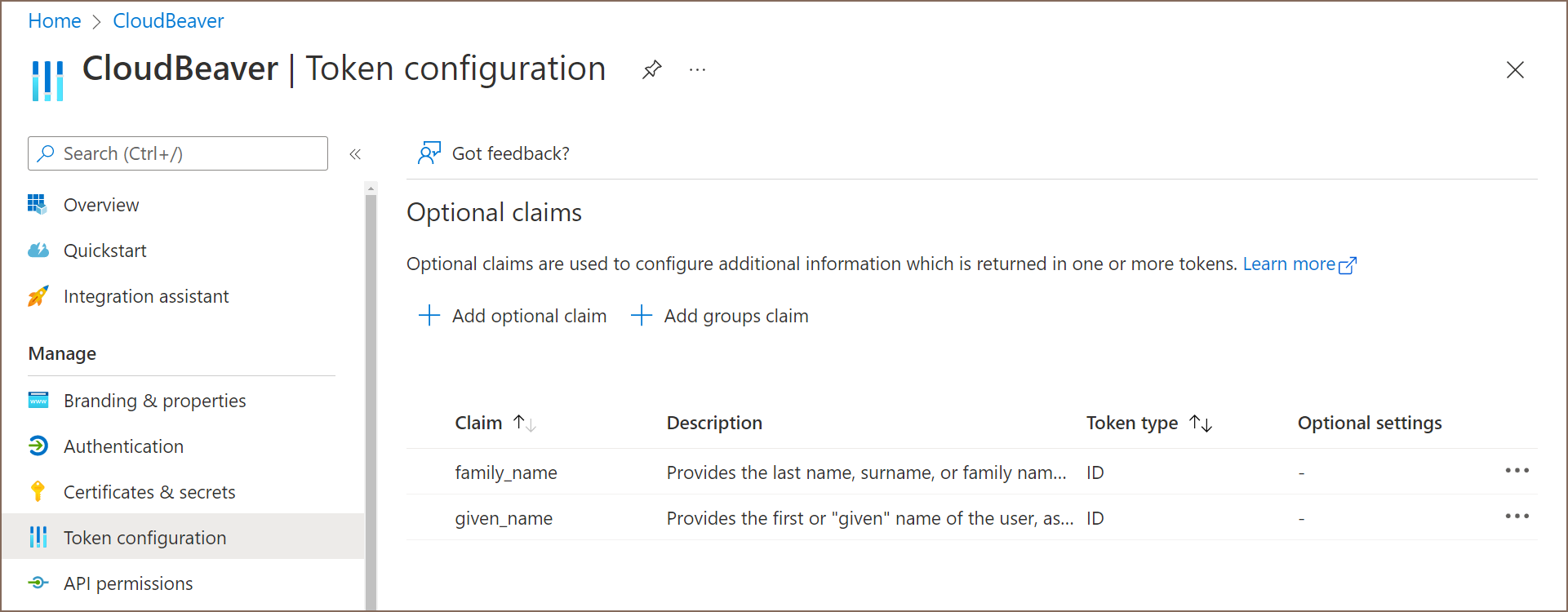
To allow users to choose Azure AD as an authorization method, a new identity provider must be created:
- Go to the Identity Providers tab and create a new configuration using the Azure AD details.

- Set Domain / Tenant ID
Open Azure Active Directory/Your Directory/Overview page and copy the Tenant ID or Primary domain (these values are equivalent) value into the Cloudbeaver Azure AD provider Tenant ID field. How to get Tenant ID value in other ways you can read here.

- Set Application (client) ID
Open the application page registered in this step point 1 and copy the value into the Cloudbeaver Azure AD provider Application (client) ID field.
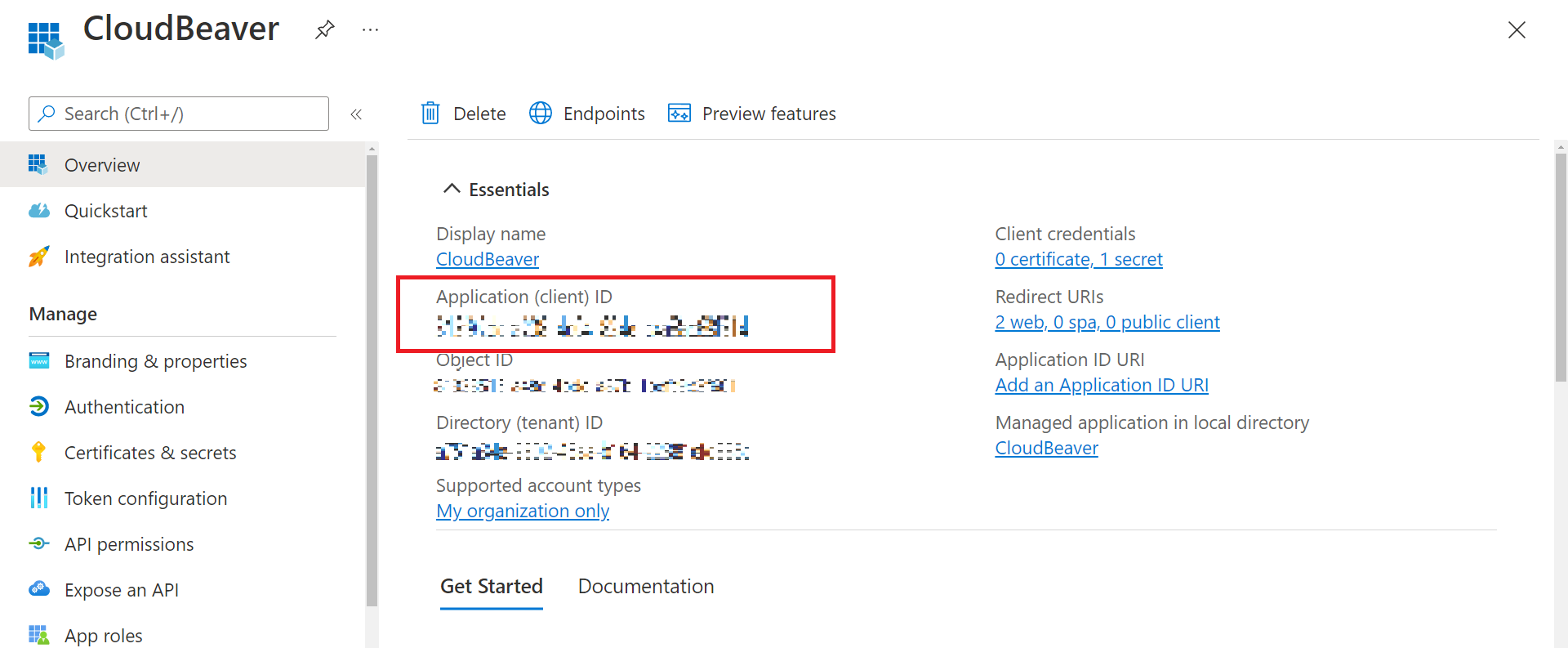
-
Set Secret Key
Copy the value of the secret key created in this step point 2 into the Secret Key field. -
Save the Identity Provider configuration
- Open Azure AD provider configuration in Cloudbeaver and copy the Redirect link

- Add a redirect link to the Azure AD application (select Web as platform) - official Microsoft documentation
The new Federated tab becomes available after creating the configuration in the CloudBeaver authentication dialog. The user can select the configuration and thereafter login to the application using SSO.

You can use Azure AD authentication to gain access to SQL Server deployed in Azure Cloud.
- On your Enterprise Application page, click API Permissions tab an add permission
user_impersonationinAzure SQL DatabaseAPI - In your SQL Server you need to map Azure AD users into database users. See Microsoft documentation: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/authentication-aad-configure?view=azuresql&tabs=azure-powershell#create-contained-users-mapped-to-azure-ad-identities
- Application overview
- Demo Server
- Administration
- Supported databases
- Accessibility
- Keyboard shortcuts
- Features
- Server configuration
- CloudBeaver and Nginx
-
Domain manager

- Configuring HTTPS for Jetty server
- Product configuration parameters
- Command line parameters
- Local Preferences
-
Team Edition Overview

-
Getting started with Team Edition

-
Team Edition Server Configuration

-
Projects in Team Edition

-
Teams in Team Edition

- Team Edition Deployment
-
Roles in Team Edition

-
Git integration in Team Edition

-
Datasets in Team Edition

-
CloudBeaver Community
-
CloudBeaver AWS
-
CloudBeaver Enterprise
-
Deployment options
-
Development